DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Current, I =
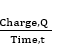
■ q = ne where n is the number of electrons
■ V = IR
■ Ammeter is always connected in series in a circuit through which the current is to be measured.
■ Potential difference, V =
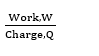
■ Voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the points between which the potential difference is to be measured.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
Table of Contents
ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
1. Why are metals good conductors of electricity whereas glass is a bad conductor of electricity? Give reason.
Ans. Metals have large number of free electrons. So, they are good conductors of electricity. Glass has extremely limited free electrons. So, it is a bad conductor of electricity.
2. Name the instrument used to measure the electric potential difference.
Ans. Voltmeter.
3. What is the SI unit of electrical potential?
Ans. volt.
4. Name the instrument used to measure electric current in a circuit.
Ans. Ammeter.
5. What is meant by potential difference between two points?
Ans. Potential difference between two points is the work done per unit charge in moving a unit tad positive charge from one point to another point in an electric field.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
6. State the relation between work, charge and potential difference for an electric circuit.
Ans. Potential difference = work/charge
7 What is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter?
Ans. The resistance of an ideal voltmeter is infinite.
8 Mention the condition under which charges can move in a conductor. Name the device which is used to maintain this condition in an electric circuit.
Ans. If there is a potential difference across the two ends of a conductor, then the charges can move Electric cell or a battery can maintain an electric current in an electric circuit.
9. How are ammeters and voltmeters connected in a circuit? What do they help us measure?
Ans. An ammeter is always connected in series in a circuit. It measures the electric current flowing in the circuit. A voltmeter is always connected in parallel in a circuit. It measures the difference across a conductor.
10. Define the unit of current.
Ans. The unit of electric current is ampere. Electric current is said to be one ampere if one coulomb of charge flows through the cross-section of the conductor in one second.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
11. Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
Ans.
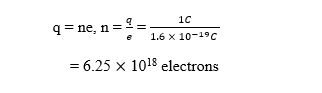
12. Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
Ans. A cell or battery.
■ The potential difference, V, across the ends of a given metallic wire in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the current, I, flowing through it. This is called Ohm’s law.

Where p is electrical resistivity of the material of the conductor, is the length of the conductor l is the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
13. What is electrical resistivity?
Ans. Electrical resistivity of a material is defined as the resistance of the object, made of the material, of unit length and unit area of cross-section.
14. What happens to the resistance of a conductor when the length of the conductor is reduced to half?
Ans. When length is reduced to half, the resistance also reduces to half of its original value.
15. Why do we use copper and aluminium wires for transmission of electric current?
Ans. Copper and aluminium have low resistivity. So, they are good conductors of electricity. Hence they are used for transmission of electric current.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
16. Numerical: How much current will an electric bulb draw from 220 V source if the resistance of the bulb is 1200 2? If in place of bulb, a heater of resistance 100 2 is connected to the source, calculate the current drawn by it.
Resistivity of wire does not depend on length and area of cross-section. So, new resistivity will be equal to the original resistivity.

18. List two distinguishing features between the resistance and resistivity of a conductor.
Ans. (i) Resistance of a conductor depends on the length and area of cross-section of the conductor. On the other hand, resistivity of a conductor is independent of length and area of cross section of the conductor.
(ii) Unit of resistance is ohm. Unit of resistivity is ohm-metre.
■ The total potential difference across a combination of resistors in series is equal to the sum of potential difference across the individual resistors.
■ When several resistors are joined in series, the resistance of the combination equals the sum of their individual resistances and is thus greater than any individual resistance.
■ The reciprocal of the equivalent resistance of a group of resistances joined in parallel is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
19. (a) Why an ammeter likely to burn out if you connects it in parallel?
(b) Why is series arrangement not found satisfactory for domestic lights?
Ans. (a) If ammeter is connected in parallel, a large current flows through it because it is a low resistance device. Thus, large heat is produced. It may burn the ammeter.
(b) If domestic lights are connected in series, then all lights are switched off even when only one light fuses.
■ For a steady current I, the amount of heat H produced in time t is
H = VIt
Where V is the potential difference.
■ H I²Rt (Joule’s law of heating)
■ Power, P = VI = 1² R
■ 1W = 1 volt × 1 ampere
■ The commercial unit of electric energy is kilowatt hour, commonly known as ‘unit’. 1 kWh = 3·6 × 106 J
20 What is the commercial unit of energy?
Ans. Kilowatt hour (kWh).
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
21. What material is generally used for making an electric fuse?
Ans. Copper or tin-lead alloy.
22. Name the material used for making the filament of a bulb.
Ans. Tungsten
23. What is the difference between kilowatt and kilowatt hour?
Ans. Kilowatt is the unit of electric power. Kilowatt hour is the commercial unit of electric energy
24. Numerical: Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V and the other 60 W at 220 V, are connected in parallel to a 220 V supply. Find the current drawn from the supply line.
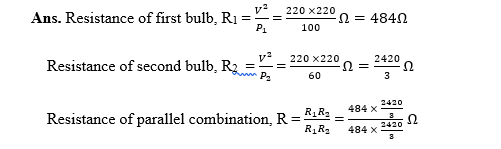
25. Should the heating element of an electric iron be made of iron, silver or nichrome wire?
Ans. The heating element of an electric iron should be made of nichrome because
(i) the resistivity of nichrome is greater than that of iron and silver. Thus, more heat is produced in the nichrome wire.
(ii) melting point of nichrome wire is greater than that of iron and silver. Thus, the nichrome wire does not melt easily on heating.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
26. Which gas is filled in the electric bulb and why?
Ans. Inactive gas like nitrogen or argon is filled in the electric bulb. This increases the life of the tungsten filament of the bulb.
27. Numerical: An electric bulb draws a current of 0-8 A and works on 250 V on the average 8 hours a day. If energy costs Rs. 3 per kWh, calculate monthly bill for 30 days.
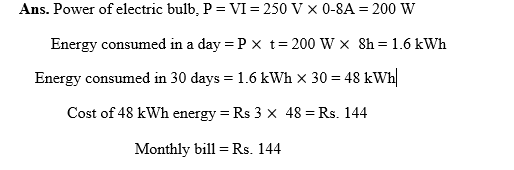
28. Numerical: In a house, four 60 W electric bulbs are lighted for 2 hours and two 100 W bulbs are lighted for 4 hours every day. Calculate the energy consumed in the house for 30 days.
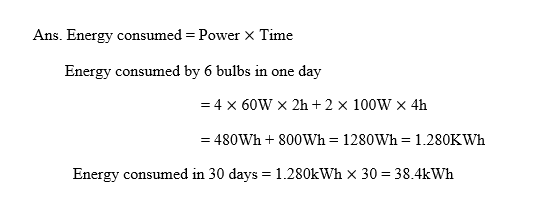
29. Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal? Ans. The resistivity of an alloy is more than the resistivity of a pure metal. So, more heat is produced in an alloy than in pure metal. Moreover, alloy does not burn or oxidise easily even at higher temperature.
30. Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
Ans. Resistance of cord of electric heater is less than the resistance of heating element. Thus, more heat is produced in the heating element and less heat is produced in the cord. Due to more heat, heater element glows.
31. Give two advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with battery.
Ans. (i) When devices are connected in parallel, they draw the current as per their requirement. So, they work properly.
(ii) If any device in parallel fuses, the working of the other devices will not be affected.
32. What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by an electric current?
Ans. Electric power determines the rate at which energy is delivered by an electric current.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
ALSO VISIT :
10TH CBSE
| Also Learn: | Attempt the Quiz on Mathematics | Attempt the Quiz on Social Science (Economics) | |
| GLOBALISATION AND INDIAN ECONOMY MONEY AND CREDIT MIND MAP FOR NATIONALISM IN EUROPE LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION REAL NUMBERS QUESTIONS ON CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION CLASS 10 | Real Numbers | Development Sectors of Indian Economy Money and Credit Globalisation and Indian Economy Consumer Rights |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS
