Table of Contents
WORK POWER AND ENERGY JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK POWER AND ENERGY JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS

41. One of the forces acting on a particle is conservative, then
(a) Its work is zero when the particle moves exactly once around any closed path
(b) Its work equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle
(c) It obeys Newton’s second law
(d) Its work depends on the end points of the motion, not on the path followed
Ans. (a), (d)
42. Mark the correct statement(s)
(a) Total work done by internal forces of a system on the system is always zero.
(b) Total work done by internal forces of a system on the system is sometimes zero.
(c) Total work done by internal forces acting between the particles of a rigid body is always zero.
(d) Total work done by internal forces acting between the particles of a rigid body is sometimes zero.
Ans. (b), (c)
43. Which of the following can be negative?
(a) Kinetic energy
(b) Potential energy
(c) Mechanical energy
(d) Energy
Ans. (b), (c), (d)
44. Which of the following may or may not be conserved
(a) Energy
(b) Potential energy
(c) Mechanical energy
(d) Kinetic energy
Ans. (b), (c), (d)
45. For an isolated system in the absence of any dissipative effect.
(a) Kinetic energy is conserved
(b) Potential energy is conserved
(c) Energy is conserved
(d) Mechanical energy is conserved
Ans. (c), (d)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK POWER AND ENERGY JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS
46. In case of explosion of a bomb, which of the following change?
(a) Kinetic energy
(b) Mechanical energy
(c) Chemical energy.
(d) Energy
Ans. (a), (b), (c)
47. A block hangs freely from the end of a spring. A boy then slowly pushes the block upwards so that the spring becomes strain free. The gain in gravitational potential energy of the block during this process is not equal to
(a) The work done by the boy against the gravitational force acting on the block
(b) The loss of energy stored in the spring minus the work done by the tension in the spring
(c) The work done on the block by the boy minus the work done by the tension in the spring plus the loss of energy stored in the spring
(d) The work done on the block by the boy minus the work done by the tension in the spring
Ans. (a), (b), (c), (d)
48. The potential energy U, in joule of a particle of mass 1 kg, moving in the xy plane, obeys the law U = 3x+4y, where (x, y) are the coordinates of the particle in meter. If the particle is at rest at (6, 4) at time r=0, then
(a) The particle has constant acceleration
(b) The work done by the external forces, from the position of rest of the particle and the instant of the particle crossing x axis is 25 J
(c) The speed of the particle when it crosses the y axis is 10m/s
(d) The coordinates of the particle at time t=4s are (-18.-28)
Ans. (a), (b), (c), (d)
49. A block is suspended by an ideal spring of force constant k. If the block is pulled down by applying a constant force F and if maximum displacement of the block from its initial
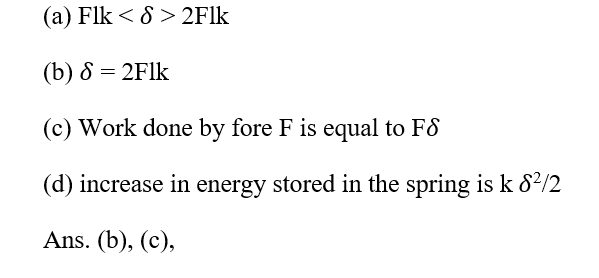
,
50. A horizontal plane supports a plank with a block placed ot as shown in Fig. A light elastic string is attached to the block which is attached to a fixed point O.
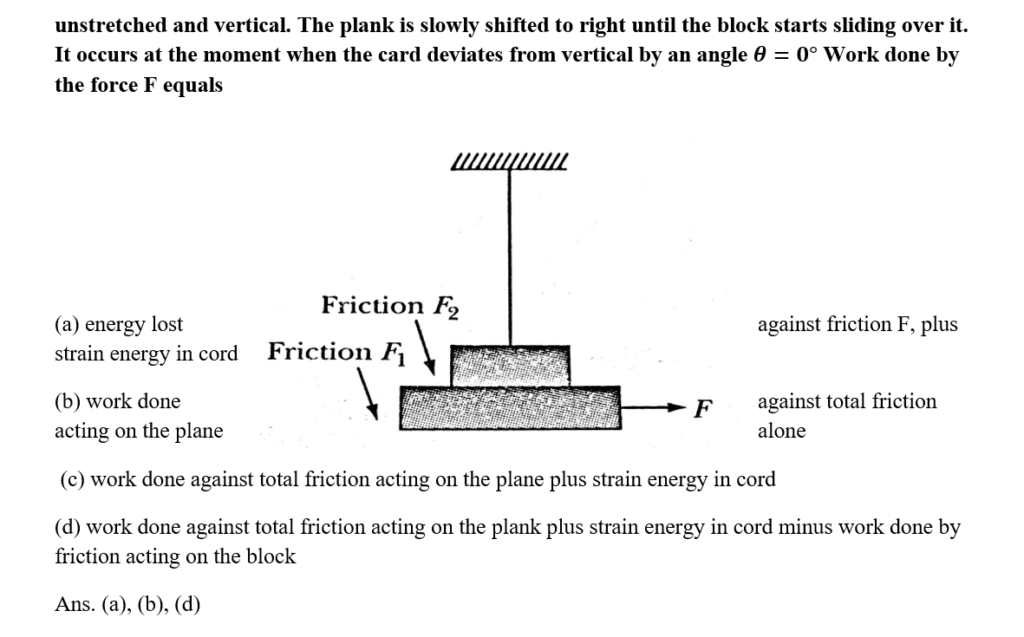
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK POWER AND ENERGY JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS
