DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
Table of Contents
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
38.Name the organs producing sperms and ova respectively in humans.
Ans Sperms-Testis, Ova-Ovary
39.Name the organ in humans which produces
Ans.(i) Male germ cell-Testis
(ii) Female germ cell-Ovary.
40. What is fertilisation? Where does it occur in a human female?
Ans. Fertilisation is the process of fusion of male sex cell/sperm male/gametes with the female sex cell/ovum/egg to form a diploid zygote.
In human female, it occurs in fallopian tube.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
41. Name the two types of mamalian gametes. How are these different from each other!
Name the type of reproduction they are involved in. Write the advantage of this type of
reproduction.
Ans. (i) Male sex cells/sperms; female sex cells/ovum/egg.
(ii) A male gamete/sperm is a dart-like having a cap-like acrosome and a tail which helps the
sperm to move toward egg. The egg is a small rounded structure having abundant stored
food material, a nucleus. It consists of whitish albumen and yellow yolk. It is immobile.
The sex-cells/gametes are involved in sexual reproduction. The sexual reproduction results in
variations, better adaptability, vigour and vitality of individuals.
42.(a) Name the organ that produces sperms as well as secretes a hormone in human males.
Name the hormone it secretes and write its functions.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs.
(c) Explain how the developing embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Ans. (a) Organ-Testes Hormone-Testosterone
Function (i) Formation of secondary sexual characteristics (ii) Regulate formation of sperms.
(b) Fallopian tube.
(c) The developing embryo get nourishment from the mother body through placenta. An
umbilical cord attach the growing embryo with the placenta. Useful substances from the
mother and wasteful substances from embryo. foetus are exchange through placenta.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
43. State the changes that take place in the uterus when:
(a) Implantation of embryo has occurred.
(b) Female gamete/egg is not fertilised.
Ans. (a) After implantation uterus becomes thick and spongy. The finger like outgrowths. villi from the embryo, along with uterine wall form a special spongy disc shaped structure called Placenta. The villi of embryo comes in contact with blood sinuses of uterus. Exchange of useful materials from mother to embryo and removal of waste substances from embryo to mother takes place through placenta.
(b) If the egg is not fertilised, the thick and spongy lining of uterus is not needed any longer. It slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous. It is called menstruation and usually lasts for about 2-8 day.
44. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction? Write the importance of such
Ans. Basic requirements of sexual reproduction are (i) different types of parents i.e., biparental. (ii) meiosis during gamete formation in diploid organisms. (iii) formation of sex-cells/gametes. (iv) fertilisation (v) zygote formation which develop in to new individuals.
Importance: (i) Production of variations (ii) better adaptability (iii) vigour and vitality of di offspring (v) genetic variations play a role in evolution of new forms.
45. Name the hormone secretion of which is, responsible for dramatic changes in appearance in girls when they approach 10-12 years of age.
Ans. Estrogen (= oestrogen) produced by growing follicles inside the ovary.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
46. List two unisexual flowers.
Ans. Water Melon, Papaya.
47. Write the full expansion of HIV.
Ans. Intra-uterine contraceptive device.
48. Define puberty.
Ans. It is the beginning of development for sexual maturity which occurs at the age of 10- 14 years in girls and 13- 15 years in boys. Fully formed primary sex organs start secreting hormones for slow development of secondary sex organs and secondary sex characters,
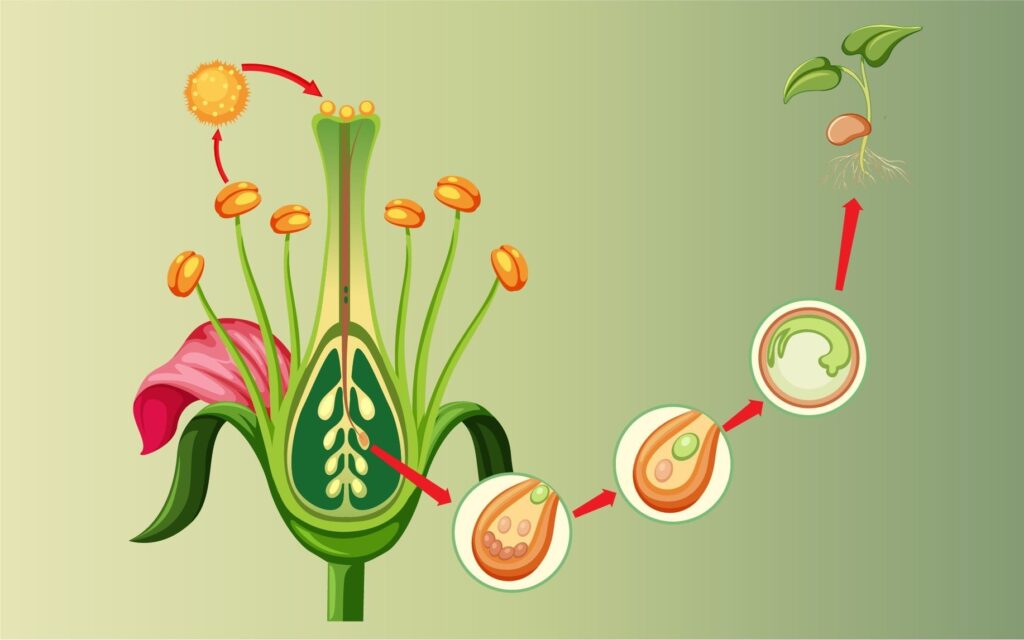
49. What is pollination? How does it take place?
Ans. Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma. Pollination between anther to the stigma of the same flower is called self pollination. In occurs through contact between the two.
Pollination between anther of one flower and stigma of another flower is cross pollination. It requires an external agency which may be abiotic (wind, water) or biotic (insects, birds, bats, worms)
50. Name the type of asexual reproduction in
(a) Planaria (b) Rhizopus (c) Spirogyra (d) Hydra.
Ans. (a) Planaria-regeneration
(b) Rhizopus-spore formation
(c) Spirogyra-fragmentation
(d) Hydra-budding
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
51. Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law. State two reasons.
Ans. (i) The test has been banned since due to desire of male child, there has been large scale female foeticide.
(ii) This has resulted in declining female-male sex ratio.
52. What is placenta? State its two roles during pregnancy.
Ans. Placenta is a spongy vascular structure formed by the joint activity of maternal and foetal tissues in the wall of uterus that connects foetus with uterus.
Roles: (i) Providing nutrition to the foetus.
(ii) Taking away wastes of the foetus.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
53. Explain the following methods of contraception giving one example of each (i) Barrier method (ii) Hormonal imbalance method. (iii) Surgical method.
Ans. (i) Barrier Method: To prevent contact of sperm and egg e.g., Condom, cervical cap.
(ii) Hormonal Imbalance Method: It is commonly carried out by the ladies through regular use of oral pill. They inhibit ovulation through suppression of FSH.
(iii) Surgical Method: It is of two types:
(a) Vasectomy: The two vasa deferentia of the male are blocked by cutting and tying.
(b) Tubectomy: The two fallopian tubes of the female are blocked by cutting and tying or
54. Expand AIDS. List any four methods of prevention (control) of AIDS.
Ans. AIDS-Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Methods of Prevention: (i) Avoiding unprotected sex. (ii) Use of disposable syringes and needles (ii) Use of disposable blades and razors. (iv) Compulsorily complete sterilization of all equipment used in dental treatment and surgery. (v) Proper screening of blood before transfusion.
55. Write two causes of human population explosion. Explain with the help of suitable examples, how this explosion can be checked.
Ans. Population explosion is the rapid rise in human population.
Causes: (i) Decrease in death rate.
(ii) Longer life span. Both are due to progressively improving health care facilities.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
Check: Population explosion can be checked only through fertility control or family planning. This can be achieved through
(i) Education: There is an inverse ratio between education and population growth.
(ii) Population Education: It is imparting knowledge to public about the effects of excessive population, advantages of small families and means to achieve it.
(iii) Marriageable Age: Number of births is reduced young person’s marry late. Gainful employment and higher social status of women also reduce birth rate.
(iv) Easy Availability of Birth Control Means: This will reduce reluctance on the part of eligible couples to adopt family planning measures.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
56. What are the functions of testis in the human male reproductive system? Why are these located outside the abdominal cavity? Which is responsible for bringing about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty?
Ans. Functions of testis: Produces sperms and male sex hormone called testosterone.
Location of Testis: Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity (In testicle behind penis) as maturation of sperms requires a temperature lower by 2°C than that of the body.
Puberty changes in Boys: They are caused by hormone testosterone.
57. What are chromosomes? Explain how in sexually reproducing organisms the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained.
Ans. Chromosomes are linear strands of DNA and associated proteins that occur in nucleus of eukaryotic cells carry genes and function in transmission of hereditary information. The chromosome number is halved at the time of gamete formation and is maintained by fertillsation.
58. (a) Name the parts 1 to 5 of human female reproductive system.
(b) Name the part in which fertilization takes place in the system.
Ans. (a) 1 fallopian tube,
2 — ovary,
3 — Uterus,
4 — cervix,
5 — vagina.
(b) Fallopian tube.
59.What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name four such diseases. Which one of them damages the immune system of human body?
Ans. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs). They are diseases which are transmitted through sexual contact with infected persons.
Examples. 1. Gonorrhoea. 2. Syphilis 3. Genital Warts 4. AIDS.
Damage to Immune System. AIDS caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) damages human immune system because the virus multiplies in macrophages and helper T-4 lymphocytes.
60. Explain double fertilization in plants.
Ans. The phenomenon of two male gametes fusing with different cells in the same embroyo sac to produce two different structures is called double fertilization
One male gamete fuses with oosphere (egg) to form diploid zygote. It is called generative fertilization Zygote grows to form embryo. The second male gamete fuses with diploid secondary nucleus of central cell. It produces a triploid primary endosperm cell. The fusion is called triple fusion or vegetative fertilization. It produces a nutritive tissue called endosperm.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
61. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Ans. Sexual reproduction has the following advantages over asexual reproduction:
(i) Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes coming from male and female parents. Since the fusing gametes come from two different and sexually distinct individuals, the offsprings exhibit diversity of characters.
(ii) Meiosis during gametogenesis provides opportunities for new combination of genes. It plays a prominent role in the origin of new species and leads to variation required for evolution.
62. Reproduction is linked to stability of population of a species. Justify the statement.
Ans. In reproduction, copying of parental DNA blue print occurs and the same is passed on to the offspring with minor variations. This consistency leads to the stability of the species.
63. Trace the path of sperm during ejaculation and mention the gland and their functions associated with the male reproductive system.
Ans. Sperms are passed from testis into the vas deferens and then to the urethra before ejaculation. On their way out, they receive secretions of seminal vesicle and prostate gland which provide nutrition to the sperms as well as facilitate their transport.
64. How does fertillization take place? Fertilization occurs once in a month. Comment. Ans. During sexual intercourse the male partner, ejaculates and results in the entry of sperms into vagina the female reproductive tract of the female.
Female releases egg from the ovary which move in the fallopian tube
Sperms move upwards in the uterus and fuse with egg to form the zygote. This process is called fertilization and it occurs in fallopian tube.
Egg is released every month around 14th day from the start of menstruation in the female.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
ALSO VISIT :
10TH CBSE
| Also Learn: | Attempt the Quiz on Mathematics | Attempt the Quiz on Social Science (Economics) | |
| GLOBALISATION AND INDIAN ECONOMY MONEY AND CREDIT MIND MAP FOR NATIONALISM IN EUROPE LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION REAL NUMBERS QUESTIONS ON CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION CLASS 10 ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS | Real Numbers | Development Sectors of Indian Economy Money and Credit Globalisation and Indian Economy Consumer Rights |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10
