DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Money Creation by the Commercial Banks: Commercial banks contribute to money supply by creating credit. They do it by advancing loans (in terms of demand deposits) many times more than their cash reserves. They do it on the bass of the historical experience that the deposit-holder never turn up enmass to withdraw their deposits. That, the liability towards the deposit-holders can be managed by keeping only a small percentage of deposits as cash reserves.
Credit Multiplier

It shows the number of times the commercial banks can create credit per unit of their cash reserves with the RBI in India, CRR is fixed by the RBI.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
The Central Bank is an apex bank of the entire banking system of a country RB1 is the central bank of India.
Functions: (i) Bank of issuing notes, (ii) Banker to the government, (iii) Banker’s bank and supervisory role, (iv) Lender of the last resort, (v) Custodian of foreign exchange, (vi) Clearing house, function, (vii) Control of credit.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Central of Money Supply by the Central Bank
Monetary Policy the policy to control the supply of credit/money in the economy. It aims at correcting the situations of inflation and deflation in the economy, Instruments of monetary policy are broadly classified as: (i) Quantitative instruments, and (ii) Qualitative instruments. These are also called instruments of credit control.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Quantitative Instruments of Monetary Policy:
(i) Three policy rates: (a) Bank rate. (b) Repo rate, and (c) Reverse repo rate.
(ii) Two polity ratios: (a) CRR, and (b) SLR
(iii) Open market operations
Qualitative Instruments of Monetary Policy:
(i) Margin requirement
(ii) Rationing of credit, and
(iii) Moral suasion
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Table of Contents
BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Choose the correct option:
1. In the context of commercial bank, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Note-issuing authority of the country
(b) Creates credit on the basis of cash reserves
(c) Accepts deposits of the general public
(d) Both (b) and (c)
2. Commercial banks create money by way of :
(a) time deposits
(b) demand deposits
(c) treasury bills
(d) bill of exchange
3. Which of the following is not concerned with banking organisation?
(a) Bank rate
(b) Fiscal deficit
(c) Credit creation
(d) Cash reserve ratio
4. Credit cards issued by the banks:
(a) encourage consumer spending
(b) increase aggregate demand in the economy
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
5. The main aim of the commercial banks is:
(a) social welfare
(b) to earn profits
(c) to provide services to the people
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
6. Maximum credit that the commercial banks can legally create depends on their
(a) gold reserves
(b) cash reserves with the RBI
(c) statutory liquidity ratio
(d) term deposits
7. Term deposits are those:
(a) against which no cheque can be issued
(b) against which no interest is paid to the depositors
(c) which are a part of

supply of money
(d) none of these
8. The percentage of demand deposits which the commercial banks are legally required to maintain as their liquid assets is called:
(a) CRR
(b) repo rate
(c) SLR
(d) reverse repo rate
9. SLR requires the commercial banks to build their liquid assets by way of :
(a) reserves of cash
(b) reserves of gold
(c) reserves of unencumbered securities
(d) all of these
10. Central bank is an apex bank of the country that:
(a) controls the entire banking system of the country
(b) issues currency
(c) acts as a banker to the government
(d) all of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
11. In India, the central bank is :
(a) Federal Reserve System
(b) Federal System
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) both (a) and (b)
12. Maximum credit that the commercial banks can legally create is indicated by:
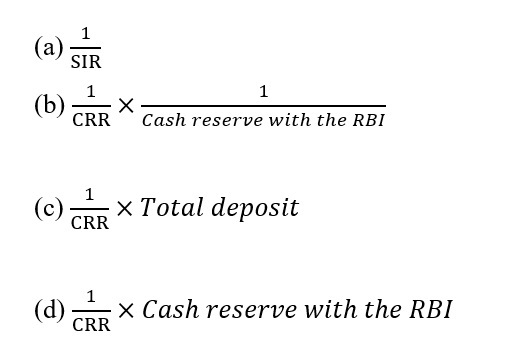
13. Credit control means
(a) contraction of credit only
(b) extension of credit only
(c) extension and contraction of money supply
(d) none of these
14. Which of the following is not the instrument of credit control?
(a) CRR
(b) SLR
(c) Bank rate
(d) Managed floating
15. Which of the following does not come under quantitative methods of monetary policy?
(a) Open market operations
(b) Cash reserve ratio
(c) Moral suasion
(d) Repo rate
16. Open market operations as an instrument of credit control are performed by:
(a) the central bank of the country
(b) the commercial bank of the country
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
17. With an increase in margin requirement, availability of credit in the economy.
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) unchanged
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
18. If inflation is to be combated, the RBI:
(a) raises SLR and lowers overline CRR
(b) lowers SLR and raises CRR
(c) raises both CRR as well as SLR
(d) none of these
19. If recession is to be combated:
(a) bank rate needs to be lowered
(b) CRR needs to be lowered
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) repo rate needs to be lowered and CRR needs to be raised
20. Reverse repo rate:
(a) generates interest income
(b) is increased to curb inflation
(c) is not a policy rate
(d) both (a) and (b)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Answers
| 1. (d) | 9. (d) | 17. (b) |
| 2. (b) | 10. (d) | 18. (c) |
| 3. (b) | 11. (c) | 19. (c) |
| 4. (c) | 12. (d) | 20. (d) |
| 5. (b) | 13. (c) | |
| 6. (b) | 14. (d) | |
| 7. (a) | 15. (c) | |
| 8. (c) | 16. (a) |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
D. Matching the Correct Statements
I. From the set of statements given in Column I and Column II, choose the correct pair of statements :
| Column I | Column II | |
| (a) SLR | (i) Fixed by the commercial banks | |
| (b) Primary deposits | (ii) Derivative deposits | |
| (c) Commercial bank | (iii) Advisor to the government | |
| (d) Central Bank | (iv) Provides Clearing House facility | |
| (e) Secondary deposits | (v) Not a part of total demand deposits of the bank |
Answer
(d) Central bank-(iv) Provides Clearing House facility
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
II. Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with respective items in Column I :

Answers
(a) – (iv), (b) – (v), (c) – (i) , (d)-(iii), (e)-(ii)
Very Short Answer Objective Type Questions
1. Define credit multiplier.
Ans. Credit multiplier is the reciprocal of CRR (cash reserve ratio).

2. Define primary deposits.
Ans. Primary deposits are cash deposits with the commercial banks by the people. These are a pane demand deposits of the banks.
3. What are secondary deposits?
Ans. Secondary deposits are those deposits which arise on account of loans by the banks to the people. These are reflected as a part of demand deposits of the banks. These are also called derivative deposits .
4. What is a central bank?
Ans. A central bank is an apex institution of a country that controls and regulates the monetary and financial system of the country.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
5. Define CRR
Ans. CRR (cash reserve ratio) refers to the legally required cash reserves of the commercial banks with the central bank as a percentage of their total deposits.
6. What is SLR?
Ans. SLR (statutory liquidity ratio) refers to liquid assets of the commercial banks which they are required to maintain as a minimum percentage of their total deposits.
7. Define bank rate.
Ans. The bank rate is the rate at which the central bank of the country offers loans to the commercial banks by discounting the securities. It is also called discount rate: the rate at which securities are discounted for purpose of loans. It does not involve any collateral, and it does not allow repurchase of securities.
8. What is repo rate?
Ans. Repo rate is the rate of interest at which commercial banks can raise short-term loans from the central bank.
9. What is reverse repo rate?
Ans. Reverse repo rate is the rate of interest at which commercial banks can park their surplus funds with the central bank, for short period of time.
10. What do you mean by open market operations?
Ans. Open market operations refer to the sale and purchase of government securities in the open market by the central bank of the country.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
11. Define margin requirement.
Ans. Margin requirement refers to the difference between market value of the security offered for loans and the amount of loans offered by the commercial banks.
12. Define moral suasion.
Ans. Moral suasion refers to persuasion as well as pressure exercised by the central bank on the commercial banks to be restricted and selective in lending during inflation, and to be liberal in lending during deflation.
Reason-based Questions
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Read the following statements carefully. Write True or False with a reason.
1. Higher CRR implies higher capacity to create credit.
Ans. False. Higher CRR implies lower capacity of the commercial banks to create credit. Because, credit multiplier is the reciprocal of CRR.
2. By purchasing government securities in the open market, the central bank intends to release more money supply in the market.
Ans. True. Central bank buys government securities with a view to increase the money supply. Purchase of securities by the central bank leaves more money with the people. It also increases liquidity of the commercial banks to create more credit (in terms of demand deposits).
3. Margin requirement is raised by the central bank with a view to increasing money supply.
Ans. False. To increase money supply, the central bank lowers the margin requirement so that people are induced to raise loans and the banks are able to create more credit by way of loans.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
4. During periods of depression, commercial banks are advised to follow dear money policy.
Ans. False. To curb depression, supply of money needs to be increased. Accordingly, commercial banks are advised to pursue cheap money policy.
5. The central bank is a lender of last resort.
Ans. True. A central bank advances loan to a commercial bank when the latter fails to get financial accommodation from anywhere against approved securities.
6. The central bank is a banker to the government.
Ans. True As a banker to the government, central bank keeps the accounts of all government banks and manages government treasuries.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
7. The commercial bank has the currency authority.
Ans. False. The central bank is the sole issuing authority in the country, it has the exclusive right of note issuing .
8. In India, CRR and SLR are fixed by the commercial banks themselves.
Ans. False. In India, CRR and SLR are fixed by the RBI.
9. Demand deposits are equal to cash deposits with the commercial banks.
Ans. False Cash deposits are only primary deposits with the commercial banks, Deposits created by way of loans are secondary deposits.
Demand Deposits= Primary deposits + Secondary deposits
10. Secondary deposits of a commercial bank are always less than its primary deposits ?
Ans. False. Secondary deposits are many times more than the primary deposits of a commercial bank. Because, primary deposits are cash deposits. A commercial bank can park its cash with RBI as ‘cash reserves’. It can legally create secondary deposits (by way of loans) many times more than their cash reserves.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
11. When CRR is raised, credit creation by the commercial banks is not necessarily reduced?
Ans. True. Because commercial banks may have some excess reserves.
12. CRR and SLR work opposite to each other.
Ans. False CRR and SLR are complementary to each other. A rise in these ratios controls the creation of credit, and vice versa.
13. Market rate of interest tends to be positively related to the bank rate.
Ans. True. Increase or decrease in bank rate is often followed by increase or decrease in the market rate of interest.
14. Repo rate is the rate of interest charged by the bank on commodity loans.
Ans. False. Repo rate is that rate at which central bank offers short-term loans to commercial banks
15. Higher repo rate implies higher credit creation capacity of the banks.
Ans. False. Higher repo rate implies lower credit creation capacity of the banks. Because, banks are not induced to borrow liquidity (cash) from the RBI for enlarging their credit-market.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
16. The commercial banks design all instruments of monetary policy and the central bank controls them.
Ans. False Central bank designs all instruments of monetary policy and also controls them.
17. The commercial banks are the controller of money supply.
Ans. False. The central bank controls the money supply in the economy. The commercial banks only contribute to money supply by way of credit creation.
18. The central bank issues currency on the basis of CRR.
Ans. False. Central bank does not issue currency on the basis of CRR. The ratio CRR impacts credit creation capacity of the commercial banks.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Q. What is the significance of centralised cash reserves with central bank?
Ans. Two observations need to be noted in this context:
(i) Centralised cash reserves enable the RBI to offer financial help to the commercial banks during emergencies. It is called ‘financial accommodation’ by the RBI. Banks get financial accommodation (or financial help) in times of emergency.
(ii) Centralised cash reserves enable the RBI to exercise control over the commercial banks. Because these reserves depend on CRR (fixed by RBI in India) and by varying the CRR, the RBI can increase or decrease the credit creation capacity of the commercial banks. Accordingly, money supply in the economy is regulated.
Q. What is selective credit control?
Ans. It refers to discriminatory policy of the central bank relating to select sectors of the economy. Flow of credit to certain sectors (priority sectors) may be encouraged with a view to stimulating production in these sectors. This is a positive application of selective credit controls. On the other hand, the central bank may decide to restrict the availability of credit to certain (non-priority) sectors. Generally, during periods of inflation, availability of credit for speculative activities (like storage of food grains) is discouraged. This is a negative application of the selective credit controls.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
High Order Thinking Skills & Applications
1. If the commercial banks buy government securities, their capacity to create credit is reduced De you agree?
Ans. Yes, the given statement is correct. By allowing or inducing the commercial banks to buy government securities, the central bank soaks cash balances of the commercial banks which they could use to create credit. Accordingly, the credit creation capacity of the commercial banks is reduced.
2. Is it correct that when margins are raised, demand for loans is negatively impacted?
Ans. When margins are raised, the difference between the market value of the security offered for loans and value of loans granted becomes high. It is now expensive for the people to take loans from the banks. Therefore, demand for loans reduces in the economy Thus, the given information is correct.
3. Is repo rate an instrument of qualitative credit control?
Ans. No, repo rate is an instrument of quantitative credit control it impacts the availability of credit across all sectors of the economy.
4. If CRR is lowered, investment demand must rise. Defend or refute.
Ans. Yes, the above statement is correct if CRR is lowered, credit creation capacity of the commercial banks is enhanced. Higher availability of credit and at lower interest rate must lead to a rise in investment demand.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
5. How is quantitative credit control different from qualitative credit control?
Ans. Quantitative credit control refers to overall credit control in the economy, affecting all sectors of the economy equally and without discrimination. Qualitative credit control refers to selective credit control that focuses on allocation of credit to different sectors of the economy. Flow of credit is. encouraged to the priority sectors, while it is discouraged to the non-priority sectors.
6. Commercial banks create credit only on the advice of the government. Is it true?
Ans. No, this is false. Commercial banks do not create credit only on the advice of the government However, their capacity to create credit depends on credit policy of the central bank of the country.
7. Commercial banks do not have the note issuing authority, but they do contribute to money supply in the economy. Comment
Ans. Yes, the given statement is correct. The central bank is the sole authority of issuing notes in the country. However, by advancing loans through credit creation, commercial banks contribute to money supply in the economy.
8. What role does CRR play in the creation of credit by the commercial banks? Ans. CRR (cash reserve ratio) sets a limit up to which commercial banks can legally create credit. Example: If CRR=4% it implies that the commercial banks can create credit (by way of loans) maximum up to 25 times
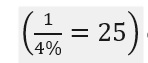
9. “Rote cuts might not be imminent”-Reserve Bank of India. Why RBI is not ready to cut the rates? Write your opinion.
Ans. Here, rate cut refers to repo rate. The RBI believes that a cut in repo rate is going to fuel retail inflation which is already high. Hence, a cut in repo rate (which will increase money supply in the economy) is not recommended.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
10. RBI lowers repo rate from 4.40% to 4.00%
Analyse the economic value of this statement from the viewpoint of (i) the households, (ii) investors, and (in) the economy.
Ans. A cut in repo rate (the rate at which commercial banks can raise loans from RBI) is expected to be followed by a cut in market rate of interest (the rate at which the commercial banks offer loans to the people). It is expected to impact the households, investors, and the economy as under
(i) Impact on Households: A cut in market rate of interest (followed by a cut in repo rate) is expected to induce borrowings for the purchase of consumer durables, as well as houses and flats. Also, the existing loans (raised against floating interest rate) will now attract lower EMI, Implying a direct monetary benefit to the households.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
(ii) Impact on the Investors: As a result of a cut in the market rate of interest, the cost of borrowings (implying the cost of capital) will reduce Accordingly, investment is expected to increase across all areas of production activity.
(iii) Impact on the Economy: When demand for consumer durables rises, aggregate demand expected to rise. Aggregate demand is also tends to rise when investment expenditure rises. Because both consumption expenditure and investment expenditure are significant components of aggregate demand. Thus, the level of planned output is expected to rise along with the lea of planned purchase in the economy. Accordingly, the equilibrium GDP level is expected to rise. Implying a rise in the growth rate of GDP.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
Analysis & Evaluation based Questions
1. How, in your opinion, credit creation by the commercial banks accelerates the pace of economic growth? Write two observations.
Ans. Following observations may be noted in this regard :
Observation-1: Credit creation accelerates the process of growth by expanding the availability of credit for purpose of investment.
Observation-2: Credit creation contributes to the process of growth by expanding size of the market for aggregate demand), as the availability of credit for the purchase of consumer durables increases
2. How improvement in banking habits of the people pushes up credit availability from the commercial banks?
Ans. When banking habits of the people improve, they start holding less money as cash-in-hand. Instead, more and more money is deposited with the commercial banks. Accordingly, cash reserves of the commercial banks start rising Higher cash reserves of the banks enable them to deposit more funds with the RBI as CRR deposits If CRR remains constant, higher CRR – deposits with the RBI gives the commercial banks the legal authority to create more credit by way of loans / credit Accordingly, availability of credit from the commercial banks is increased.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
3. How can ‘Jan-Dhan Yojana’ be used as an instrument to increase supply of money by the commercial banks? Ans. A large section of the population in India do not have their bank accounts. Jan-Dhan Yojana’ prompts people to open their bank accounts. When more and more accounts are opened then some of the cash balances with the people (or idle cash lying with the people) is bound to reach the banking system as cash deposits or primary deposits. This increase enables commercial banks to increase their cash reserves with the central bank if ∆CR (additional cash reserves with the RBI) = Rs. 10,000 and if CRR = 4%, then the additional demand deposits the banks can create
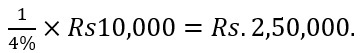
Yojana’ may be used as an instrument to increase supply of money by the commercial banks.
4. Why has the Government in India failed to combat inflation even when a series of monetary measures are available in the textbook of macroeconomics?
Ans. Monetary measures of combating/controlling inflation focus largely on moderating/lowering the demand for goods and services by making the availability of credit costlier and difficult. It does not address supply side of the problem.
While the fact of the matter is that in India inflation has often been triggered by (led by) the low market supplies. Unless supplies are boosted (particularly the supply of farm output) we shall continue to wrestle with inflation without taming (correcting) it.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
5. Analyse the impact of demonetisation (of 500 and 1,000 rupee notes) on credit creation by the commercial banks in the Indian economy.
Ans. Demonetisation has led to huge deposits of cash in the commercial banks. Primary deposits of the banks have risen significantly. This enables them to keep higher CRR-deposits with the RBI. Accordingly, credit creation capacity of the commercial banks is expected to rise.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
ALSO VISIT : BASIC CONCEPTS OF ECONOMICS
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: BANKING NOTES CLASS 12 CBSE
