DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ

HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
POINTS TO REMEMBER
Do organisms create exact copies of themselves?
■ The of new organisms from the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction.
■ Reproduction helps to replace the organisms who die natural death, by diseases or accidents. Reproduction helps to maintain the continuity of species on this earth.
■ Reproducing organisms create new individuals that look very much like themselves.
■ Reproduction at its more basic level involve making copies of the blue print of body design.
■ DNA molecules present in chromosome contain all the information of inheritance of characters is passed from parents to next generation An exact copy of DNA is passed. DNA contains all the information for making proteins.
■ Difference in DNA leading to difference in proteins leads to changed/altered body design.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
■ Reproducing cell, use chemical reactions to create two copies of DNA one copy is retained in the original cell and the other copy is pushed in the new daughter cell along with additional cellular apparatus. Therefore a cell divides to form two exactly similar cells.
■ Due to some error in the biochemical reaction there may come variations in the copying of DNA. Sometime due to drastic variations, the changed new DNA copy cannot function in the inherited cellular apparatus and the cell dies. There are many variations in DNA where the cell survives but differ from the original cell: This inbuilt tendency for variation is the basis of evolution.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
■ Ability of DNA copying during reproduction help in maintenance of body designs features, which allow the populations of organisms to adapt. to well defined habitat arniches. Reproduction is thus linked to the stability of population or species.
■ Factors governing the habitat or niche such as temperature, water level, humidity etc. change, the population once suited could wipe out. However some individuals in a population with some variations have chance to survive.
■ Variations is thus useful for the survival of species over time.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
Table of Contents
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
1. In the list if organism given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are:
(i) banana (ii) dog
(iii) yeast (iv) Amoeba
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (ii). (iii)
(c) (i), (ii)
(d) (i), (iii), (iv)
Ans. (d)
2. Offspring formed by asexual method of reproduction have greater similarity among themselves because:
(i) asexual reproduction involves only one parent
(ii) asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
(iii) asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction
(iv) asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv).
Ans. (a)
3. Character transmitted from parents to offspring are present in
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Ribosome
(c) Golgi
(d) Genes
Ans. (d)
4. Character that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show
(a) only similarities with parents
(b) only variations with parents
(c) both similarities and variations with parents
(d) neither similarities nor variations.
Ans. (c)
5. A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Spirogyra and Yeast is that:
(a) they reproduce asexually
(b) they are all unicellular
(c) they reproduce only sexually
(d) they are all multicellular
Ans. (a)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
6. In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by
(a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
(b) division of a cell into two cells
(c) divisions of a cell into many cells
(d) formation of young cells from old cells.
Ans. (a)
7. The ability of cells to divide into several cells during reproductions in Plasmodium is called:
(a) budding
(b) reduction division
(c) both similarities and variations with parents
(d) multiple fission.
8. The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is:
(a) gametes, zygote embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(c) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling.
Ans. (a)
9. The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remains constant due
(a) doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
(b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
(c) doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
(d) halving of chromosomes after gametes formation.
Ans. (b)
10. In Rhizoups, tubular thread-like structure bearing at their tips are called:
(a) Filaments
(b) Hyphae
(c) Rhizoids
(d) Roots.
Ans. (b)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
11. Vegatative propagation refers to formation of new plants from:
(a) stem, roots and flowers
(b) stem, roots and leaves
(c) stem, flowers and fruits
(d) stem, leaves and flowers.
Ans. (b)
12. Factor responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on slices of bread are:
(i) large number of spores
(ii) availability of moisture and nutrients in bread
(iii) both similarities and variations with parents
(iv) presence of tublar branched hyphae.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (b)
13. Reproduction is essential for living organisms in order to:
(a) keep the individual organism alive
(b) fulfill their requirement
(c) maintain growth
(d) continue the species generation after generation.
Ans. (d)
14. In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes (germ cells) are:
(a) stamen and anther
(b) filament and stigma
(c) anther and ovary
(d) stamen and style
Ans. (c)
15. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(a) pollination, fertillisation, seedling, embryo
(b) seedling, embryo, fertillisation, pollination
(c) pollination, fertillisation, embryo, seedling
(d) embryo. seedling, pollination, fertillisation
Ans. (c)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
16. Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between:
(a) pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style.
Ans. (b)
17. Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual
(ii) They are the sexual reproductive organs
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants
(iv) After fertillization, they give rise to fruits
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (d)
18. Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (b)
19. Which among the following statements are true for sexual reproduction in following plants?
(i) It require two types of gametes
(ii) Fertillisation is a compulsory event
(iii) It always results in formation of zygote
(iv) Offspring formed are clones
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (c)
20. In Figure the parts A. B and C are sequentially
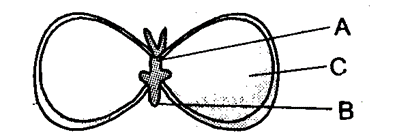
(a) cotyledon, plumule and radicle
(b) plumule, radicle and cotyledon
(c) plumule, cotyledon and radicle
(d) radicle, cotyledon and plumule
Ans. (b)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
21. Offspring formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because:
(a) sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
(b) genetic material comes from two parents of the same species
(c) genetic material comes from two parents of different species
(d) genetic material comes from many parents
Ans. (b)
22. During adolescence, several changes occur in the human body. Mark one change associated with sexual maturation in boys:
(a) loss of milk teeth
(b) increase in height
(c) cracking of voice
(d) weight gain
Ans. (c)
23. In human females, an event that reflects onset of reproductive phase is:
(a) growth of body
(b) changes in hair pattern
(c) change in voice
(d) menstruation
Ans. (d)
24. In human males, the testes in the scrotum, because it helps in the:
(a) process of mating
(b) formation sperm 25. Which among the following is not the function of testes at puberty ?
(c) easy transfer of gametes
(d) all the above
Ans. (b)
25. Which among the following is not the function of testes at puberty?
(i) formation of germ cells
(ii) secretion of testosterone
(iii) development of placenta
(iv) secretion of estrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (i)
(c) (iij) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans. (c)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
26. The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for transport of sperms is:
(a) testis →vas deferens → urethra
(b) testis → ureter → urethra
(c) testis→ urethra → ureter
(d) testis→ vasdeferens → ureter
Ans. (a)
27. Which among the following diseases is not sexually transmitted
(a) Syphilis
(b) Hepatitis
(c) HIV-AIDS
(d) Gonorrhoea
Ans. (b)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
ALSO VISIT :
10TH CBSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 MCQ
