DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
Table of Contents
MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Cost analysis refer to the study of __ in relation to different production criteria.
(a) production
(b) cost
(c) price
(d) inputs - Cost is a _ function
(a) direct
(b) derived
(c) both direct and derived
(d) none of the above - Theory of costs is restatement of the theory of _ in monetary terms
(a) demand
(b) consumer’s behaviour
(c) production
(d) all the above - _ costs relate to those costs which involve cash payments by the entrepreneur of the firm.
(a) Accounting
(b) Marginal
(c) Economic
(d) Implicit - Accounting costs are also called _ costs.
(a) economic
(b) implicit
(c) explicit
(d) opportunity
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - Wages paid to labourers, cost of raw-materials purchase, interest on the money borrowed, etc. are examples of _ cost.
(i) accounting
(ii) implicit
(iii) economic
(iv) explicit
(a) i and ii
(b) iii and iv
(c) ii and iii
(d) i and iv - Economic costs includes-
(a) Accounting cost + Explicit cost
(b) Accounting cost + Implicit cot
(c) Fixed cost + Variable cost
(d) Accounting cost + Direct cost - Economic costs equals-
(a) Explicit cost + Implicit cost
(b) Fixed cost + Variable cost
(c) Accounting cost + Explicit cost
(d) none of the above - _ costs are the value of foregone opportunities that do not involve any contractual obligation of cash payment.
(a) Explicit
(b) Implicit
(c) Accounting
(d) Hidden - _ includes all payments made to factors of production and opportunity cost.
(a) Accounting costs
(b) Economic costs
(c) Implicit costs
(d) Explicit costs
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- An entrepreneur must recover his _ cost if he wants to earn normal and abnormal profits.
(a) accounting
(b) implicit
(c) economic
(d) all the above - Which of the following are implicit costs?
(i) A shop taken on rent by entrepreneur
(ii) Savings invested to start business
(iii) An individual is both owner and manager of business
(iv) A farmer takes a farm on rent
(a) i and ii
(b) iii and iv
(c) ii and iii
(d) i and iv - Which of the following are explicit costs?
(i) A producer borrows money to start a factory
(ii) A producer invests his savings to start a factory
(iii) Wages paid to workers
(iv) An individual is both owner & manager of business
(a) i & ii
(b) iii & iv
(c) i & iii
(d) ii & iv - The difference between Economic Cost and Accounting Cost is equal to _
(a) Implicit cost
(b) Explicit cost
(c) Marginal cost
(d) none of the above - All but one is not included in the books of account? Which one?
(a) Taxes
(b) Electricity charges
(c) Cost of raw-material
(d) Imputed salary of owner
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - _ costs involve actual expenditure of funds on wages, material, rent, etc.
(a) Opportunity
(b) Outlay
(c) Economic
(d) Implicit - The cost that a firm incurs in purchasing or hiring, the services of various productive factors is referred to as-
(a) Explicit cost
(b) Fixed cost
(c) Implicit cost
(d) Variable cost - Explicit costs are also known as-
(a) Accounting costs
(b) Outlay costs
(c) Out-of-Pocket costs
(d) All the above - For an economist, the cost means-
(a) Accounting Costs
(b) Economic Costs
(c) Outlay Costs
(d) Sink Cost - Implicit costs are also known an-
(a) Opportunity costs
(b) Imputed costs
(c) Notional costs
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Opportunity cost refers to-
(a) money expenses incurred on purchasing or hiring factor, services
(b) the next best alternative
(c) involving cash payment
(d) all the above - Opportunity cost refers to-
(a) Cost of opportunity foregone
(b) Comparison between the policy that was chosen and the policy that was rejected
(c) Costs relating to sacrificed alternatives
(d) all the above - The cost of one thing in terms of the alternative given up is known as-
(a) Production cost
(b) Accounting cost
(c) Opportunity cost
(d) Real cost - Opportunity costs find its application in situations _
(a) for short run and long run decision making
(b) capital expenditure budgeting
(c) when the supply of input factors is strictly limited
(d) all the above - Opportunity costs are a result of _
(a) Abundance of resources
(b) Scarcity of resources
(c) Technology obsolescence
(d) Cost controls
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - All but one are true about opportunity cost. Which one is not true?
(a) Opportunity costs are recorded in the books of account.
(b) Opportunity costs are applicable to those factors which have alternative uses.
(c) Opportunity cost is also known as ‘alternative cost’
(d) Opportunity cost is also known as ‘displacement cost’ - If no sacrifice is involved, then the opportunity cost is
(a) very high
(b) very low
(c) zero
(d) both ‘b’ & ‘c’ - The concept of opportunity cost helps us to know that-
(a) resources are scarce,
(b) resources have alternative uses,
(c) how scarce resources get allocated in different production activities
(d) all the above - If you give up a full-time job to go to college, the major cost is –
(a) tuition fees
(b) room and board
(c) the income you could have earned from job
(d) social expenses - If a firm’s machinery, has no possible alternative use, its opportunity cost is –
(a) high
(b) low
(c) zero
(d) none of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- If you own a cottage in Shimla which you could rent for August and September to some family for a net gain of ₹ 20,000/- after all expenses and taxes, the opportunity cost of living in it yourself for summer is _
(a) ₹ 10,000
(b) ₹ 20,000
(c) ₹ 30,000
(d) ₹ 40,000 - Cost of getting something involves losing something else means –
(i) accounting costs
(ii) opportunity costs
(iii) explicit costs
(iv) implicit costs
(a) Only i
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iii
(d) ii and iv - The costs which can be identified easily and indisputably with a unit of operation, a product, a department, a plant or a process are called-
(i) direct cost
(ii) indirect cost
(iii) traceable cost
(iv) non-traceable cost
(a) Only i
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iii
(d) ii and iv - _ costs are not identified readily and indisputably to specific product, process, department, plant, operations, etc.
(a) Indirect costs
(b) Traceable costs
(c) Non-traceable costs
(d) Both ‘a’ & ‘c’ - Accounting process recognizes-
(a) direct costs
(b) indirect cost
(c) only direct costs
(d) both direct and indirect costs
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - The function which gives least cost combinations of inputs corresponding to different levels of output is called-
(a) Production function
(b) Demand function
(c) Cost function
(d) Supply function - Cost functions are derived from _
(a) Demand function
(b) Supply function
(c) Isoquant function
(d) Production function - _ refers to the functional relationship between cost of a product and the various determinants of cost.
(a) Cost function
(b) Isoquant function
(c) Production function
(d) Supply function - In a cost function, the total cost or cost per unit is a/an _
(a) Dependent Variable
(b) Independent Variable
(c) Either ‘a’ or ‘b’
(d) Neither ‘a’ nor ‘b’ - In a cost function, the prices of factors of production is a/an _
(a) Dependent Variable
(b) Independent Variable
(c) Either ‘a’ or ‘b’
(d) Neither ‘a’ nor ‘b’
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Which one of the following is the dependent variable in a cost function?
(a) Level of capacity utilization
(b) Lot size of output
(c) Scale of operations
(d) Total Cost - Which one of the following is an independent variable in a cost function?
(a) Cost per unit
(b) Total cost
(c) Managerial efficiency
(d) None of the above - All but one are independent variables. Which one is not independent variable?
(a) Quantity of output
(b) Prices of factors of production
(c) Per unit cost of production
(d) Time Period under study - Which one of the following is not a determinant of the firm’s cost function?
(a) Price of firm’s output
(b) Production function
(c) Price of labour
(d) Rent paid for use of building - The functional relationship between output and the long-run cost of production is called _
(a) Cost function
(b) Production function
(c) Long-run Cost function
(d) Long-run Production function
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - Law of Returns to Scale forms the basis of _ cost function
(a) Long-run
(b) Short-run
(c) Fixed
(d) all the above - A cost function determines the behaviour of cost with change in _
(a) Output
(b) Input
(c) Technology
(d) Wages - Increase in the size of a firm and its production capacity determines _
(a) Short-run production function
(b) Long-run production function
(c) Fixed production function
(d) None of the above - When a firm operates with a given scale of production it affects the _
(a) Long-run production function
(b) Fixed production function
(c) Short run production function
(d) All the above - Find the odd one-
(a) Output
(b) Price of raw-materials
(c) Time period
(d) Total cost
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- The costs which do not change with the level of output are called :
(i) Supplementary Costs
(ii) Money Costs
(iii) Overhead Costs
(iv) Prime Cost
(a) i & ii
(b) ii & iii
(c) i & iii
(d) i, ii, iii & iv - The costs which change with the level of output are called _
(a) Prime cost
(b) Direct cost
(c) Variable cost
(d) All the above - The costs which remain constant at all the levels of output are called _
(a) Supplementary Costs
(b) Fixed Costs
(c) Overhead Costs
(d) All the above - Fixed costs includes-
(a) Historical costs
(b) Explicit costs
(c) Implicit costs
(d) Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ - At zero level of output _ cost can never be zero.
(a) Variable
(b) Fixed
(c) Direct
(d) Real
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - At zero level of output cost _ is zero.
(a) Fixed
(b) Overhead
(c) Variable
(d) Real - _ costs are incurred even before production starts
(a) Fixed
(b) Variable
(c) Real
(d) Marginal - _ costs are incurred after the production actually starts.
(a) Fixed
(b) Variable
(c) Marginal
(d) Real - At zero level of output Fixed Cost must be greater than Variable Cost.
(a) False
(b) Partially True
(c) True
(d) None of the above - Fixed Costs are a function of _
(a) Time
(b) Output
(c) Both time and output
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Variable Costs are a function of _
(a) Time
(b) Output
(c) Both time and output
(d) All the above - _ costs are directly or positively related to output.
(a) Fixed
(b) Stair-step
(c) Semi-Variable
(d) Variable - When production level is zero, then fixed cost is-
(a) zero
(b) negative
(c) positive
(d) equal to variable cost - Which of the following indicates fixed costs?
(a) Electricity Bill
(b) Wages to daily labourers
(c) Expenses on transportation
(d) Interest on fixed capital - Variable costs include costs of-
(a) Hiring the building for the factory
(b) Purchase of heavy machines
(c) Pay wages to factory manager
(d) Paying for power and fuel
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - Which one of the following is correct?
(a) TC = TFC × TVC
(b) TC = TFC ÷ TVC
(c) TC = TFC + TVC
(d) TC = TFC – TVC - Which cost increases continuously with the increase in production?
(a) Average cost
(b) Marginal cost
(c) Fixed cost
(d) Variable cost - When output is increased variable cost also rises initially at _ rate and later at _ rate.
(a) diminishing; constant
(b) increasing; constant
(c) diminishing; increasing
(d) constant; increasing - The costs which are neither perfectly variable, nor absolutely fixed when output level are changed are _
(a) Variable costs
(b) Semi Variable costs
(c) Stair Step costs
(d) Prime costs - _ costs are independent of the level of output.
(a) Fixed
(b) Variable
(c) Marginal
(d) Semi Variable costs
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
71.TVC can be calculated as-

- TC reflect the behaviour of-
(a) TFC
(b) TVC
(c) AFC
(d) None of the above - At zero level of output Total Cost of Production is equal to-
(a) Total Fixed Cost
(b) TotalVariableCost
(c) Marginal Cost
(d) Explicit Cost - Total Fixed Cost Curve is indicated by a-
(a) Positively sloped Curve
(b) Vertical Straight Line Curve
(c) Horizontal Straight Line Curve
(d) Negatively sloped Curve - Total cost curve shoots from a point on Y-axis means-
(a) we are referring to the short period
(b) we are referring to the long period
(c) we are referring to the market period
(d) we are referring to the secular period - In the short period, TC = ∑ MC Is it correct ?
(a) Yes
(b) No, as TC = TFC + ∑ MC
(c) Partially correct
(d) none of the above - Total Variable Cost initially rises at a diminishing rate due to-
(a) increasing returns to factor
(b) increasing returns to scale
(c) diminishing returns to factor
(d) diminishing returns to scale - Total Variable Cost curve shoots upwards from-
(a) a certain point on quantity axis
(b) a certain point on cost axis
(c) origin
(d) Any of the above - TFC curve will be a straight line –
(a) Parallel to X-axis
(b) Parallel to Y-axis
(c) Sloping upward from left to right
(d) Sloping downward from left to right - Total Variable Cost curve originate from the point of origin means-
(a) Variable cost is zero at zero output
(b) Variable cost has to be incurred at zero output
(c) Variable cost is diminishing
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- The total cost curve and total variable cost curve are parallel because-
(a) Vertical distance between the two is total fixed cost which is constant
(b) behaviour of total cost depends upon total variable cost
(c) change in total cost is only due to change in variable cost
(d) all the above - The vertical distance between TVC and TC is equal to –
(a) Marginal Cost
(b) Total Fixed Cost
(c) Average Variable Cost
(d) None of the above - The fixed cost per unit of output is called-
(a) Average Fixed Cost (b) Total Fixed Cost
(c) Marginal Cost (d) None of the above - In the short run, when output of a firm increases, its average fixed cost-
(a) rises continuously
(b) falls continuously
(c) remain constant
(d) first rises and then falls - Average Fixed Cost curve _
(a) slope upwards
(b) slope downwards
(c) is TJ’ shaped
(d) is ‘S’ shaped
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - Total Variable Curve is _ shaped
(a) ‘U’ shaped
(b) Inverted’U’shaped
(c) Inverted ‘S’ shaped
(d) ‘C’ shaped - Average Fixed Cost curve is indicated by-
(a) a rectangular hyperbola
(b) a straight line parallel to X-axis
(c) a straight line parallel to Y-axis
(d) a ‘U’ shaped curve - Average Fixed Cost curve will never touch-
(a) X-axis
(b) Y-axis
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) none of the above - Average Variable Cost equals-
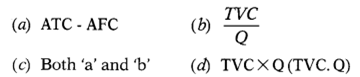
- Which of the following falls continuously?
(a) Marginal Cost
(b) Average Fixed Cost
(c) Average Variable Cost
(d) Total Fixed Cost
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Average Variable Cost falls as output is expanded-
(a) upto normal capacity output
(b) beyond normal capacity output
(c) all the levels of output
(d) Nothing can be said - Beyond normal capacity output, as output in-creases AVC will-
(a) remain constant
(b) decrease
(c) increase
(d) nothing can be said - Average variable cost is inversely related to _
(a) MP of variable factor
(b) AP of variable factor
(c) TP
(d) nothing can be said - AVC falls as output increases upto normal ca-pacity due to-
(a) constant returns to scale
(b) diminishing returns to factor
(c) increasing returns to factor
(d) negative returns to factor - AVC curve is-
(a) ‘S’ shaped
(b) ‘U’ shaped
(c) Inverted ‘S’ shaped
(d) Inverted’U’shaped
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - _ and _ curves start from the same point on Y-axis which is above the origin.
(a) TFC and TVC
(b) TVC and TC
(c) TFC and TC
(d) None of the above - Two curves which are inverted ‘S’ shaped are –
(a) TFC and TVC
(b) TVC and TC
(c) TC and AVC
(d) AFC and AVC - Average Cost curve is-
(a) Horizontal Line parallel to x-axis
(b) Inverted ‘S’ shaped
(c) Inverted ‘U’ shaped
(d) ‘U’ shaped - When output is increased Average Cost at all the levels of output includes both AVC and AFC means that-
(a) AC curve will always lie above the AVC curve
(b) AC curve will always lie below the AVC curve
(c) AC and AVC are parallel to each other with same vertical distance throughout
(d) None of the above - The vertical gap between AC and AVC curves as the output increases.
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remain constant
(d) None of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Since AFC can never be zero, _ and _ curves never intersect each other
(a) AC and MC
(b) AC and AFC
(c) AC and AVC
(d) None of the above - The two inverted ‘S’ shaped short run cost curves are parallel to each other and maintain a constant distance of ₹ 100. Which cost is indicated by ₹100?
(a) Total Variable Cost
(b) Total Cost
(c) total Fixed Cost
(d) Average Fixed Cost - Find the odd one out-
(a) Salary to manager of the company
(b) Payment of insurance premium for insurance of factory
(c) Interest on loan taken from Union Bank
(d) Payment of excise duty - Average Fixed Cost falls as the output rises because-
(a) AFC and output are inversely related
(b) AFC and output are positively related
(c) AFC and output are not related
(d) All the above - Production at the loss of _ may continue in short run.
(a) Variable Cost
(b) Fixed Cost
(c) Marginal Cost
(d) Direct Cost
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - Production at the loss of _ cannot be continued in short run.
(a) Direct Cost
(b) Fixed Cost
(c) Marginal Cost
(d) Variable Cost - Which of the following statements is correct of the relationship among the short run costs?
(a) ATC = AFC – AVC
(b) AVC = AFC + ATC
(c) AFC = ATC + AVC
(d) AFC = ATC -AVC - Average Total Cost equals-

- Average Total Cost means-
(a) The general average cost
(b) The average cost of producing one unit
(c) The cost of producing the last unit
(d) None of the above - Average Cost curve contains in it-
(a) Normal Profits
(b) No Normal Profits
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) None of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- Average Cost curve is a _
(a) ‘S’ shaped curve
(b) T shaped curve
(c) ‘U’ shaped curve
(d) Straight Line - When expressed as an average, it shows a continuous fall with increase in output-
(a) the average cost of a firm
(b) the fixed cost of a firm
(c) marginal cost
(d) variable cost - An addition to the total cost caused by producing one more unit of output is called _
(a) average cost
(b) marginal cost
(c) fixed cost
(d) variable cost - Marginal Cost varies inversely with _ in short run
(a) average product of variable factor
(b) total product
(c) marginal product of variable factor
(d) both ‘a’ and ‘b’ - Marginal Curve is _
(a) ‘U’ shaped
(b) ‘L’ shaped
(c) ‘S’ shaped
(d) downward sloping continuously
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - At the minimum average cost, a firm can produce the _
(a) maximum output
(b) optimum profit
(c) optimum output
(d) marginal output - Any change in Marginal Cost will lead to a change in firm’s _
(a) total fixed cost
(b) total variable cost
(c) average fixed cost
(d) both ‘a’ and ‘c’ - With increase in output, the average fixed cost will fall in _
(a) very long period
(b) long period
(c) market period
(d) short period - Marginal Cost is the slope of _ curve.
(a) total variable cost
(b) total fixed cost
(c) average cost
(d) all the above - When total variable cost rises at a diminishing rate, marginal cost _
(a) rises
(b) remain constant
(c) falls
(d) none of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- When TVC rises at an increasing rate, MC _
(a) rises
(b) falls
(c) remain constant
(d) none of the above - Graphically, the area under the Marginal Cost curve is _
(a) TFC
(b) TVC
(c) TC
(d) AC - Marginal Cost Curve cuts the Average Cost Curve at its _
(a) falling part
(b) rising part
(c) minimum point
(d) both ‘a’ and ‘b’ - Marginal Cost is independent of
(a) fixed cost
(b) variable cost
(c) opportunity cost
(d) output - All but one are ‘U’ shaped
(a) The AVC curve
(b) The AC curve
(c) The MC curve
(d) The AFC curve
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - Find the Odd One out of the following
(a) TCn – TCn-1
(b) TFCn – TFCn-1
(c) TVCn-TVCn -1
(d) TCn-(TVCn-1+TFCn-1) . - The point at which marginal cost equate average cost shows-
(a) The maximum Profit
(b) The equilibrium point of the consumer
(c) The plant capacity
(d) The minimum price of the product - Which of the following is incorrectly matched?
(a) MC – ‘U’ shaped
(b) AFC – Rectangular Hyperbola
(c) TC – ‘J’ shaped
(d) AVC – ‘U’ shaped - If a table shows number of units produced and average cost of each unit, one can calculate-
(a) AVC
(b) MC
(c) TC
(d) All the above - Consider the following statements and point the correct one-
(a) If MC curve is below the AC curve, then the AC curve must be rising
(b) When MC curve is above the AC curve, then the AC curve must be falling
(c) MC cost curve cuts the AC curve at the minimum point of AC curve
(d) AC pulls up or down the MC Sp
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
- When AC is at its minimum, then-
(a) AC >MC
(b) AC < MC
(c) AC = MC
(d) All the above - Per unit cost of a commodity is called-
(a) fixed cost
(b) variable cost
(c) average cost
(d) marginal cost - When MC curve cuts AC curve-
(a) AC = MC
(b) AC > MC
(c) AC < MC
(d) both AC and MC are falling - What happens to Average Cost when MC > AC?
(a) AC will fall
(b) AC will rise
(c) AC will remain constant
(d) None of the above - Marginal cost includes-
(a) fixed cost and variable cost
(b) only fixed cost
(c) only variable cost
(d) None of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE - If the marginal cost of production is less than the average cost then-
(a) MC curve lies under the AC curve
(b) AC would be falling
(c) MC cost pulls down AC
(d) All the above - MC is greater than AC when production is in a state of _
(a) increasing returns
(b) diminishing returns
(c) constant returns
(d) None of the above - AC is greater than MC, so long as –
(a) AC is falling
(b) AC is rising
(c) AC is constant
(d) All the above - MC = AC when –
(a) AC is falling
(b) AC is rising
(c) AC tends to stabilize
(d) None of the above - The distance between AC and AVC curves tends to _ at higher level of output
(a) increase
(b) remain constant
(c) reduce
(d) None of the above
- ATC and AVC curves tend to intersect at some level of output
(a) Statement is Incorrect
(b) Statement of Correct
(c) Statement is Partially Correct
(d) None of the above - The difference between ATC and AVC:
(a) is constant
(b) is total fixed cost
(c) gets narrow as output falls
(d) is the average fixed cost - Can AC fall, when MC is rising?
(a) No
(b) Yes
(c) Can’t say
(d) None of the above - When MC < AVC, _ with increase in the output
(a) AVC rises
(b) AV C falls
(c) AVC remain constant
(d) AVC curve cut MC curve - When MC becomes equal to AC and AVC, they _
(a) begin to rise
(b) begin to fall
(c) become constant
(d) Any of the above - There will be productive efficiency when-
(a) MC = AC
(b) firm is producing at the minimum point of Average Cost Curve
(c) MC curve cuts the AC curve
(d) All the above - Marginal Cost is _
(a) Always less than the Average Cost
(b) Always more than the Average Cost
(c) Equal to the Average Cost at its minimum point
(d) Never equal to Average Cost
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
ALSO VISIT :MCQ ON PRODUCTION AND COST
SUPPLY AND ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY MCQ CLASS 12
MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND MCQ CLASS 12
THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
MICROECONOMICS AND MICROECONOMICS MCQ
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONCEPTS OF COST AND REVENUE
