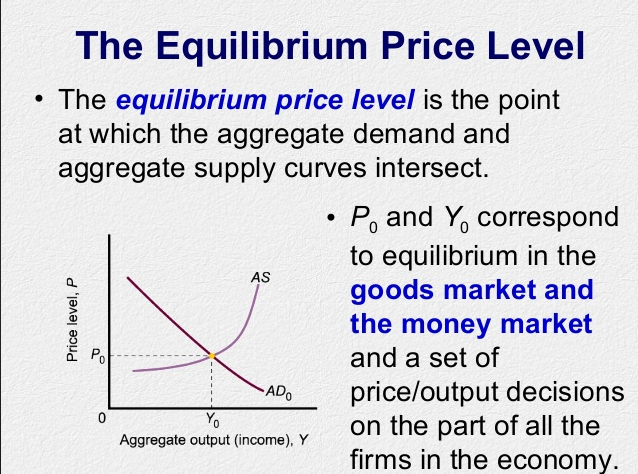
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
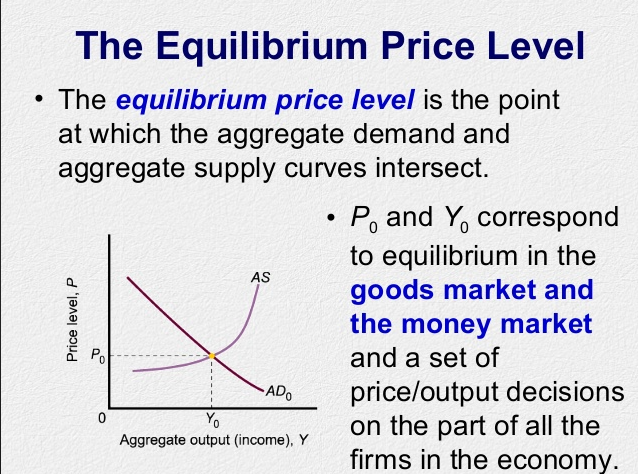
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
Table of Contents
EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- Price depends on –
(a) utility and scarcity
(b) Cost of production
(c) transferability
(d) all the above - The basic behavioural principle which apply to all market conditions –
(a) A firm should produce only if its TR ≥ TVC
(b) A firm should produce at a level where its MC = MR
(c) MC curve cuts the MR curve from below.
(d) All the above - Total revenue can be found out by –


4.When marginal revenue is zero, total revenue will be –
(a) lowest
(b) highest
(c) negative
(d) zero
5.If MR < 0, then the TR will be –
(a) rising
(b) highest
(c) falling
(d) zero
6.The change in the total revenue that results from a one unit change in sales is –
(a) Total Revenue
(b) Average Revenue
(c) Marginal Revenue
(d) both c and d
7.The revenue per unit of called as – one commodity sold is
(a) Total Revenue
(b) Marginal Revenue
(c) Average Revenue
(d) None of the above
8.AR can be found out by the formula –

9.Which concept of revenue is called price?
(a) TR
(b) AR
(c) MR
(d) None of these
10.If a producer sells 4 units of a good at ₹ 10 per unit and 5 units at ₹ 8 per unit, marginal revenue would be –
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- Which of the following statement is incorrect –
(a) Demand and supply determine price of a commodity
(b) At equilibrium price quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
(c) Demand factor influences price more.
(d) Equilibrium price can change. - When demand and supply increase equally, then –
(a) both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity remain unchanged.
(b) both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity increase
(c) equilibrium price remains unchanged but equilibrium quantity increases
(d) equilibrium price changes but equilibrium quantity remains unchanged. - If increase in demand is more than increase in supply, then –
(a) equilibrium price will fall but equilibrium quantity will increase
(b) equilibrium price will increase but equilibrium quantity will decrease
(c) both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will increase
(d) both equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will decrease - When demand increases equilibrium price will increase only if –
(a) supply also increases
(b) supply also decreases
(c) supply remains same
(d) if the elasticity remains the same - The equilibrium price remains constant only if demand and supply
(a) increase unequally
(b) decrease unequally
(c) increase equally
(d) none of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - The price will decrease if demand remains same and –
(a) supply increases
(b) supply decreases
(c) supply is more than the previous level
(d) none of these - In the short period equilibrium price is –
(i) higher than long run price
(ii) higher than market price
(iii) lower than market price
(iv) lower than long run price
(a) i & ii
(b) ii & iii
(c) iii & iv
(d) i & iii - The inter-action of market demand and supply curves determines the –
(a) equilibrium price
(b) reserve price
(c) both a & b
(d) none of these - Uniform price for homogeneous product at any one time is the essential condition of –
(a) monopolistic competition
(b) oligopoly
(c) perfect competition
(d) duopoly - For maximizing profit, the condition is –
(a) AR = AC
(b) MR = AR
(c) MR = MC
(d) MC = AC
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - MC = MR = AR means equilibrium position of a firm –
(a) in the long period
(b) in the short period under imperfect com-petition
(c) in the short period under perfect competition
(d) under perfect competition. - Under perfect competition –
(a) MC = Price
(b) MC > Price
(c) MC < Price
(d) none of these - All but one are correct about perfect competition –
(a) Large number of buyers and sellers
(b) Homogeneous product
(c) Differentiated product
(d) Uniform price
- An increase in demand for a commodity causes –
(a) an increase in equilibrium price
(b) an increase in equilibrium quantity
(c) both a & b
(d) none of these - Which of the following is/are the features of perfect competition ?
(i) Large number of buyers and sellers
(ii) Identical product
(iii) Free entry and exit
(iv) No transportation cost
(a) i, ii and iii
(b) ii, iii and iv
(c) i, ii, and iv
(d) i, ii, iii and iv
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - The demand curve of a commodity faced by a competitive firm is –
(a) very elastic
(b) perfectly inelastic
(c) very inelastic
(d) perfectly elastic - In the short period, a perfectly competitive firm earns –
(a) normal profit
(b) super normal profit
(c) can incur losses
(d) all the above - Under perfect competition the price of commodity
(a) can be controlled by a firm
(b) cannot be controlled by a firm
(c) controlled up to some extent by a firm
(d) none of the above - AR and MR curve coincide in –
(a) Monopoly
(b) Monopolistic Competition
(c) Perfect Competition
(d) Oligopoly - Firms are of optimum size in the long period in case of –
(a) Monopoly
(b) Perfect competition
(c) Monopolistic competition
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- The condition of the long run equilibrium for a competitive firm is –
(a) MC = MR = AR
(b) MC = AC = AR
(c) MC = MR = AC
(d) MC = MR = AR = AC - In the long run, firms only earn normal profits is a feature of –
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopoly
(c) both a & b
(d) none of these - The industry’s demand curve and the average revenue curve are same in case of –
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopoly
(c) oligopoly
(d) none of the above - All the characteristics of monopolistic competition except –
(a) Large number of buyers and sellers
(b) Freedom of entry and exit
(c) Excess production capacity in long run
(d) Full control over price of commodity - There is no difference between firm and industry in case of –
(a) pure monopoly
(b) pure oligopoly
(c) duopoly
(d) perfect competition
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - The demand curve of consumers for product produced by firm is indicated by –
(a) the average cost curve of a firm
(b) the marginal cost curve of a firm
(c) the average revenue curve of a firm
(d) the average revenue curve of an industry. - If in the long run super normal profits can be made by a firm, it means the firm belongs to
(a) perfect competition market
(b) monopolistic competition market
(c) monopoly market
(d) oligopoly market - If e >1 on average revenue curve –
(a) MR is positive and TR is rising
(b) MR is negative and TR is falling
(c) MR is zero and TR is maximum
(d) none of these - When MR is zero the elasticity of demand on AR curve is –
(a) e < 1 and TR is maximum
(b) e = 1 and TR is maximum
(c) e > 1 and TR is rising
(d) none of these - Entry to the market for new firms is blocked in –
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopoly
(c) oligopoly
(d) monopolistic competition
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- When the firm charges different prices to different customers for the same commodity, it is engaged in –
(a) price determination
(b) price rigidity
(c) price discrimination
(d) none of these - Lux Supreme, Rexona, Dove Soap, Pears Soap, Liril Soap, etc. indicates –
(a) perfectly competitive market
(b) monopoly market
(c) monopolistic competitive market
(d) duopoly market - If price and marginal revenue are same then the demand curve must be –
(a) perfectly inelastic and vertical
(b) highly elastic and downward sloping
(c) perfectly elastic and horizontal
(d) highly inelastic and downward sloping - If under perfect competition, the demand curve lies above the average cost curve, the firm would –
(a) make normal profits
(b) incur losses
(c) make super normal profits
(d) profit is indeterminate - Monopoly price is the function of –
(a) MC of production
(b) price elasticity of demand
(c) neither (a) nor (b)
(d) both (a) and (b)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - Railways is an example of –
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopoly
(c) oligopoly
(d) monopolistic competition - The cross elasticity of demand for monopolist’s product is –
(a) zero
(b) less than zero
(c) infinite
(d) unity - A market situation in which there are only few firms producing differentiated product which are close substitutes is –
(a) monopolistic competition
(b) oligopoly
(c) duopoly
(d) perfect competition - The cross elasticity of demand for the product of a firm under perfect competition is –
(a) zero
(b) less than zero
(c) infinite
(d) unity - Demand curve of a firm is indeterminate in case of –
(a) monopoly
(b) oligopoly
(c) duopoly
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- At every level of output AR = MR in case of –
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopoly
(c) oligopoly
(d) all the above - For maximization of profits, MR = MC is the first order condition –
(a) only under monopoly
(b) only under perfect competition
(c) both under monopoly as well as perfect competition
(d) in any type of market - Which of the following statements are correct with regard to firm’s equilibrium –
(i) MR = MC
(ii) MC curve cuts the MR curve from below
(iii) TR = TC
(iv) MR = AR
(a) i & ii
(b) ii & iii
(c) iii & iv
(d) none of these - An individual firm is only output adjuster at ruling market price in –
(a) monopoly
(b) oligopoly
(c) perfect competition
(d) monopolistic competition .
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - There are few firms selling homogeneous or differentiated products in –
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Oligopoly
(c) Monopolistic competition
(d) None of these - When demand is elastic, MR is _
(a) negative
(b) positive
(c) zero
(d) one - The theory of monopolistic competition is developed by-
(a) H.E. Chamberlin
(b) Mrs.JoanRobinson
(c) Dr. Marshall
(d) Nicholoas Kaldor - The point where P = AC is called –
(a) profit earning point
(b) loss making point
(c) breakeven point
(d) shut down point - TR is a straight positively sloping line from origin is under-
(a) perfect competition
(b) monopoly
(c) duopoly
(d) oligopoly - If a monopolist resorts to price discrimination, price will be higher in the market where demand is-
(a) unitary elastic
(b) elastic
(c) inelastic
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- A monopolistic firm has a position of ATC = price in the _
(a) short run equilibrium
(b) very short run equilibrium
(c) long run equilibrium
(d) any period of time - The difference between least cost output and profit maximizing output is called _
(a) reserve capacity
(b) excess capacity
(c) normal capacity
(d) abnormal capacity - _ is the market structure where there is a single buyer.
(a) Monopsony
(b) Monopoly
(c) Oligopsony
(d) Duopoly - At all the level of output AR = MR in _
(a) a perfect competition market
(b) a monopoly market
(c) a oligopoly market
(d) all the above - Under perfect competition, the MC curve at equilibrium will be-
(a) constant
(b) rising
(c) falling
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - Market price is the price that prevails in a _
(a) very short period market
(b) short period market
(c) long period market
(d) secular period market - The market in which normal price prevails is a _ market.
(a) Market period
(b) short period
(c) long period
(d) secular period - Excess capacity is not found under
(a) Monopoly
(b) Monopolistic Competition
(c) Oligopoly
(d) Perfect Competition - Which of the following is not a characteristics of a “price taker”?.
(a) TR = P X Q
(b) AR = Price
(c) Negatively sloped demand curve
(d) Marginal Revenue = Price - In monopolistic competition, a firm is in long run equilibrium _
(a) at the lowest point of the LAC curve
(b) at the falling part of the LAC curve
(c) at the rising part of the LAC curve
(d) when, price = MC
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
- Which market explains that Marginal Cost is equal to price for attaining equilibrium.
(a) Perfect Competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Oligopoly
(d) Monopolistic Competition - When a market is in equilibrium or has cleared it means _
(a) No shortages exist
(b) Quantity demanded equals quantity sup-plied
(c) A price is established that clears the market
(d) All the above - If a competitive firm doubles its output, its total revenue-
(a) doubles
(b) more than doubles
(c) less than doubles
(d) none of these - Which is the first order condition for the profit of a firm to be maximum?
(a) AC = MR
(b) MC = MR
(c) MR = AR
(d) AC = AR - Full capacity is utilized only when there is
(a) Monopoly
(b) Perfect Competition
(c) Price Discrimination
(d) Oligopoly
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12 - In the very short run period, the price of the commodity is influenced most by-
(a) demand
(b) supply
(c) cost
(d) production - Long run normal prices is that which is likely to prevail-
(a) all the times
(b) in market period
(c) in short-run period
(d) in long-run period - The degree of monopoly power is measured in terms of difference between-
(a) Marginal Cost and the price
(b) Average Cost and Average Revenue
(c) Marginal Cost and Average Cost
(d) Marginal Revenue and Average Cost
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
ANSWER KEY
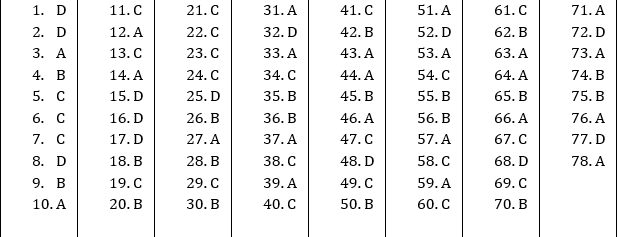
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12
ALSO VISIT :MCQ ON PRODUCTION AND COST
SUPPLY AND ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY MCQ CLASS 12
MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND MCQ CLASS 12
THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
MICROECONOMICS AND MICROECONOMICS MCQ
MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EQUILIBRIUM PRICE MCQ CLASS 12