DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
CONSUMER BEHAVIOR: CARDINAL AND ORDINAL ANALYSIS FOR 12TH ICSE BOARD ECONOMICS, Objective questions for 12th ICSE Board, CONSUMER BEHAVIOR: CARDINAL AND ORDINAL ANALYSIS FOR 12th ICSE MCQ FOR ECONOMICS , CONSUMER BEHAVIOR: CARDINAL AND ORDINAL ANALYSIS FOR Mock Test for 12th Class ICSE Board.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
Table of Contents
MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
1. Utility depends on the ____ of a want.
(a) intensity
(b) quality
(c) novelty
(d) uniformity
2. All but one are the commodities that have both utility and usefulness except-
(a) pencil
(b) notebook
(c) tobacco
(d) clothes
3. Utility is-
(a) a subjective and relative concept
(b) morally or ethically colourless
(c) different from pleasure
(d) all the above
4. Utility may be defined as-
(a) power of a commodity to satisfy wants
(b) usefulness of a commodity
(c) desire for a commodity
(d) none of the above
5. The utility of a commodity is ____
(a) its accepted social value
(b) the extent to which it is of practical use
(c) the fact that it is wanted by some people
(d) its relative scarcity
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
6. Utility is measured in terms of-
(a) Grams
(b) Seconds
(c) Centimeter
(d) Utils
7. Utility is-
(a) usefulness
(b) moral implications
(c) legal implications
(d) none of the above
8. The cardinal approach postulates that utility can be ____
(a) compared
(b) measured
(c) ranked
(d) all the above
9. Cardinal Utility Theory is associated with-
(a) W.S. Jevons
(b) Dr. A. Marshall
(c) H.H. Gossen and Walras
(d) All the above
10. Cardinal Utility approach is also known as-
(a) Indifference Curve Analysis
(b) Hicks and Allen Approach
(c) Marginal Utility Analysis
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
11. Marginal Utility Approach is also called-
(a) Ordinal Utility Analysis
(b) Hicks and Allen Approach
(c) Cardinal Utility Analysis
(d) All the above
12. According to marginal utility analysis, utility can be measured as-
(a) 1st, 2nd, 3rd ……
(b) 1,2,3, ……
(c) Nominal numbers
(d) All the above
13. Cardinal measure of utility is required in-
(a) Marginal Utility Theory
(b) Indifference Curve Theory
(c) Revealed Preference Theory
(d) None of the above
14. Which of the following approaches uses MONEY as a measuring rod of utility-
(a) Ordinal
(b) Cardinal
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) Neither ‘a’ nor ‘b’
15. Which of the theories is applicable under Cardinal Approach to Utility?
(a) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(b) Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
(c) Consumer Surplus Theory
(d) All the above
16. All but one are the assumptions of the Cardinal Utility Theory. Which one is not the assumption?
(a) Rational Consumer
(b) Constant Marginal Utility of money
(c) Perfectly Competitive Market
(d) Independent Utilities
17. Which of the following assumptions ignores the presence of complementary and substitute goods in Cardinal Utility Theory?
(a) Rational Consumer
(b) Constant Marginal Utility of money
(c) Independent Utilities
(d) None of the above
18. The price that a consumer is ready to pay for a commodity represents the utility he is expecting from the commodity means-
(a) Utility is measurable
(b) Utility is not measurable
(c) Money is the measuring rod of utility
(d) Both ‘a’ and ‘c’
19. Consumer makes all calculations carefully and then purchase the commodities in order to maximize his utility means consumer is-
(a) careless
(b) rational
(c) irrational
(d) unpredictable
20. Which of the following statements regarding ordinal utility is true?
(a) Utility can be measured, but cannot be ranked in order of preferences
(b) Utility can be measured only
(c) Utility can neither be measured nor be ranked in order or preferences
(d) Utility cannot be measured, but can be ranked in order of preferences
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
21. The cardinal approach to utility assumes marginal utility of money is-
(a) Zero
(b) Constant
(c) Increasing Trend
(d) Decreasing Trend
22. ____ is the sum total of the utility derived from additional units of a commodity
(a) Average utility
(b) Marginal utility
(c) Total utility
(d) Ordinal utility
23. _____ is the addition made to the total utility by the consumption of additional unit of a commodity
(a) Marginal Utility
(b) Total Utility
(c) Average Utility
(d) Ordinal Utility
24. Marginal Utility can be stated by-
(a)
(b) Additional utility derived from additional unit of a commodity
(c) TUn – TUn-1
(d) All the above
25. Utility of a good can be termed as the ____
(a) Monetary value a consumer gains from consuming a particular good
(b) The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and actually pays
(c) The satisfaction a consumer derives from the consumption of a particular good
(d) The desire to consume a good
26. Marginal Utility-
(a) is always positive
(b) is always negative
(c) can be positive or negative but not zero
(d) can be positive or negative or zero
27. Total Utility can be calculated as-
(a) TU = Σ MU
(b) TU = MU1 + MU2 + MU3 + MUn
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) none of the above
28. When only ONE unit of the commodity is consumed-
(a) MU = TU
(b) MU > TU
(c) MU < TU
(d) none of these
29. When marginal utility is negative, total utility is-
(a) zero
(b) diminishing
(c) maximum
(d) minimum
30. When total utility is maximum, marginal utility becomes-
(a) zero
(b) unity
(c) positive
(d) negative
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
31. Total Utility is ____ when marginal utility is positive
(a) maximum
(b) diminishing
(c) increasing
(d) minimum
32. When TU is increasing at a diminishing rate, MU must be-
(a) increasing
(b) decreasing
(c) constant
(d) negative
33. MU of a particular commodity at the point of saturation is-
(a) zero
(b) unity
(c) greater than unity
(d) less than unity
34. Which of the following equation is incorrect?
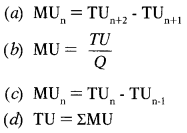
35. The rate of which TU changes is indicated by-
(a) MU
(b) TU
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) none of these
36. With the increase in consumption by ONE unit of the commodity, TU increases from 120 to 150, then marginal utility is-
(a) 50
(b) 1.25
(c) 0.88
(d) 30
37. The shape of MU curve is-
(a) upward sloping
(b) Concave to origin
(c) downward sloping
(d) straight line
38. TU starts diminishing when-
(a) MU is positive
(b) MU is increasing
(c) MU is negative
(d) MU is constant
39. TU curve-
(a) always rises
(b) always falls
(c) first falls and then rises
(d) first rises at a diminishing rate, reaches maximum point and then falls
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
40. MU curve will be below X-axis when-
(a) MU is positive
(b) MU is negative
(c) MU is zero
(d) MU is constant
41. What is called the point of satiety?
(a) The point where MU >0
(b) The point where MU < 0
(c) The point where MU = 0
(d) None of these
42. ____ states that marginal utility of a good diminishes as the consumer consumers additional units of a good.
(a) The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
(b) The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(c) Revealed Preference theory
(d) None of the above
43. MU curve of a consumer is also his ____
(a) indifference curve
(b) total utility curve
(c) supply curve
(d) demand curve
44. ____ curve is the slope of the TU curve.
(a) MU Curve
(b) Average Utility Curve
(b) Supply Curve
(d) Indifference Curve
45 At saturation point the slope of total utility curve is ____
(a) rising
(b) falling
(c) zero
(d) none of these
46. Constant Marginal Utility of Money means ___
(a) quantity
(b) importance
(c) composition
(d) Both ‘a’ and ‘c’
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
47. A curve which first move upwards then down wards is naturally ____
(a) Marginal Utility Curve
(b) Average Utility Curve
(c) Total Utility Curve
(d) Demand Curve
48. The peradox of value means that-
(a) people are irrational in consumption choices
(b) the total utilities yielded by commodities do not necessarily have relationship to their prices
(c) value has no relationship to utility schedule
(d) free goods are goods that are essential to life
49. The value paradox (diamond and water paradox) arises because-
(a) Water has too low price
(b) Value in use differs from utility
(c) Diamonds are too high priced
(d) Value-in-use differs from value-in-exchange
50. In ONE COMMODITY, case, the consumer is at equilibrium when-

51. The second samosa consumed gives lesser satisfaction to Mohan. This is a case of-
(a) Law of Demand
(b) Law of Diminishing Returns
(c) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(d) Law of Supply
52. Marginal Utility of a commodity depends on its quantity and is –
(a) inversely proportional to its quantity
(b) not proportional to its quantity
(c) independent of its quantity
(d) none of the above
53. Which of the following is NOT an assumption of Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
(a) Homogenity
(b) Continuity
(c) Standard Unit
(d) None of the above
54. MU of one commodity has no relation with MU of another commodity implies-
(a) assumption of uniform quality
(b) assumption of rational consumer
(c) assumption of independent utilities
(d) assumption of reasonable quantity
55. Consumer in consumption of single commodity ‘X’ will be at equilibrium when-
(a) MUx = Px
(b) Mux >Px
(c) Mux < Px
(d) all the above
56. if Mux >Px then consumer-
(a) is not at equilibrium
(b) he will buy more of X good
(c) he will buy less of X good
(d) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
ANSWER KEY
| A | C | D | A | C | D | D |
| B | D | C | C | B | A | B |
| D | C | C | D | B | D | B |
| C | A | D | C | D | C | A |
| B | A | C | B | A | B | A |
| D | C | C | D | B | C | B |
| D | A | C | B | C | B | D |
| D | C | A | D | C | A | D |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
ALSO VISIT:SUPPLY AND ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY MCQ CLASS 12
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
