DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
POINTS TO REMEMBER AND IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
Making Order Out Of Chaos- Early Attempt At The Classification Of Elements
■ Classification of elements is primarily based on the similarity in their properties.
■ Dobereiner was first to group the elements into triads in which atomic mass of central element was arithmetic mean of the other two.
■ Newland gave the law of octaves according to which on arranging the element in order of increasing atomic weight every eighth element had properties similar to the first.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
Table of Contents
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
1. Did Dobereiner’s triad also exist in the columns of Newlands’ octaves? Compare and find out.
Ans. Yes, some of the Dobereiner’s triads could also be found in the columns of Newlands’ octaves For example, two such triads in Newland’s columns are Li, Na, K and Be, Mg, Ca.
2. What were the limitations of Newland’s law of octaves?
Ans. Some of the limitations of Newland’s law of Octave are :
■It was limited to lighter elements having atomic masses up to 40 u, i.e., up to calcium only.
■It was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in future. But several elements were discovered after that.
■Some similar elements were separated from one another while some dissimilar elements like Co, Ni and halogens (Cl, Br, I) were put in same column.
■After the discovery of noble gases, eighth element no longer remained similar to first one
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
3. What were the limitations of Dobereiner’s triads?
Ans. All elements known at that time could not be arranged as Dobereiner’s triads. For example three elements like N, P and S have similar properties but they could not fit into Dobereiner’s triads
Making Order Out Of Chaos-Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
■Mendeleev arranged the elements in increasing order of their atomic masses and he pointed out that elements with similar properties were repeated after regular intervals of 2, 8, 8, 18, 18, 32.
■Mendeleev predicted the existence of some yet to be discovered elements on the basis of gaps in his periodic table.
■Beside all success in his arrangement, there were few anomalies also.
■In Mendeleev’s periodic table elements with similar properties were placed in same vertical column called group. In short, there were nine vertical columns and seven horizontal rows called periods.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
4. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, the elements were arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses. However, cobalt with atomic mass of 58
In Mendeleev’s periodic table cobalt (Co) with a higher atomic mass of 58.93 u is placed before nickel (Ni) due to the following reasons:
(i) The properties of cobalt are similar to those of rhodium (Rh) and iridium (Ir), and
(ii) The properties of nickel are similar to those of palladium (Pd) and platinum (Pt).
5. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his periodic table?
Ans. Mendeleev used atomic masses of the elements as the criteria for creating his periodic table. In this table, the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic masses.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
6. Give an account of process adopted by Mendeleev for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at periodic law?
Ans. Mendeleev used mainly two criteria in creating his periodic table. Atomic masses of elements and similarity in the formulae of hydrides and oxides of various elements. When he did so most of elements got arranged in order of increasing atomic masses. Thus, when the various elements were arranged in order of their increasing atomic masses, elements having similar properties fell under one another in the same vertical column called the group. He further observed that repetition of elements with similar physical and chemical properties occurred after certain regular intervals. On the basis of these observations, Mendeleev proposed his Periodic Law which stated that “the physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.”
7. Why do you think that the noble gases should be placed in a separate group?
Ans. In the Medeleev’s periodic table, the elements have been arranged in the different groups on the basis of valency. For examples, the elements placed in group I have valency equal to one. Same is the case with the elements placed in other groups. Since the noble gas elements He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn have zero valency, they could not find a place in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. These have been placed in a separate group called zero group in the modified Periodic Table.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
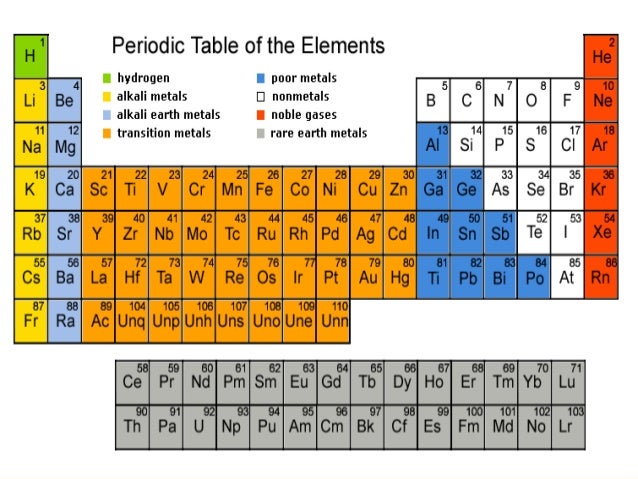
Making Order Out Of Chaos-The Modern Periodic Table
■The Modern Periodic Table is based on modern periodic law which states that the properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic number.
■In Modern Periodic Table, the elements are arranged in 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows called periods.
■Group contains elements having same number of electrons in the outer most shell of electrons.
■Period contains elements having same outer shell of electrons but different number of valence electrons.
■Elements thus, arranged, show periodicity in properties including atomic size, valency, metallic and non-metallic character.
8. What is common in the elements belonging to the same period in the periodic table.
Ans. The element belonging to the same period has same number of electron shells.
9. Why is chlorine and bromine kept in the same group of the periodic table?
Ans. The valence shell configuration of both chlorine and bromine is same. The same numbers of valence electrons (7) are present in both. That is why they have been placed in the same group of periodic table.
10. Why does atomic radius change as we move from left to right in a period?
Ans. As we move along the period from left to right, the nuclear charge increases gradually by one unit and each time additional electron goes to same shell of electrons. As a result, attractive force between nucleus andelectron shell increases and size decreases.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
11. Chlorine (atomic number 17) is more electronegative than sulphur (atomic number 16). Explain
Ans. Chlorine and sulphur belong to same period. Nuclear charge of chlorine is higher than that of sulphur and its size is smaller than sulphur. Both these factors cause chlorine to have greater attraction for electrons and thus, electro negativity of chlorine is more than that of sulphur.
12. The atomic numbers of three elements X, Y and Z are 9, 11 and 17 respectively. Which of these two elements will show similar characteristics and why?
Ans. Among these the elements with atomic number 9 (2, 7) and 17 (2, 8, 7,) belong to the same group of periodic table and hence, they exhibit similar characteristics.
13. How does electronic configuration of an atom relate to its position in the modern periodic table?
Ans. In modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers. The electronic configuration of elements is also based on their atomic numbers. Therefore, position of element in the periodic table is also related to the electronic configuration of the elements. The electronic configuration can help us to predict the location of element in the periodic table.
For example
Period = Number of electron shells:
Group = Number of valence electrons (if the number is less than 3)
= 10 + Number of valence electrons (if the number is between 3 to 8)
14. Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev’s Periodic Table and the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans. The main points of difference are given below in tabular form:
| Mendeleev’s Periodic Table | Modern Periodic Table |
| 1. Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses. | 1. Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers. |
| 2. There is no provision for separate position for isotopes of an element since their atomic masses are different. | 2. Separate position for isotopes of an element are not required because they have the same atomic number. |
| 3. Some elements with higher atomic masses have been placed before elements of lower atomic masses. | 3. No such discrepancy arises because elements are arranged in serial order of their increasing atomic number irrespective of their atomic masses. |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
15 Identify the elements with the following property and arrange them in increasing order of their reactivity.
(a) An element which is a soft and reactive metal.
(b) The metal which is an important constituent of limestone.
(c) The metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature.
Ans. (a) Sodium (Na) or Potassium (K).
(b) Limestone is calcium carbonate, therefore, the important constituent of limestone is calcium.
(c) Metal which exists in the liquid state at room temperature is : mercury (Hg).
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
16.Properties of the elements are given below. Where would you locate the elements following in the periodic table?
(a) A soft metal stored under kerosene.
(b) An element with variable (more than one) valency stored under water.
(c) An element which is tetravalent and forms the basis of organic chemistry.
(d) An element which is an inert gas with atomic number 2.
(e) An element whose thin oxide layer is used to make other elements corrosion by the process of “anodising“.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
Ans. (a) Sodium (Group 1 ; Period 3) or Potassium (Group 1 ; Period 4)
(b) Phosphorus (Group 15; Period 3). It shows a valency of 3 and 5
(c) Carbon (Group 14; Period 2)
(d) Helium (Group 18; Period 1).
(e) Aluminium (Group 13; Period 3)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
17. Write two reasons responsible for the late discovery of noble gases.
Ans. (i) Noble gas elements were not present in the crust of earth as minerals like other elements. They are present in air to a very small extent.
(ii) Noble gas atoms have stable electronic configuration of their outermost shells. They do not combine with atoms of other elements. That is why noble gas elements were discovered quite late.
18. “Hydrogen occupies a unique position in modern periodic table”. Justify the statement.
Ans. Hydrogen occupies a unique position in the modern periodic table because of the following reasons:
(i) Both hydrogen and alkali metals have similar outer electronic configuration (both have one electron in the valence shell). Therefore, some of the properties of hydrogen are similar to those of alkali metals and hence it can be placed in group 1 along with alkali metals.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
(ii) Both hydrogen and halogens have similar outer electronic configuration (both have one electron less than the nearest noble gas configuration). Therefore, some of the properties of hydrogen are similar to those of halogens and hence it can be placed in group 17 along with halogens.
(iii) In some properties, differs both from alkali metals and halogens. For example, the oxide of hydrogen, i.e., H₂O is neutral but the oxide of alkali metals (i.e., Na2 O, K2O, etc.) are basic while those of halogens (i.e., Cl207 , Br2 O5, 1205, etc.) are acidic.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
19. How could Modern periodic table remove the various anomalies of Medeleev’s periodic table?
Ans. 1. Position of isotopes: Isotopes of the element could find the same place in the modern periodic table because they have same atomic number.
2. Some pairs of elements like Co and Ni were earlier misfit in the Mendeleev’s periodic table. Similarly K with atomic mass 39 u was placed after Ar with atomic mass 40 u. Such anomalies have been automatically removed.
3. Uncertainty in predicting of new element which existed in Mendeleev’s periodic table because atomic masses do not increase in a regular manner in going from one element to another. This limitation has also been removed in modern periodic table once the atomic number was taken as the basis of arrangement.
20. Three elements A, B, C have 3, 4, 2 electrons respectively in their outermost shell. Give the group number to which they belong in the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans. (i) Element A has 3 valence electrons, therefore, its valency is 3 and thus belongs to group 13
(3 + 10).
(ii) Element B has 4 valence electrons, therefore, its valency is 4 and it belongs to group 14 (4 + 10).
(iii) Element C has two valence electrons, therefore, its valency is 2 and it belongs to group 2.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
21 What is periodicity in properties of elements with reference to Modern Periodic Table ? Why do all the elements of same group have similar properties?
Ans. Periodicity in properties means repetition of similar properties of elements after regular intervals when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers in modern periodic table. This is due to repetition of elements with similar electronic configuration of outer shell after regular intervals.
Elements present in the same group have similar electronic configuration of outermost shell of electrons. They have same number of valence electrons and same valency. Hence, their chemical behaviour is also same. For example elements of group 17 i.e., halogens have 7 electrons in valence shell. They are electronegative elements and tend to form monovalent anions.
22. How does the tendency of elements to gain electrons change as we move from left to right in a period. State the reason for this change.
Ans. As we move across the period from left to right nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases. As a result the tendency to gain electrons or electronegative character also increases from left to right.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
23. (a) State Modern Periodic Law.
(b) Name the scientist who first of all showed that atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
Ans.(a) Modern Periodic Law: The law states that properties of the elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers. It means that when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers elements with similar properties are repeated after regular intervals.
(b) Henry Moseley showed by his experiments that atomic number of the element is more fundamental property than atomic mass.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
ALSO VISIT :
| Also Learn: | Attempt the Quiz on Mathematics | Attempt the Quiz on Social Science (Economics) |
| GLOBALISATION AND INDIAN ECONOMY MONEY AND CREDIT MIND MAP FOR NATIONALISM IN EUROPE LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION REAL NUMBERS QUESTIONS ON CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION CLASS 10 ELECTRICITY CLASS 10 QUESTIONS HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE CLASS 10 | Real Numbers | Development Sectors of Indian Economy Money and Credit Globalisation and Indian Economy Consumer Rights |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CLASS 10
