DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Do organisms create exact copies of themselves?
■ The of new organisms from the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction.
■ Reproduction helps to replace the organisms who die natural death, by diseases or accidents. Reproduction helps to maintain the continuity of species on this earth.
■ Reproducing organisms create new individuals that look very much like themselves.
■ Reproduction at its more basic level involve making copies of the blue print of body design.
■ DNA molecules present in chromosome contain all the information of inheritance of characters is passed from parents to next generation An exact copy of DNA is passed. DNA contains all the information for making proteins.
■ Difference in DNA leading to difference in proteins leads to changed/altered body design.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Reproducing cell, use chemical reactions to create two copies of DNA one copy is retained in the original cell and the other copy is pushed in the new daughter cell along with additional cellular apparatus. Therefore a cell divides to form two exactly similar cells.
■ Due to some error in the biochemical reaction there may come variations in the copying of DNA. Sometime due to drastic variations, the changed new DNA copy cannot function in the inherited cellular apparatus and the cell dies. There are many variations in DNA where the cell survives but differ from the original cell: This inbuilt tendency for variation is the basis of evolution.
■ Ability of DNA copying during reproduction help in maintenance of body designs features, which allow the populations of organisms to adapt. to well defined habitat arniches. Reproduction is thus linked to the stability of population or species.
■ Factors governing the habitat or niche such as temperature, water level, humidity etc. change, the population once suited could wipe out. However some individuals in a population with some variations have chance to survive.
■ Variations is thus useful for the survival of species over time.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
Table of Contents
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
1. When a cell reproduces, what happens to its DNA?
Ans. DNA replicates to form two copies of DNA in a reproducing cell.
2. Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Give one reason.
Ans. In the process of copying of DNA, some variations/errors come each time, due to the deletion or insertion of wrong nucleotides.
3. Why is variation important for a species?
Ans. Variations help in the stability of population of species by adapting to the changed environmenta conditions.
4. Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of living beings. Give reasons in support of the statement.
Ans. (i) It ensures continuation of life.
(ii) Helps in preparation of species.
(iii) Replacement of dead individuals.
(iv) Introduction and transfer of variations.
5.How do variations arise in organisms? “Variations is useful for the survival of species, Justify the statement with the help of an example.
Ans. During preparation of DNA copies hundred of biochemical reaction occur which are liable to go wrong and form a different DNA copies, though similar but not identied to the original. It give rise to variations, altered by design and function.
Variations function as preadaptation to the environmental changes. Despite use of many insecticides the insects have not been wiped out, due to presence of requisite variation. The surviving insects multiply and grow in number.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
6. Name the life process of an organism that helps in the growth of its population.
Ans. Reproduction.
7. Where is DNA found is the cell?
Ans. Nucleus, plastids and mitochondria.
8. No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. Why?
Ans. Due to presence of variations.
9. What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate in the reproductive process?
Ans. It produces mutations which give rise to useful, harmful and neutral variations in the progeny.
10. What is DNA?
Ans.DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a self replicating biochemical that is carrier of genetic rep information for expression of hereditary traits and transfer to the next generation.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
11.What the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproductive process? How does the amount of DNA remain constant each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals?
Ans.(a) Inaccuracy in DNA copying. Even small errors in DNA copying produce variations or mutations. Some of these mutations may be drastic as to kill the cells and stop the reproductive process. Others are minor and form the basis of varied traits.
(b) Meiosis halves the amount of DNA while fertilization doubles the amount of DNA
12. Justify the following statements:
(a) Variation is beneficial for the species over a period of time.
(b) New offspring produced are similar to their parents, but not identical.
(c) Binary fission is different in Amoeba and Leishmania.
(a) Vartions function as preadaption to changed enviroment.
(b) New offspring are similar to their parents because they have obtained the genetic traits from the same. They are, however, not identical because of chance separation, chance combination of chromosomes and recombination of genes due to crossing over.
(c) In Amoeba binary fission can occur in any plane while in Leishmania it vertical plane
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
13. What is the importance of DNA copying during reproduction? Why offspring are formed by asexual reproduction genetically similar to their parents?
Ans. Importance of DNA Copying: It plays a role in cell division and reproduction Offspring formed by Asexual Reproduction. Asexual reproduction is uniparental. The genetic material present in the offspring is unaltered copy of DNA present. Therefore, they are genetically similar to the parents.
14. What is the information source in the cell nucleus for making proteins. State the basic events in reproduction.
Ans. (i) Information Source: DNA
(ii) Basic Events in Reproduction: DNA replication, growth of cellular machinery and cell division.
15. Why is variations beneficial to the species but not necessary for the individual?
Ans. Populations of organisms are well adapted to their habitats or niches, each characterised by a specific set of factor. Habitat and niches change over time. For example temperature, water level can go up or down under the drastic conditions, whole populations may be wiped out but few would find chance to survive. The surviving variants individuals reproduce and develop, a new kind of organisms suited the changed environment. Variation is thus helpful in survival of species over time.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Modes of Reproduction used by single organisms
■ The modes by which various organisms reproduce depend upon the body design of the organism.
■ In unicellular organisms cell divison or fission leads to the formation of new individuals.
■ Many bacteria and protozoa simply split into two equal halves during cell divison.
■ Fission is of two types binary fission and multiple fission. Binary fission has different patterns may he transverse or longitudinal or irregular.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Amoeba shows irregular binary fission where splitting of two cells during division can take place in any plane.
■ Multiple fission occurs in some protozoan and some unicellular algae where a parent cell divides and splits internally to form a number of daughter individuals. In Plasmodium, a malarial parasite, many daughter cells are produced simultaneously by multiple fission. In Amoeba multiple fission occurs in cyst stage under unfavourable conditions.
■ In Paramecium, binary fission is transverse while in Euglena and Leishmonia (a protozoan having whip like flagellum and cause kala azar) binary fission occur in vertical plane.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ In budding e, g., Yeast a small part of the body of an organism, grows out as a bud that further to become a new organism e.g., yeast.
■ In Hydra, a multicellular organism a small out growth called “Bud” is formed from the side of the body by repeated cell division. Bud develops into small hydra by developing mouth and tentacles. Finally this new hydra detaches from the body of parent Hydra and lives as new organism.
■ Many multicellular organisms with simple body organization such as Spirogyra breaks up to many pieces or fragments which grow in to new individuals.
■ Regeneration is the phenomenon where a fully differentiated organism have the ability to give rise to new individual organisms from their body part, e.g., Hydra and Planaria.
■ Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells which divide to form large number cells which later undergo differentiation and change to form various cell types and tissues. These changes occurring in an organised sequence is celled development.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ There are organisms in which there is regeneration of lost parts, and not a method of reproduction e.g. regeneration of a tail in lizard, lost arm in star fish.
■ Spore formation is another method of asexual reproduction in which a parent plant produces hundreds of microscopic units called spores. Spores after dispersal under favourable conditions germinate to form new plants e.g., Rhizopus, Ulothrix, Penicillium etc.
■ Vegetative reproduction is the formation of new plants from the vegetative parts like root, stem, leaves buds etc. This property of the plants is commercialy exploited by artificial method of vegetative reproduction.
■ The cutting is a small piece of root, stem and leaves cut off from the plant, used as vegetative propagate e.g., Sugar cane, Rose, Durauta, citrus.
■ Layering a small young branch is defoliated in the middle. The defoliated part is given a slight cut, pegged down and covered with soil. It is called a layer. After few days the injured part develop roots. The layer can now be cut off from the parent and planted separately e.g.. Jasmine, grapevine.
Air layering to performed where branches do not occur near soil e.g.,Litchi, pomegranate.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Grafting involve the technique of joining shoot system of one plant over the stump of another related plant so as to form a composite single plant e.g. , mongo, guava, apple, pear, peach.
■ Vegetative reproduction is useful in (i) multiplication of seedless plant (ii) uniform yield us (iii) maintainance of good quality (iv) genetically similar plant and (v) high rale of survival of the new plants (iv) quick method of reproduction. (vii) Plant produced by vegetative reproduction bear flowers and fruits earlier than raised from seeds (viii) only method of reproduction in plants, which have lost the capacity to produce seeds e.g., banana, rose etc.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Tissue culture is a technique in which plants are grown under aseptic conditions and controlled temperature. New plants are grown from a piece of plant part, tissue, from the cells of growing shoot tip cells are then placed in an artificial medium where they divide rapidly to form a mass of undifferentiated cells called callus. The callus is then transferred to another medium containing plant hormones auxins, cytokinins for growth and development. Small plant lets appear on the callus, are then transferred to the soil to make them grow into mature plants.
Tissue culture technique is useful because (1) Many new plants can be grown from one parent in disease free condition. (ii) technique used commonly for ornamental plants. (iii) It is a very fast technique to produce hundred of plants in a few weeks time. (iv) Plants can be grown throught the year. (v) Very little space is needed for developing new plants.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
16 How does planaria reproduce. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Ans. Regeneration It is asexual method.
17. How does Plasmodium reproduce. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Ans. Normally Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission (Schizogony and sporogony) both in man (liver and blood cells) and mosquito (stomach wall) it is asexual.
How, ever it reproduces in the gul of mosquito.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
18. What is vegetative propagation? State two advantages and two disadvantages of this method.
Ans. It is the process of formation of new plants from root stem and leaves under appropriate conditions.
Advantages
(i) Multiplication of seedless plants.
(ii) Maintainance of good quality
(iii) survival rate of daughter plants nearly 100 %.
Disadvantages:
(i) Over crowding
(ii) Vegetative propagues cannot be stored for long time
(iii) Undesirable characters cannot be eliminated.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
19. What happens when:
(a) Accidentally, Planaria gets cut into many pieces?
(b) Bryophyllum left falls on the wet soil ?
(c) On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts?
Ans. (a) In Planaria each pieces grows into a complete organism a process called regeneration.
(b) The buds present in the notches along the leaf margin of Bryophyllum develop in to new plants.
(c) On rupturing of the sporangia of Rhizopus very small light spores are released in the air. Under favourable conditions spores germinate in to new Rhizopus individuals. The spores have thick walls to protect them till the availability of most surface.
20. What is regeneration ? Give one example of an organism that shows this process and one organism that does not. Why does regeneration not occur in the latter ?
Ans. It is the ability to repair injured parts and replace the ones lost through accident or autotomy/ (Self amputation). e.g., tail in wall lizard However it is helpful in multiplication of some animals from broken or cut pieces e.g., Hydra, Planaria.
Regenaration is due to the presence of specialised cells which proliferate and differentiate giving rise to various cell types. Mammals including man have no regeneration due to the absence of these specialised cell. There is limited power of healing of injured parts, not replacement.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
21 Describe reproduction by spores in Rhizopus.
Ans. Spore formation: It is the most common method of asexual reproduction in algae, fungi etc. In fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor, etc., a structure called sporangium develops on the hypha during spore formation. The nuclei within the sporangium divide repeatedly forming many daughter nuclei. Each daughter nucleus gets surrounded by a small amount of cytoplasm and develops into a spore. The spores are liberated from the sporangium on ripening. The spores are light, very small in size, hence, help in dispersal by air.
22. (a) Differentiate between binary and multiple fission. Name an organism that reproduces by multiple fission.
(b) Vegetative reproduction is beneficial to plants that are propagated asexually. Give two advantages.)
Ans. (a) In binary fission a unicellular organism divides into two equal daughters. In multiple fission it gives rise to several (more than 2) individuals. Some residue may be left in multiple fission while no such wastage occurs in binary fission.
(b) Multiple fission occurs in Plasmodium (Malaria Parasite).
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
23.(a) Name any two plants that reproduce through grafting.
(b) List any two benefits to an organism that reproduces through spores.
Ans. (a) Grafting: It is performed in case of high quality Apple, Mango, Pear and some other plants. (any two)
(b) Benefits of Spore Formation : (i) Spores are a means of dispersal. (ii) They are often thick-walled and take part in perennation. (iii) A large number of spores are often formed at one time so that rapid multiplication can occur.
24. “Multicellular organisms cannot divide cell by cell.” List two reasons to justify this statement.
Ans.(i) In multicellular organisms, cell by cell division is a method of growth and not a method of multiplication as in unicellular organisms.
(ii) Multicellular organisms have developed complex and specialized reproductive structures which are not possible in single called organisms.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
25.(a) Leaves of Bryophyllum fallen on ground produce new plants whereas the leaves of Jasmine do not. Why?
(b) Write two points of differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
(a) Leaves of Bryophyllum possess adventitious buds in their marginal notches. The buds sprout to produce plantlets when leaves fall on soil. Leaves of Jasmine cannot undertake asexual reproduction as they do not develop adventitious buds.
(b)
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| 1. Parents: It is monoparental. | 1. It is generally biparental |
| 2. Meiosis: Meiosis does not occur during asexual reproduction. There are no gametes and no fertilization. Ex: Binary fission in Amoeba, Budding in Yeast | 2. Meiosis occurs. Gametes are formed and fertilization occurs in sexual reproduction. Ex: Offspring in Wheat, Human. |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
26. How does the process of budding differ from the process of spore formation?
Ans.
| Budding | Spore Formation |
| 1. Number One or a few buds develop over the body of an individual. | 1. A very large number of spores develop from an individual. |
| 2. Dispersal: It is limited. | 2. Spores are dispersed far and wide. |
| 3. New Individual: The bud directly grows into a new individual. Ex. Hydra. | 3. A spore germinates and then forms a new individual. Ex. Rhizopus. |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
27.The organisms formed by asexual reproduction are considered as clones. Why ? State the advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction.
Ans. Organisms formed through asexual reproduction are considered clones as they are genetically similar to one another as well as their parent.
Sexual reproduction is advantageous over asexual reproduction as it produces a lot of variations due to reshuffling of chromosomes and crossing over. This provides better adaptability, more vigour and vitality to the offspring.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
28. Explain vegetative propagation with the help of two example. List two advantages of vegetative propagation.
Ans.Vegetative propagation is the formation of new plants from vegetative propagules or parts (stem, leaf, root, bud) of a parent plant.
(i) Duranta/Bougainvillea: It is multiplied with the help of stem cuttings. 20-30 cm long stem pieces of one year old branches are placed in the moist soil in their natural position during spring or rainy season. The cuttings develop roots and shoots to form new plants.
(ii) Jasmine/Grape Vine: It is multiplied by layering. One year old basal branch is defoliated in the middle, given a small cut (v-shaped, tongue-like or ring-like), pegged and covered with soil. The branch now called layer, develops adventitious roots within 1-2 months. It is then separated as new plant.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
29.What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism ? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction.
Definition: Multiple fission is a mode of asexual reproduction in a unisexual organism where a single parent produces a number of daughter individuals.
Mechanism: The nucleus of the parent cell divides repeatedly to form a number of daughter nuclei Cytoplasm gathers around each nucleus followed by development of cell membranes to (a) Expl form daughter cells. The parent cell bursts open to release the daughter individuals. Example Plasmodium (Malaria Parasite).
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
30. What happens when (a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces (b) A mature spirogyra filament attains considerable length (c) On maturation sporangia burst.
(a) Planaria: Regeneration
(b) Spirogyra: Fragmentation
(c) Sporangium: The mature sporangium bursts to expose spores that are picked up by air and dispersed. On settling at suitable medium each spore germinates and forms a new Give a re individual.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
31.Explain the terms “fission” and “regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction.
Fission: It is a mode of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms in which a parent cell divides to form two or more individuals. In binary fission, a parent cell divides into two similar daughters e.g., Amoeba, Paramecium, Leishmania. In multiple fission the contents of a unicellular individual divide into several daughters, e.g., Plasmodium.
Regeneration: It is the ability of an individual to form lost or broken part, sometimes the entire individual from a piece of the parent body through dedifferentiation of mature cells and activity of reserve cells. The ability to form a new individual from a part of the body is well developed in simple animals like Hydra and Planaria. It is restricted to the formation of only broken parts in complex organisms.
32.What is vegetative propagation ? When is it used ? Name three methods of vegetative propagation.
Ans.Vegetative Propagation: Production of new plants from vegetative parts.
When Used: Vegetative propagation is carried out during favourable period for obtaining fast growth and multiplication of economically and horticulturally important plants. It is the only known method of propagation in seedless species and varieties of plants, e.g., Sugarcane, Banana.
Methods: (i) Cuttings: Generally pieces of stems but can also be of roots and leaves. (ii) Layering (iii) Grafting (iv) Tissue culture or micropropagation is the latest technique for rapid multiplication of plants.
33.Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organism? Give reason. Ans. Yes; cell division in unicellular organism results in the formation of two daughter cells new individuals.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
34.What is a clone? Why do offsprings formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable in to similarity?
Ans. Clone refers to the exact replica of an organism formed by asexual reproduction. Since all organisms produced by asexual reproduction possess exact copies of the DNA of their parent such offsprings show great similarity.
35. Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water, but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for this.
Ans. Water cannot provide energy while sugar solution does so. This is the reason why yeast gro and multiply in sugar solution.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
36.Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration all considered as asexual types of reproduction ? With neat diagrams explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Budding, fragmentation and regeneration involve only one parent by mitotic divison. secondly gametes are involved in reproduction. There is no fertilisation. Regeneration of Planaria. can be cut in to any number of pieces and each pieces grows into a complete organisms. Here regeneration is carried out by specialised cells which proliferate to form large number of cells. from this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to becomes various cell types and tissues. All these changes occur in a organised sequence, collectively celled development.
37.Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for survival of an individual but for the stability of a species Justify.
Ans. Reproduction is a process by which an organisms create more individuals by spending lot of energy. It is not a essential process like other needed to maintain the life of an individual Reproduction has no role in processes intake of food (nutrients), respiration and subsequent release of energy.
Reproduction, however is essential for the stability of the species as it plays a role in Continuation of species. In bringing variations,
(ii) and (iii) In increasing numbers and replacing old individuals with new organisms.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Sexual Reproduction
■ It needs both sexes, male and female to produce new generation.
■ Variations due to the errors in DNA copying mechanism are useful in a population for ensuring the survival of the species. It is possible only with reproductive mode that allow more and more variation to be generated.
■ Generation of variations during DNA copying is a slow process. The variations in DNA get accumulated from generation to generation. Thus any two individuals would have different pattern of accumulated variations.
■ Combining variation from two or more individuals would thus create new combination of variants. Each combination would be new since it involve two different individuals.
■ Sexual reproduction incorporates a process of combining DNA from two different individuals.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ To prevent the doubling of DNA in each generation organisms have special lineage of cells in special organs which have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA as compared to non-reproducing cells, known as germ cells/sex cells/gametes.
■ Germ cells combine from two different individuals during sexual reproduction to form a new individuals, by re-establishing the number of chromosomes and DNA content in new generation.
■ Zygote grows and develop in to an organisms having high specialised tissues and organs with sufficient stored energy.
■ As the body design more complex, the germ cells also specialise. The larger, with more stored energy, non-motile called female gamete/egg/ovum and the smaller one, with less energy, more-active and motile called male gamete/ sperm/antherozoid.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
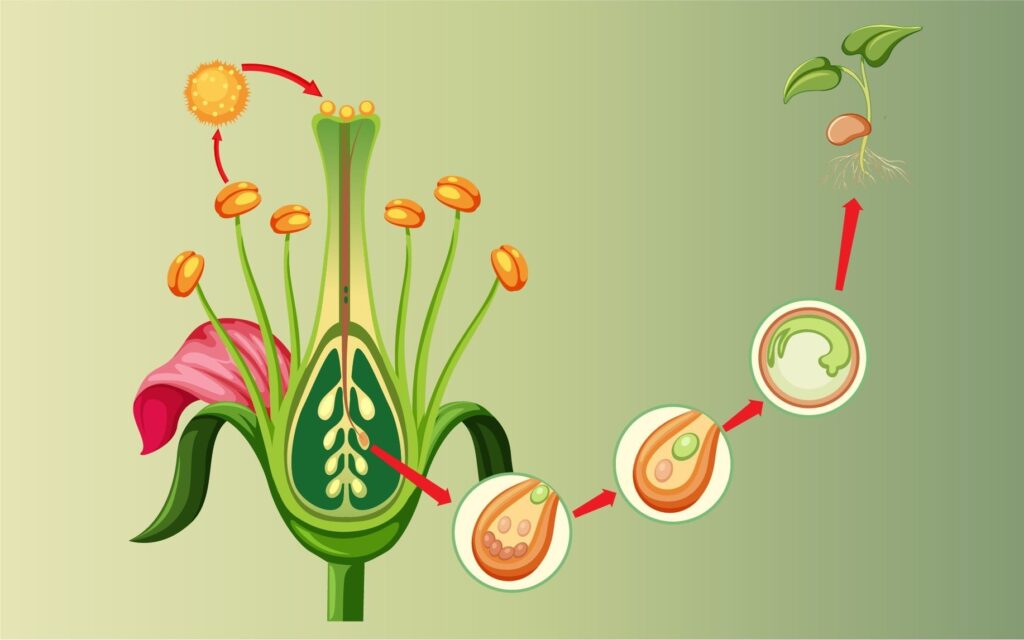
■ Sexual Reproduction in Flowering plants Flower a modified shoot meant for sexual reproduction. It has sepals and petals non-essential parts while stamens-male part and carpets female part are reproductive organs which produce germ cells.
■ Flowers may be unisexual having either male or female part e.g., papaya, cucurbit or bisexual having both stamen and carpel e.g., Rose, mustard etc.
■ Stamen is the male reproductive part produce yellowish pollen grains (n) in the pollen-sac of anther.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Carpel is the female reproductive part having basal ovary, middle style and terminal receptive part stigma. Ovary contains many ovules and each ovule contains egg/ovum.
■ The pollen grains produced in stamens are transferred to the stigma in same flower is called self pollination or when the pollen is transferred from one flower to another is called cross pollination.
■ Pollen grains once on the stigma, produce pollen tubes which reach the ovary through style.
■ Pollen tube contains male gametes. once inside the ovule, it release male gametes which fuse with egg to form zygote. Zygote under goes repeated divisions to form an embryo.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ A Embryo consists of radicle, plumule and cotyledons.
■ An ovule develops thick coat to form seed. The ovary grows in size and matures to form fruit. The sepals, petals, stamens and style shrivel and fall off.
■ The seed contains embryo- the future plant which under suitable condition of temperature, oxygen and water develops in a seedling. This process is called germination.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
Reproduction in Human beings
■ In human body, many changes appear as he/she grows from childhood to youth. Thus period Fer from childhood to youth is called adolescence and the stage in which an individual attains maturity and functioning of sex-organs is called puberty.
■ In this teenage period beside increase in height or weight, appearance of body changes. proportion change, new features (beard, moustaches, hair, breast development) appear, alongwith change in psychological emotions and sensations.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Common changes in boys and girls, is growing of thick hairs in armpits, around genital organs and darkening of skin in this area, thinner hair appear on legs and arms and face, skin Th becomes oily, appearance of pimples, awareness about our body and those of other develop.
■ In girls breast size increase, darkening of skin around nipples, start of menstruation-menarche.
■ Boys develop thick hair on face, voice cracks, penis begins to enlarge and erect, sometimes at days dreams or night.
■ These changes appear over months and years, may happen early and quick in some and in other very slowly. Each change does not become complete quickly. Those change comprise sexual maturation of body.
■ The creation of germ cells to participate in sexual reproduction is another specialised function. The resources of body are also directed in achieving the maturation of reproductive tissue while the rate of general body growth slow down. This period is called puberty.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Sexual mode of reproduction in animals, comprise of joining together of body of two individuals for internal transfer of germ cells for fusion a process called copulation and joining of germ cells-fertilisation.
■ In mammals the baby is carried in mother’s womb/uterus for quite a long period, give birth and then breast-fed the baby
■ It all needs maturity of female reproductive system as well as breast.
■ Humans are unisexual and human reproducing is highly evolved. Testes in males and ovaries in female are primary sex organs.
■ Male reproductive system consists of structures that produce male gametes/ sperms and deliver the sperms to the site of fertilisation.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ A male reproductive system ducts and a pair of testes, genital ducts (a pairs of epididymes. e efferentiatia, ejaculatory ducts and a single urethra) store and carry the sperms produced is testes out of the body) and accessory glands (a pair of seminal vesicles a prostate gland and a pair of cowper’s glands-secretions serve to nourish transport and mature sperms) are supporting organs (scrotum-maintains temperature 2-3 °C lower than the body temperature. Penis-release the semen in to vagina by ejaculation).
■ Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in a thin pouch of skin called scrotum which help in thermo regulation, maintaining temperature 2-3 °C lower than body temperature. Testosterone the male hormone is produced inside the testes help in regulating sperm formation and production of secondary sexual characters characteristic of boys at the time of puberty.
■ Sperm are delivered by vas defrens which unite with a small tube from urinary bladder to form urethra a common passage for sperms and urine.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Vas defrens along its path receives secretion of accessory glands, to form semen-a fluid containing sperms.
■ A sperm consist of head containing nucleus with a cap, middle piece and a tail which help in swimming towards female gamete/ovum/egg.
■ Female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries and accessory organs a pair of oviducts (transport ova), uterus (protects and nourishes the developing foetus) vagina (receives penis, sperms and birth canal) external genitalia (site for coetus and birth of child) and Bartholin’s glands (secrete mucus) and a pair of mammary glands (secrete milk)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Female gamete/sex cells/eggs/ ova are produced in the ovaries.
■ Female hormone oestrogen is also produced in the ovaries which help in egg formation and development of secondary sexual characteristic of a girl at the time of puberty.
■ In females at the time of birth ovaries contain thousands of immature eggs. on reaching puberty majority of eggs degenerate and at menstruation time one egg is produced every monthly in one of the ovaries.
■ The egg is carried from the ovary by a thin tube oviduct/fallopian tube to the uterus, after fertilization in posterior part of the tube.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Uterus is a large, elastic bag-like structure which opens into vagina, a extensible tube which receives the penis during copulation.
■ Sperms released during ejaculation, move through the vagina, uterus and reach oviduct when they encounter the egg. One of the sperm fuses with egg to form zygote. Zygote starts dividing and move towards uterus and gets implanted, which already prepared itself to receive and nurture the growing embryo. For this purpose, the lining of uterus become thickened and richly supplied with blood vessels to nourish the embryo.
■ Placenta is a special tissue which makes connection between growing embryo and mother’s blood to get nutrient, O, and also to eliminate its waste, Placenta consists of numerous finger like projection villi surrounded by blood spaces on the mother side. Placenta provide a large surface for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother blood to the embryo. Waste substance produced by embryo are removed by transferring them into mother’s blood through the placenta
■ A long umbilical cord, connects the growing embryo and the uterine wall of mother through placenta.
■ It takes nine months for the complete development of a baby inside mother’s womb.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ A child is delivered due to strong rhythmic contractions the muscles of ulterus. During every month ovary releases one egg and the uterus also prepares to receives fertilised egg. The lining becomes thick and strong with large number of blood vessels to nourish the embryo if fertilization had taken place. If the egg is not fertilised within one day of its release it degenerate. Lining of uterus is no more needed. So the lining slowly. breakdown, comes out through the vaginas, as blood and mucus. This cycle is called menstruation and occurs roughly every month. The menstruation last for 2-8 days.
■ Some degree of sexual maturation does not mean that the body or the mind is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. All of us are under differ kind of pressure about these issues.
■ Many diseases can be sexually transmitted these include bacterial infections such as gonorrhea and syphilis and viral infections-as warts and HIV-AIDS. Use of condoms during sex helps to prevent transmission of STDs.
■ Unwanted and unplanned pregnancies adversely affect the body, mind and health of a woman. Use of contraceptive help in avoiding pregnancy.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
■ Creation of mechanical barrier so that sperm does not reach the egg, are (i) Condoms, Diaphrgm (ii) Intrauterine devices inserted in vagina cause side effects due to irritation in uterus. They are such as loops and copper-T (iii) Hormonal contraceptive, oral pills e… mala-D, male-N. Egg are not released and fertilisation can not occur. (iv) spermicides chemical that kill sperms e.g., foam tables, jellies creams etc. (v) Surgical methods are now a days used though they are safer but complications can come due to infection or if not performed properly.
■ In vasectomy a small part of genital duct-vas defrentia is cut and tied at end in males. In tubectomy, oviduct in females are removed and cut ends are ligated, so that there is no fertilisation.
■ Unwanted pregnancies can be removed by medical termination method called abortion (M.T.P.). Absortion is misused by the couple who do not want a female child as sex of baby is revealed through amniocentesis. It leads to illegal sex-selective abortions of female foetuses It has disturbed sex-ratio. For a healthy society sex-ratio must be maintained
■ Due to alarming decline in sex-ratio Govt. has banned prenatal sex determination by law.
■ The rate of birth and death in a given population determine its size.
■ Large population make difficult to improve the standard of living, create inequality in society leads to poor standard of living for many people.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
