DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
Table of Contents
THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
1. Demand in economic sense means-
(a) mere desire for a commodity
(b) mere ability to pay price of the commodity
(c) mere wiling to pay the price of the commodity
(d) desire backed by ability and willingness to pay for the commodity desired
2. In economics, demand refers to-
(a) quantity demanded at a particular time
(b) quantity demanded backed by ability to pay
(c) quantity demanded of all goods
(d) quantity demanded at a particular price in a given period of time
3. The concept of demand demonstrates that-
(a) demand is always with reference to price
(b) demand is referred to in a given period of time
(c) buyer’s ability and willingness to pay
(d) all the above
4. Demand is a
(a) flow concept Le. quantity per unit of time
(b) stock concept
(c) wealth concept
(d) none of the above
5. Demand concept explains the ________ behaviour in response to change in price of a good.
(a) producer’s
(b) seller’s
(c) consumer’s
(d) none of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
6. Individual Demand is also called-
(a) industrial demand
(b) market demand
(c) household’s demand
(d) all the above
7. ________ means quantity demanded of a good by a single consumer at various prices per unit of time.
(a) Market Demand
(b) Individual Demand
(c) Industrial Demand
(d) None of the above
8. _______ means the aggregates of the quantities
demanded by all consumers in the market at different prices per unit of time.
(a) Market Demand
(b) Individual Demand
(c) Industrial Demand
(d) Household Demand
9. All but one are the factors which affect individual demand. Find the odd one out.
(a) Price of related good
(b) Income of the consumer
(c) Tastes and preferences of consumer
(d) Number of consumers in the market
10. _________ is a tabular presentation showing different quantities demanded by buyers at different levels of prices in a given period.
(a) Supply Schedule
(b) Demand Schedule
(c) Production Schedule
(d) Cost Schedule
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
11. A demand schedule is shown as-
(a) a result of increase in the size of the family
(b) a result of change in tastes and preferences
(c) a function of price
(d) all the above
12. Market Demand is the sum total of-
(a) all quantities that producer’s can produce
(b) all quantities actually sold in the market
(c) all quantities demanded by individual households and consumers
(d) all the above
13. Demand of a good of several consumers when added together is called _______ demand.
(a) individual
(b) market
(c) joint
(d) independent
14. When a good can be used to satisfy two or more wants, it is said to have _______ demand.
(a) composite
(b) competitive
(c) joint
(d) market
15. Indirect demand of a good is also known as _______ demand.
(a) direct
(b) derived
(c) joint
(d) competitive
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
16. Which of the following is a determinant of Individual Demand?
(a) Cost of production
(b) Nature of commodity
(c) Economic Policies of the Government
(d) Tastes and Preferences of consumers
17. Which of the following is NOT the determinant of demand?
(a) Price of the commodity
(b) Price of related commodities
(c) Income of consumer
(d) None of the above
18. How are APPLES and ORANGES related when as a result of rise in price of Apples, demand for Oranges increases?
(a) Substitute goods
(b) Complementary goods
(c) Normal goods
(d) Inferior goods
19. If two goods are complementary then rise in the price of one results in-
(a) rise in demand for the other
(b) fall in demand for the other
(c) rise in demand for both
(d) none of these
20. If the demand for CNG increases as price of petrol increases, the two goods are-
(a) Normal goods
(b) Complementary goods
(c) Substitute goods
(d) Superior goods
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
21. Comforts lies between-
(a) inferior goods and necessaries
(b) luxuries and inferior goods
(c) necessaries and luxuries
(d) none of the above
22. When price of commodity rises, the demand for it _______ .
(a) rises
(b) contracts
(c) remain constant
(d) becomes negative
23. When the price of petrol goes up, demand for two-wheelers will-
(a) rise
(b) fall
(c) remain same
(d) none of these
24. An increase in the income of a consumer has effect on demand in general.
(a) no
(b) negative
(c) opposite
(d) positive
25. The demand for Scooter and petrol is an example of _______ demand.
(a) joint
(b) composite
(c) competitive
(d) market
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
26. _______ goods are those goods which are used for the production of other goods.
(a) Durable
(b) Producer’s
(c) Non-Durable
(d) Consumer’s
27. _______ goods are those which are used for final consumption.
(a) Durable
(b) Producer’s
(c) Non-Durable
(d) Consumer’s
28. Bread, Milk, Readymade clothes, T.V., etc. are examples of _______ goods
(a) perishable
(b) producer’s
(c) consumer’s
(d) inferior
29. The goods which cannot be consumed more than once, like milk are known as _______ goods.
(a) non-durable consumer goods
(b) producer’s
(c) inferior
(d) durable consumer goods
30. _______ goods meets only our current demand.
(a) producers
(b) durable consumer goods
(c) non-durable consumer goods
(d) inferior
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
31. The goods which can be consumed more than once over a period of time are known as _______ goods.
(a) non-durable consumer goods
(b) producer’s
(c) durable consumer goods
(d) inferior
32. When demand of any good depends upon the demand of another good, it is said to have _______ demand.
(a) joint
(b) derived
(c) competitive
(d) direct
33. The total demand for steel in the country denotes _______ demand.
(a) industry
(b) company
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) autonomous
34. If the demand for a product is independent of the demand for other goods, it is called as _______ demand.
(a) company
(b) industry
(c) autonomous
(d) derived
35. If the construction activity in housing sector, infrastructure, etc. rises, the demand for cement will _______ as it has _______ demand.
(a) rise ; autonomous
(b) fall; autonomous
(c) rise ; derived
(d) none of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
36. Demand for steel produced by Tata Iron and Steel Company is an example of _______ demand.
(a) industry
(b) company
(c) autonomous
(d) joint
37. When demand of any good reacts immediately to price changes, income changes, etc. it is said to have _______ demand.
(a) short-run
(b) long-run
(c) very short run
(d) very long run
38. A relative price is-
(a) price expressed in terms of money
(b) what you get paid for babysitting your cousin
(c) the ratio of one price to another
(d) equal to a money price
39. The quantity demanded of a good or service is the amount that-
(a) consumer plan to buy during a given period at a given price.
(b) firms are willing to sell during a given time period at a given price.
(c) a consumer would like to buy but may not be able to afford.
(d) is actually bought during a given period at a given price.
40. Coca-Cola and Thumbs-Up are substitutes. A rise in the price of Coca-Cola will _______ the demand of Thumbs-Up and the quantity demanded of Thumbs-Up will _______ .
(a) increase ; increase
(b) increase; decrease
(c) decrease ; decrease
(d) decrease; increase
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
41. If the price of Orange Juice falls, the demand for Apple Juice will _______ .
(a) increase
(b) decrease
(c) remain the same
(d) become negative
42. The demand for consumer goods is a _______ demand.
(a) direct
(b) indirect
(c) constant
(d) company
43. If the price of inferior goods fall, the demand for them will _______.
(a) rise
(b) fall
(c) remain constant
(d) become zero
44. The Law of Demand states _______ relation between demand and price of a commodity.
(a) a direct
(b) positive
(c) an indirect
(d) no
45. When total demand for a commodity whose price has fallen increases, it is due to
(a) income effect
(b) substitution effect
(c) complementary effect
(d) price effect
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
46. With a fall in the price of a commodity
(a) Consumer’s real income increases
(b) Consumer’s money income increases
(c) Consumer’s real income falls
(d) Consumer’s money income falls
47. When we draw a market demand curve, we _______.
(a) do not consider tastes, incomes and all prices
(b) assume that tastes, incomes and all other prices change in the same way price changes
(c) assume that tastes, incomes and all other prices are irrelevant
(d) assume that tastes, incomes and all other prices remain the same
48. All but one of the following are assumed to remain the same while drawing individual’s demand curve for a commodity. Which are is it?
(a) The tastes and preferences of the consumer
(b) Income of consumer
(c) The price of the commodity
(d) The prices of related commodities
49. A fall in price of a commodity leads to _______.
(a) a shift in demand curve
(b) a rise in consumer’s real income
(c) a fall in demand
(d) none of the above
50. If a fall in price of ‘y’ results in a decrease in the sale of ‘x’, the two good appear to be-
(a) substitute goods
(b) complementary goods
(c) inferior goods
(d) neutral goods
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
51. Which of the following is not a complementary good for pen?
(a) refills
(b) paper
(c) notebook
(d) rice
52. _______ goods are the goods which can be used with equal case in place of each other.
(a) Neutral
(b) Normal
(c) Complementary
(d) Substitute
53. Which of the following pairs of goods are an example of substitutes?
(a) Tea and Sugar
(b) Tea and Coffee
(c) Pen and Ink
(d) Shirt and Trouser
54. When the price of a substitute of good ‘X’ falls, the demand for good ‘X’
(a) rises
(b) falls
(c) remains unchanged
(d) None of these
55. If the demand rises with the rise in consumer’s real income, such a good is called _______.
(a) Normal goods
(b) Neutral goods
(c) Inferior goods
(d) Luxury goods
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
56. Giffen goods are-
(a) Normal goods
(b) Inferior goods
(c) Luxury goods
(d) Neutral goods
57. As the consumer’s income increases, the demand for necessaries of life will increase _______ to the increase in income.
(a) Less than proportionate
(b) More than proportionate
(c) Proportionate
(d) Nothing can be said
58. As the consumer’s income increases, the demand for comforts and luxuries will increase _______ to the increase in income.
(a) Less than proportionate
(b) More than proportionate
(c) Proportionate
(d) Nothing can be said
59. During boom period in economy, the demand for goods in general _______.
(a) rises
(b) falls
(c) remains same
(d) none of these
60. Larger the size of population of a country _______ is the demand for goods and services in general.
(a) lower
(b) ineffective
(c) neutral
(d) higher
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
61. In case the consumer expects a steep rise in price of Potatoes in future, his current demand for it will _______.
(a) remain same
(b) fall
(c) rise
(d) none of the above
62. All but one of the good’s demand is not affected by changes in weather conditions-
(a) Ice-cream
(b) Woollen clothes
(c) Cold drinks
(d) Wheat
63. If the government increase the rate of indirect taxes on goods and services, the demand for then will _______ in general.
(a) rise
(b) fall
(c) remain neutral
(d) be ineffective
64. If the government reduces the tax on any pro-duct, the demand for the product _______ in the short run.
(a) rises
(b) falls
(c) remain unchanged
(d) tax has nothing to do with the demand of any product
65. If the demand for petrol remains unchanged with rise in its price, it means petrol is a _______
(a) Normal good
(b) Necessity
(c) Luxury good
(d) Inferior good
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
66. If quantity demanded of good ‘X’ is plotted against the price of its substitute good ‘Y’, the demand curve will be-
(a) Vertical Straight line
(b) Positively sloped
(c) Horizontal Straight line
(d) Negatively sloped
67. Consider the following figure:
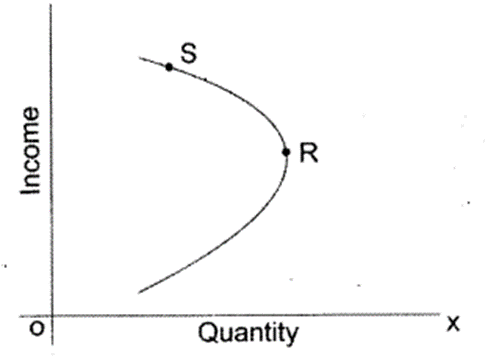
In the above figure, RS part of the demand curve represents-
(a) Superior good
(b) Inferior good
(c) Normal good
(d) Giffen’s good
68. In case of normal goods the income effect is _______
(a) zero
(b) negative
(c) positive
(d) constant
69. Income effect on demand of a good is _______.
(a) positive for normal goods
(b) always positive
(c) negative for normal goods
(d) always negative
70. The Law of Demand is explained by-
(a) Cardinal approach
(b) Ordinal approach
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) Neither ‘a’ nor ‘b’
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
71. The Law of Demand refers to functional relation between-
(a) Price & Supply
(b) Price & Cost
(c) Price & Income
(d) Price & Demand
72. The term “Ceteris Paribus” in the Law of Demand means-
(a) All factors except one remain constant
(b) All factors remain constant
(c) All factors are variable
(d) None of the above
73. Which of the following is a variable and influencing factor in the Law of Demand?
(a) Consumer’s Income
(b) Consumer’s Tastes and Preferences
(c) Price of related goods
(d) Price of the good
74. The phrase “Other things being equal” in the Law of Demand means-
(a) Income of the consumer remain unchanged
(b) Price of related goods remain unchanged
(c) Tastes and Preferences of consumer remain unchanged
(d) All the above
75. The total effect of price change of a good is-
(a) Substitution Effect + Income Effect
(b) Substitution Effect + Price Effect
(c) Substitution Effect + Demonstration Effect
(d) Demonstration Effect + Veblen Effect
76. Substitution Effect subscribe to the inverse relation between Px and Qx in case of-
(a) normal goods only
(b) inferior goods only
(c) normal and inferior goods both
(d) none of the above
77. Income Effect does not subscribe to the inverse relation between Px and Qx in case of-
(a) both normal and inferior goods
(b) inferior goods
(c) normal goods
(d) none of the above
78. The Law of Demand will fail in case of inferior goods only if-
(a) Substitution Effect is greater than Income Effect
(b) Income Effect is greater than’Substitution Effect
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) Neither ‘a’ nor ‘b’
79. The Law of Demand is a _______ statement.
(a) Positive
(b) Normative
(c) Descriptive
(d) Both ‘a’ and ‘c’
80. _______ refers to the effect of change in the price of a product on the consumer’s purchasing power.
(a) Real Income Effect
(b) Substitution Effect
(c) Consumer’s Surplus
(d) None of the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
81. When the price of Thumbs-up falls, other things being constant, buyers substitute Thumbs-up for Coca-Cola. This is called-
(a) Price Effect
(b) Substitution Effect
(c) Income Effect
(d) Veblen Effect
82. _______ refers to the buyer’s reaction to a change in the relative prices of two products, keeping the total utility constant.
(a) Consumer’s Surplus
(b) Income Effect
(c) Substitution Effect
(d) None of the above
83. The Law of Demand can be explained by-
(a) The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(b) Indifference Curves
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) Neither ‘a’ nor ‘b’
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
84. Consumers buy a good till Px = MUx. If the price falls, the consumer will reach equilibrium-
(a) at a lower quantity
(b) at a higher quantity
(c) at zero quantity level
(d) all the above
85. “Petrol is becoming cheaper, yet the demand for cars is not rising”. This statement indicates that-
(a) The Law of Demand is not operative for cars
(b) The Law of Demand is operative for petrol
(c) The Demand Curve for cars will shift
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
86. Downward slope of the demand curve shows-
(a) positive relationship between price and quantity demanded
(b) inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
(c) no relationship between price and quantity demanded
(d) none of the above
87. In case of NORMAL GOODS, demand curve shows:
(a) a negative slope
(b) a positive slope
(c) zero slope
(d) none of these
88. Law of Demand fails in case of –
(a) normal goods
(b) Giffen goods
(c) inferior goods
(d) both ‘b’ and ‘c’
89. In case of Giffen’s Paradox, the slope of the demand curve is-
(a) parallel to X-axis
(b) positive
(c) negative
(d) parallel to Y-axis
90. A Giffen good is one for which a small change in price results in-
(a) zero income effect out weighted by a positive substitution effect
(b) zero income effect being equal to zero substitution effect
(c) negative income effect out weighed by a positive substitution effect
(d) none of these
91. The Law of Demand indicates the
(a) direction of change in demand of a commodity
(b) magnitude/amount of change in demand of a commodity
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) elasticity of demand
92. In case of Giffen goods, demand varies _______ with the price.
(a) inversely
(b) directly
(c) proportionately
(d) none of these
93. Analysis of the relationship between demand of a commodity and prices of related commodities is-
(a) Price Demand analysis
(b) Income Demand analysis
(c) Cross Demand analysis
(d) Market Demand analysis
94. _______ observed that when the price of inferior goods fall, the demand for such goods also fall.
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Dr. Alfred Marshall
(c) Ragnar Frisch
(d) Sir Robert Giffens
95. The Law of Demand was propounded by _______ in his book ‘Principles of Economics’.
(a) Lord Keyens
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Dr. Alfred Marshall
(d) Ragnar
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
96. The tendency of low income group to imitate the consumption pattern of high income group is known as _______ effect.
(a) Demonstration
(b) Copy
(c) Prestige
(d) Veblen
97. The Law of Demand is applicable for _______.
(a) Giffen’s Goods
(b) Prestige Goods
(c) Necessary Goods
(d) Normal Goods
98. When price changes and proportionate change in market demand is more than proportionate change in individual demand implies that the market demand curve is _______ than the individual demand curves.
(a) Steeper
(b) Flatter
(c) Vertical
(d) None of the above
99. A positively sloped demand curve implies
(a) Violation of the law of demand
(b) Giffen good
(c) Income effect is negative and greater than substitution effect
(d) All the above
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
| D | 11. A | 21. C | 31. C | 41.B | 51.D | 61.C | 71.D | 81.B | 91.A |
| D | 12. C | 22. B | 32. B | 42.A | 52.D | 62.D | 72.A | 82.C | 92.B |
| D | 13. B | 23. B | 33. A | 43.B | 53.B | 63.B | 73.D | 83.C | 93.C |
| A | 14. A | 24. D | 34.C | 44.C | 54.B | 64.A | 74.D | 84.B | 94.D |
| C | 15. B | 25. A | 35.C | 45.D | 55.C | 65.B | 75.A | 85.D | 95.C |
| C | 16. D | 26. B | 36.B | 46.A | 56.B | 66.B | 76.C | 86.B | 96.A |
| B | 17. D | 27.D | 37.A | 47.D | 57.A | 67.B | 77.B | 87.A | 97.D |
| A | 18. A | 28. C | 38.C | 48.C | 58.B | 68.C | 78.B | 88.D | 98.B |
| D | 19. B | 29. A | 39.A | 49.B | 59.A | 69.B | 79.D | 89.B | 99.D |
| B | 20. C | 30. C | 40. A | 50.A | 60.D | 70.C | 80.A | 90.C |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
ALSO VISIT :MCQ ON PRODUCTION AND COST
SUPPLY AND ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY MCQ CLASS 12
MCQ ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOR WITH ANSWERS
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND MCQ CLASS 12
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: THEORY OF DEMAND FOR CLASS 11 MCQs
