DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
Table of Contents
MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
Q1. Fill in the blanks:
- Our skeleton consists of bones, ……….. And………… .
- ……..… is the chief component of our skeleton.
- Shape wise the bones can be classified as…………, …..……, ……….and……..
- The central hollow part of the long bones it known as…………….
- A bone becomes soft and flexible when placed in dilute………………..
Ans. (i) cartilage, ligaments
(ii) Bone
(iii) Long, short, flat, irregular
(iv) Bone marrow
- Hydrochloric acid.
Q2. Mátch the bones (Column I) with the kind of joint (Column II)
Column I (Bones) Column II (Joint)
(i) Humerus and shoulder girdle (a) Partially moveable
(ii) Two adjacent vertebrae (b) Gliding
(iii) Skull and upper end of back-bone (c) Immovable
(iv) Bones of brain box (d) Ball and socket
(v) Rib and breast bone (e) Pivot
Ans. (i)-(d), (ii) – (b), (iii) — (e), (iv) – (c), (v) — (a)
Q3. Your external ear (pinna) is supported by
(a) Bone
(b) Cartilage
(c) Tendon
(d) Capsule
Ans. (b) Cartilage
Q4. The type of joint found at shoulder is also found at
(a) Elbow
(b) Knee
(c) Ankle
(d) Hip
Ans. (d) Hip
Q.5. which one the following categories of vertebrae are correctly numbered
(a) Cervical-7
(b) Thoracic – 10
(c) Lumbar-4
(d) Sacral-4
Ans. (a) Cervical-7
Q 6. Human skeleton altogether contains 206 bones. Which of these are the 6 bones?
(a) Neck vertebrae (b) Ear ossicles
(c) Carpals (d) Metacarpals
Ans. (b) Ear ossicles
Q7. Name any two parts of your body where the supporting skeleton is made of cartilage instead of bone.
Ans. External ear, nose.
Q8. What is the difference between a true rib and a floating rib?
Ans. True ribs. The first seven pairs of ribs, attached directly to the sternum by means of coastal cartilages are called as true ribs.
Floating ribs. The last two pairs of ribs, not connected to – the sternum at all are known as floating ribs.
Q9. Do the muscles pull the structures, or push them? Explain briefly.
Ans. Each muscle usually has two ends, a fixed end where the muscle originates and a movable end which pulls some other part. This movable end is drawn out to form a tough structure called tendon. Tendon is attached to the bone. The muscles when stimulated by a nerve, contracts, become shorter and thicker and thus it pulls the bone at the movable end.
Q10. What are antagonistic muscles? Give one
Ans. Skeletal Muscles work in pairs, each opposing the action of the other in the pair, like some muscles contracting while others relaxing Muscles which produce opposite movements are called antagonistic muscles. The biceps and triceps of hand are antagonists. When biceps contract the arm is pulled upward (bending of lower arm over the upper arm) in this position the triceps relax. When the triceps contracts, the biceps, relax so the lower arm is straightened. Therefore these two muscles are antagonistic.
Q11. Some people in old age complain of stiff joints. What do you think could be a possible reason for it?
Ans. Some joints like shoulder joint, knee joint need to be held firmly in position to be well lubricated. Such joints contain lubricating fluid called the synovial fluid, which serves as a cushion between the bones and removes friction during movements. In the old age, the amount of synovial fluid gets reduced and due to loss of lubrication and increased friction people complain of stiff joints.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
Q12. What are the uses of skeleton in our body?
Ans. The endoskeleton of vertebrates is made of bones and cartilages and has following important uses:
- It affords protection to delicate organs of the body such as heart, lungs, brain, spinal cord, sense organ etc.
- It provide support to the body and helps in preserving a definite shape.
- It provides a suitable surface for the attachment of the muscles and ligaments.
- Some bones provide lever arrangement.
- Some part of the skeleton help in breathing and hearing.
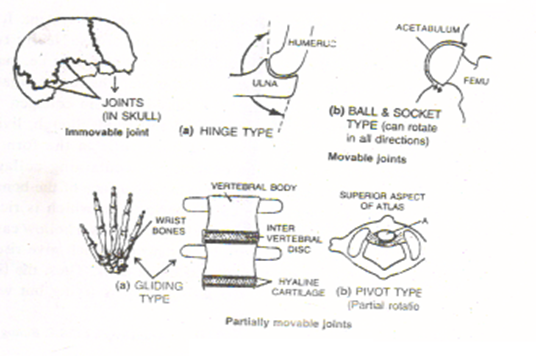
Q13. What are the different types of joints ? Give one example of each type.
Ans. A joint is formed where two or more bones meet. These are of following types:
- Immovable joints. In this no movement is possible between the two bones. The sutures between the bones of the brain box are examples of immovable joint.
- Partially movable joints. Slight movement is possible between two bones. The joints between rib and the breast bone or between the vertebrae are the examples of above joints.
- Movable joints. Varying degrees of movement are possible between the two jointed bones. Movable joints are of four types:
- Hinge joints allow the movement in one plane only e.g. between the humerus and ulna and in the knees, elbows, fingers etc.
- Ball and socket joints allow the greatest freedom of movement e.g., shoulder joint and hip joint.
- Gliding joints between the bones of the wrist and those of the ankles.
- Pivot joints allow rotation about an axis e.g. the juncture between the head and the upper end of the back bone.
- Synovial joints. Some joints allow considerable degree of movement e.g. the knee joint is held in position by strong ligaments and well protected by an outer fibrous layer.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
Q14. What is the difference between ligament and tendon? What are their functions?
Ans.
| Tendon | Ligament |
| 1. Tendons connect muscles to bones | Ligaments connect two bones, |
| 2. Tendons are inelastic. | Ligaments are elastic. |
| 3. They are arranged in bundles. | They are arranged freely. |
| 4. They are made of white fibres or collagen fibres. | They are formed of yellow fibres or elastic fibres. |
Function of Tendons.
(i)Attach muscles to the portions of the skeleton.
(ii) Serves to move the various bones and cartilages of the skeleton.
Function of Ligament
(i) Serves to strengthen the joints.
(ii) Prevents dislocation.
(iii) Sometimes covers the exposed portion of the joint.
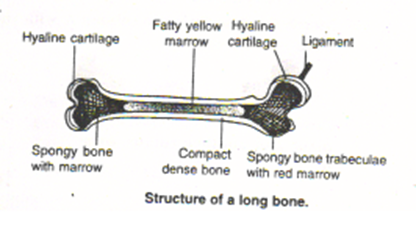
Q15: What are bones made of? Are the bones living or non living? Give reason.
Ans. Bone is the main component of our skeletal system. It is made up of organic and inorganic materials. Nearly two third part of the entire bone substance is inorganic i.e. made up of calcium, phosphate and carbonate. The rest is organic material consisting largely of fibrous protein collagen.
Bone is a highly calcified, hard and rigid, though, living skeletal tissue. It consists of bone cells in the form of concentric rings called oesteocytes containing collagen fibres and mineral salts. The external surface of the bone is covered by membrane called periosteum which is richly supplied with blood vessels. A long bone has a hollow cavity in the middle, filled with bone marrows which give rise to either white blood cells or red blood cells. Thus, the bone as long as present in the living body is living but when taken out its cells dies and the bone is said to be dead (non living).
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
Q16.What is a synovial joint?
Ans. A joint in which there is a space between articulating bones is called synovial joint
The joint enables free movement e.g. elbow joint.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION CLASS 9 ICSE
ALSO VISIT:
9TH ICSE
| Also Learn: | Also study: | Attempt the Quiz | Attempt the Quiz | Attempt the Quiz |
| ATOMS AND MOLECULES | Skin “The jack of all trades” | CIRCLES– MATHEMATICS | QUIZ ON GRAVITATION- PHYSICS | Quiz on polynomials |
| GRAVITATION | QUIZ 2 ON CIRCLES | QUIZ ON ATOMS AND MOLECULES-CHEMISTRY | Quiz on work, power and energy | |
| MENSURATION | QUIZ 3 ON CIRCLES | Quiz on Periodic classification of elements | Quiz on Distance formula | |
| Archimedes Principle | Quiz on Quadrilaterals | Quiz on Periodic table | Quiz on polynomials |
