DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Table of Contents
NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Fill in the Blanks
(i) Nervous system controls and …… the working of all parts of the body.
Ans. coordinates
(ii) The terminal portions of the axons have swollen bulb-like structure called ………..
Ans. synaptic knob
(iii) Certain chemicals called…… are stored in synaptic knob.
Ans. neurotransmitters
(iv) The axon transmits ……… away from the cell body to a synapse.
Ans. impulses
(v) A bundle of axons enclosed in a tubular sheath is called……….
Ans. nerve
(vi) Dendrites and axon are collectively called……
Ans. neuritis
(vii) Grey matter is mainly composed of…….
Ans. cytons
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
(viii) The part of the brain concerned with the body balance is……..
Ans. cerebellum
(ix) There are ……. layers of meanings in the brain.
Ans. three
(x)… is the tough, fibrous outermost covering of brain.
Ans. Duramater
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
(xi) The fluid-filled between the meanings is called…..
Ans. cerebrospinal fluid
(xii) ……… forms the posterior part of the CNS.
Ans. Spinal cord
(xiii) …… movements are under our conscious control.
Ans. Voluntary
(xiv) ……. movements are not under our conscious control.
Ans. Involuntary
(xv)……….. is thin, transparent membrane covering the eye.
Ans. Conjunctiva
(xvi) The three layers of the eye are …, ….. and…..
Ans. sclera, choroid, retina
(xvii) The place of best vision in the retina of eye is……
Ans. yellow spot
(xviii) Place of no vision in the retina of the eye is………
Ans. blind spot
(xix) ………. is the capacity of the eye to focus at different distances.
Ans. power of accommodation
(xx)……… vision is the condition in which both the eyes participate in viewing an object.
Ans. Binocular or Stereoscopic
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
(xxi) Astigmatism is corrected by using….or…. lenses.
Ans. spherical , cylindrical
(xxii) Cochlea is filled with……….
Ans. endolymph
(xxiii) Tympanic chamber is filled with……
Ans. perilymph
(xxiv) The middle ear is separated from the external ear by the…..
Ans. tympanic membrane
(xxv) Area in middle ear having auditory sense cells is……
Ans. organ of Corti
(xxvi) …….. is also known as external ear.
Ans. Pinna
(xxvii) The three small bones in the middle ear are called …….
Ans. ear ossicles
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Match the Columns
1. Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Neurotransmitter | 1. Mylinated sheath |
| B. Covering on myelin sheath | 2. Acetylcholine |
| C. Nodes of Ranvier | 3. Neurolemma |
| D. Neurofibrils | 4. Cyton |
| E. Neurites | 5. Connection neuron |
| 6. Dendrites and axon | |
| 7. Command and control system |
Ans. A – 2, B – 3, C – 1, D – 4, E – 6
2. Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Diencephalon | 1. Forebrain |
| B. Cerebrum | 2. Spinal cord |
| C. Cerebellum | 3. Hypothalamus |
| D. Central canal | 4. Hindbrain |
| E. Brain stem | 5. Connects forebrain to spinal cord |
| 6. Ascending tract |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Ans. A – 3, B – 1, C – 4, D – 2, E – 5
3. Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Increase in blood sugar | 1. Voluntary action |
| B. Autonomous nervous system | 2. Involuntary action |
| C. Watching TV | 3. Sympathetic nervous system |
| D. Blinking of eye | 4. Inborn reflex |
| E. Conditioned reflex | 5. Sneezing |
| 6. Applying brakes |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Ans. A – 3, B – 2, C – 1, D – 4, E – 6
4. Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| A. External layer of eyeball | 1.Choroid |
| B. Inner layer of eyeball | 2. Orbits |
| C. Middle layer of eyeball | 3. Sclera |
| D. Socket of the skull | 4. Retina |
| E. No response to colour | 5. Cones |
| 6. Blind spot | |
| 7. Rods |
Ans. A – 3, B – 4, C – 1, D – 2, E – 7
5. Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Hammer | 1. Coiled portion of labyrinth |
| B. Auditory sense cells | 2. Extracellular fluid |
| C. Perilymph | 3. Malleus |
| D. Pinna | 4. Collection of sound waves |
| E. Cochlea | 5. Stapes |
| 6. Maintains body balance | |
| 7. Organ of Corti |
Ans. A – 3, B – 7, C – 2, D – 4, E – 1
6. Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Nissl’s granules | 1.Little brain |
| B. Cerebellum | 2. Natural reflex |
| C. Acetylcholine | 3. Cell body |
| D. Corpus callosum | 4. Prolactin |
| E. Sneezing | 5. Neurotransmitter |
| 6. 18 pairs | |
| 7. Connects two hemisphere | |
| 8. Conditioned reflex |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Ans. A – 3, B – 1, C – 5, D – 7, E – 2
1. How are cytons and axons placed in the brain and the spinal cord?
Ans. Cyton in brain The cerebral cortex is the outer folded part of the brain also called grey matter, containing all the cell bodies and dendrites of nerve cell.
Axon in brain The inner portion is composed of white matter mainly consisting of axons of the neurons. In spinal cord, grey matter is present on the inner side and white matter on the outer side.
2. Explain how the human eye adapts itself to bright light and dim light.
Ans. Iris surrounds pupil. The movement of muscle fibers of iris controls the size of pupil and regulates the amount of light entering the eye. Due to this adjustment, we blink our eyes when we see bright light or not able to see when entering a dimly lit room as pupil takes time to adjust its size according to the amount of light.
3. With reference to the functioning of the eye, answer the question that follows.
(i) What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
(ii) What is the shape of the lens during?
(a) Near vision
(b) Distant vision?
(iii) Name the two structures in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of the lens.
(iv) Name the cells of the retina and their respective pigments which get activated
(a) In the dark
(b) In light.
Ans. (i) The adjustment of the eye to enable it to focus at various distances is called power of accommodation.
(ii) The shape of lens is as follows
(a) During near vision, lens is more concave or rounded.
(b) During distant vision, lens is less convex or flat.
(iii) Ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments are the two structures in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of lens.
(iv) (a) In the dark, rod cells get activated and their pigment is rhodopsin.
(b) In the light, cone cells get activated and their pigment is iodeosin.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
4. Choose between the two options to answer the question specified in the brackets for the following.
(i) Perilymph or endolymph (Which one surrounds the organ of Corti?)
(ii) Sclerotic layer or choroid layer (Which one forms the iris?)
Ans. (i) Endolymph surrounds the of organ Corti.
(ii) Choroid forms the iris.
5. Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity. On a similar pattern fill in the blanks with suitable functions. Example: Chloroplast and Photosynthesis Eustachian tube and……..
Ans. Balance of air pressure on both sides of eardrum.
6. Which part of the human ear gives dynamic balance and state balance to the body?
Ans. Sensory cells in semicircular canal are concerned with dynamic balance and utriculus and sacculus are concerned with static balance.
7. Name the following.
(i) The cell body of a nerve cell.
(ii) The part of the brain associated with memory.
(iii) The part of the brain that carries impulses from one hemisphere of the cerebellum to the other.
(iv) The covering that maintains the shape of the eyeball.
(v) The pigmented layer present beneath the sclera.
(vi) The layer of the eyeball that forms the transparent cornea.
(vii) The layer of eyeball that provides nourishment the eye.
(viii) The layer that prevents reflection of light.
(ix) The two structures in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of the lens.
(x) The region of distinct vision.
(xi) The kind of lens required to correct myopia.
(xii) The ear ossicles, which is attached to the tympanum.
(xiii) The three small bones present in the middle ear.
(xiv) The nerve that transmits messages from ear to the brain.
(xv) The structure found in the inner ear.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Ans. (i) Cyton is known as the cell body of a nerve cell.
(ii) Cerebrum is the part of brain associated with the memory.
(iii) Pons Varolii is the part of brain that carries impulses from one hemispheres of the cerebellum to the other.
(iv) Sclera (outermost layer) is the covering that maintains the shape of eyeball.
(v) Choroid present beneath the sclera.
(vi) The transparent cornea is the continuation of sclera layer of eyeball.
(vii) Middle choroid layer provides nourishment to the eye.
(viii) Choroid prevents reflection of light.
(ix) Ciliary muscles and suspensor ligaments are the two structures in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of lens.
(x) Yellow spot is the region of distinct vision.
(xi) Myopia can be corrected appropriate power. Using concave lens of
(xii) Malleus/hammer is the ear ossicles, which is attached to the tympanum.
(xiii) Hammer, anvil and stirrup are the three small bones present in the middle ear.
(xiv) Auditory nerve is responsible to transmit messages from ear to brain.
(xv) Membranous labyrinth found in the inner ear.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
8. Mention the exact location of the following structures.
(i) Myelin sheath
(ii) Corpus callosum
(iii) Ciliary body
(iv) Yellow spot
(v) Lacrimal gland
(vi) Semicircular canals
(vii) Eustachian tube
(viii) Incus
(ix) Organ of Corti
(x) Malleus
Ans. (i) Myelin sheath surrounds axon of the neuron.
(ii) Corpus callosum is found between the two lobes of cerebrum celled cerebral hemispheres.
(iii) Ciliary body is anterior part of the eye.
(iv) Yellow spot is located exactly behind the lens on the retina of the eye.
(v) Lacrimal glands or tear glands are located at upper sideward portion of the orbits (eye sockets).
(vi) Semicircular canals are located in the inner ear.
(vii) Eustachian tube is found in the middle ear.
(viii) Incus is found in middle ear between Malleus and stapes.
(ix) Organ of Corti is located in the endolymph present in the middle canal of cochlea.
(x) Malleus is an ear ossicles (bone) present in the middle ear. Its one end is attached to eardrum.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
9. Give the biological/technical terms for the following.
(i) The protective covering of brain and spinal cord.
(ii) A thin membrane covering the entire front part of the eye.
(iii) The lens of eye losing flexibility resulting in a kind of long sightedness in middle aged people.
(iv) The structure found in the inner ear.
Ans. (i) Meanings is the technical term for the protective covering of brain and spinal cord.
(ii) Cornea is a thin covering the entire front part of eye.
(iii) Presbyopia
(iv) Membranous labyrinth is found in inner ear.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
10. Give scientific/biological reason for the following statements.
(i) A person after consuming alcohol walks clumsily.
Or
An alcoholic person walks unsteadily when drunk.
(ii) Injury to medulla oblongata leads to death.
(iii) The hand automatically shows the direction to turn a cycle without thinking.
(iv) A person from bright sunlight outside enters a poorly lit room and feels blinded for a short while.
(v) ‘We cannot distinguish colours in moonlight’.
(vi) How do you perceive the colour of an object?
(vii) Throat infections can lead to ear infections.
(viii) We should not put sharp objects into our ears.
Ans. (i) An alcoholic person when drunk walks clumsily/unsteadily because of the effect of alcohol on cerebellum. This is because cerebellum is mainly responsible for the muscular coordination.
(ii) Medulla oblongata has pneumotaxis centre which controls breathing rate. Injury to this part of the brain becomes fatal.
(iii) It is a case of conditioned reflex wherein the reflexes are acquired after birth during the course of lifetime.
(iv) When a person enters a dark room, it takes time for the pupil to re-adjust its size to allow maximum light to enter the eye. That is why, when he enters the room, he feels blinded for a short while.
(v) Moonlight is dimlight during which cone cells of our eye do not function well therefore, the colour is not well perceived. Rod cells are mainly active in moonlight.
(vi) The sensations of different colours are produced by various combinations of cones and their respective pigments.
(vii) Eustachian tube connects with the pharynx. Thus, infection in throat may also lead to ear infections.
(viii) We should not put sharp objects into our ears as they can damage our eardrum (tympanic membrane) and can lead to deafness.
11. Choose the odd one out from the following terms given and name the category to which others belong.
(i) Dendrites, medullar sheath, axon, spinal cord.
(ii) Cerebrum, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus
(iii) Haemoglobin, glucagon, iodeosin, rhodopsin.
(iv) Aqueous humour, vitreous humour, Iris, central canal
(v) Malleus, iris, stapes, incus
(vi) Semicircular canals, cochlea, tympanum, utriculus.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
Ans. (i) Odd one Spinal cord
Category Part of central nervous system
Rest others structures belong to nerve cell.
(ii) Odd one Cerebellum
Category Part of hindbrain
All others are the parts of forebrain.
(iii) Odd one Glucagon.
Category Part of peptide hormone
All others are pigments found in the body.
(iv) Odd one Central canal
Category Present in spinal cord
Rest three structures are present in eye.
(v) Odd one Iris
Category Part of eye
Rest three are bones present in human ear.
(vi) Odd one Tympanum
Category Part of external ear
All others are the different parts of internal ear.
12. Write the special functional activity of the structures given below.
(i) Relay neuron
(ii) Neurotransmitter
(iii) Iris of the eye
Ans. (i) Relay or Connecting neuron serves as a link between the sensory and motor neurons. These are mainly found in brain and spinal cord.
(ii) Neurotransmitters help in the conduction of nerve impulse.
(iii) Iris of the eye regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
13. Briefly explain the following terms.
(i) Synapse
(ii) Cranium
(iii) CSF
(iv) Reflex action
(v) Power of accommodation
Ans. (i) Synapse is the point of contact between the axon endings of one neuron with the dendrites of the other neuron. The impulse is transmitted from one neuron to the other through the synapse.
(ii) It is a box-like bony structure that protects the brain by covering it.
(iii) CSF stands for Cerebrospinal Fluid. It is the fluid that protects the brain from mechanical injuries.
(iv) A reflex action is a spontaneous, automatic and dolor involuntary response to a stimulus.
(v) Power of accommodation.
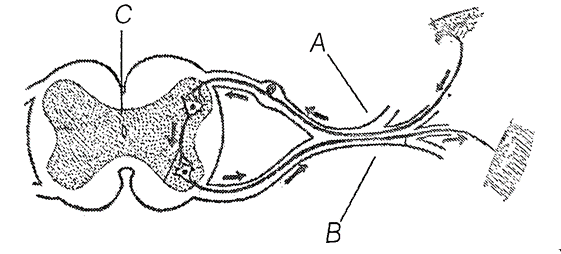
14. The diagram given below shows the internal structure of a spinal cord depicting a phenomenon. Study the diagram and answer the question that follows.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSEDOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
(i) Name the phenomenon that is depicted in the diagram. Define the phenomenon.
(ii) Give the technical term for the points of contact between the two nerve cells.
(iii) Name the parts labelled as A, B and C.
(iv) How does the arrangement of neurons in the spinal cord differ from that of the brain?
(v) Mention two ways by which the spinal cord is protected in our body.
Ans. (i) The given figure shows the phenomenon of reflex action. It is an involuntary or instantaneous reaction in response to a stimulus, e.g. coughing, blinking of eyes, sneezing, etc.
(ii) Synapse
(iii) A-Sensory neuron, B-Motor neuron, C-Grey matter
(iv) Arrangement of grey and white matter in spinal cord is opposite to that found in brain. Grey matter is in the inner side and the white matter is on the outer side.
(v) The spinal cord is well-protected by three membranous coverings known as meninges and cerebrospinal fluid.
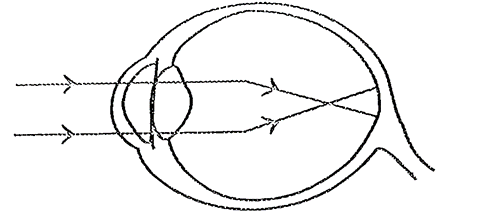
15. Given below is a diagrammatic depicting a defect of the human eye, study same and then answer the questions that follows.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
(i) Name the defect shown in the diagram.
(ii) What are the two possible reasons that cause this defect?
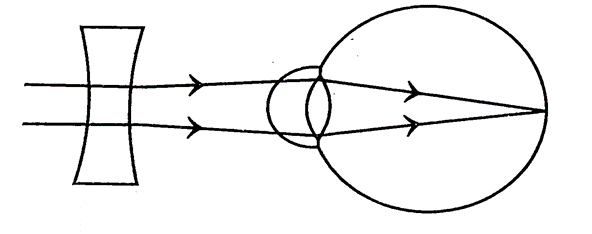
(iii) Name the type of lens used to correct this defect.
(iv) With the help of a diagram show how the defect shown above is rectified using a suitable lens.
Ans. (i) Myopia (short sightedness)
(ii) (a) Image forms before retina.
(b) Caused by excessive curvature of lens.
(iii) Concave lens
(iv)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
ALSO VISIT:
10th ICSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: NERVOUS SYSTEM CLASS 10 ICSE
