DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS NEET QUESTIONS
Table of Contents
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
The ancient people use hand-span, foot-span, finger width, palm length, the distance of a step, etc. as units of measurements. These are known as non-standard methods of measurement.
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
Bigger Units:
- For length, the bigger units use are:
(i) Astronomical unit (A.U.): It is the mean distance between Earth and Sun. 1 A.U. = 1.496 ×× 1011 m
(ii) Light year (ly): It is the distance travelled by light in vacuum, in one year. 1 ly = 9.46 ×× 1012 km
(iii) Parsec: 1 Parsec = 3.26 ly
- For mass, the bigger units use are:
(i) quintal: 1 quintal = 100 kg
(ii) metric tonne: 1 metric tonne = 1000 kg = 10 quintal
- For time:
(i) lunar month: 1 lunar month =29.5 days
(ii) Leap year
(iii) Decade
(iv) Century
(v) Millennium
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS NEET QUESTIONS
- Measurement of length
- SI unit is metre (m).
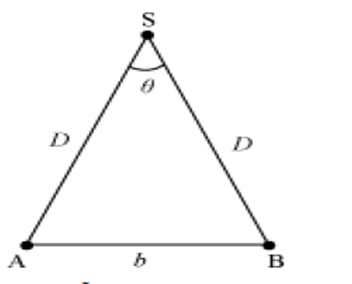
- For measurement of large distances, parallax method is used.
D =
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
- Units for expressing large distances are light year, Astronomical unit (AU), and parsec.
- 1 light year = 9.46 × 1015 m
- 1 AU = 1.5 × 1011 m
- 1 Parsec = 3.26 light years = 3.08 × 1016 m
- Units used to express small distances:
- 1 micron (1 mm) = 10–6 m
- 1 nanometre (1 nm) = 10–9 m
- 1 angstrom (1A0) = 10–10 m
- 1 fermi (1 fm) = 10–15 m
- Measurement of mass
- SI unit of mass − Kilogram
- While dealing with atoms and molecules, we use unified atomic mass unit (u or amu) as standard unit.
1 u = (1/12)th of the mass of C12 atom or, 1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
- Masses of common objects can be measured by balance.
- Large masses can be measured by using gravitational method.
- Masses of sub-atomic particles can be measured by using mass spectrograph.
- Range of variation of mass − from 10−30 kg to 1055 kg
Time measurement
- Time-measuring device – watch or clock
- Motion of hands of clock is periodic.
- Motion of pendulum is periodic and oscillatory (to-and-fro).
- Techniques – Electrical oscillators, electronic oscillators, quartz crystal clocks, atomic clocks.
Time period :- Basic unit It is the time taken by a pendulum to complete one oscillation. It is given as .
of time is second (s).
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
Types of Error :-
- Systematic errors
- Arise due to faulty instruments
- Arise due to imperfect experimental procedure
- Arise due to individual carelessness
- Random errors
- Arise due to random and unpredictable fluctuations in experimental conditions
- Least-count errors
- Associated with the resolution of the instrument
- Personal errors
- Arise due to fault of an observer in taking reading, lack of proper setting of the apparatus etc.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS NEET QUESTIONS
Ways of Expressing an Error
- Absolute error: Magnitude of the difference between the actual value of the quantity and the individual measured value
- Relative error: Ratio of the mean absolute error to the value of the quantity being measured
- Relative error = ΔXX meanΔXX mean
- Percentage error:
Percentage error = ΔXXmean×100ΔXXmean×100
Rules for determining the number of significant figures:
- All non-zero digits are significant.
- All zeroes between two non-zero digits are significant.
Zeroes preceding the first non-zero digits are not significant.
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
Zeroes at the end or right of a number are significant, provided they are on the right side of the decimal point.
If the number is less than 1, then the zero(s) on the right of the decimal point and left of the first non-zero digit are not significant. (For example: In 0.0013, the underlined zeroes are not significant)
Rules for arithmetic operations with significant figures
- For addition and subtraction, the result cannot have more digits to the right of the decimal point than either of the original numbers.
- In multiplication or division, the final result should retain as many significant figures as there are in the measurement with the least significant figures.
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
Rules for rounding off the uncertain digits
- If the rightmost digit to be removed is more than 5, then the preceding number is increased by 1.
- If the rightmost digit to be removed is less than 5, then the preceding number is not changed.
- If the rightmost digit to be removed is 5, then the preceding number is not changed if it is an even number, but it is increased by one if it is an odd number.
Units
- A unit is the chosen standard of measurement of quantity, which has the same nature as the quantity.
Systems of Units
- CGS System: Base units for length, mass and time in this system are centimeter, gram and second respectively.
- FPS System: Base units for length, mass and time in this system are foot, pound and second respectively.
- MKS System: Base units in this system are metre, kilogram and second.
- International System (SI) of Units: Based on seven base units; at present the internationally accepted system.
SI Base Quantities and Units
- Length − metre (m)
- Mass − kilogram (kg)
- Time − second (s)
- Electric current − ampere (A)
- Thermodynamic temperature − kelvin (K)
- Amount of substance − mole (mol)
- Luminous intensity − candela (cd)
Derived units
- These are units of the physical quantities which are derived from the seven basic fundamental units.
DIMENSIONS
The powers to which the fundamental units of mass, length and time are raised so as to get the required physical quantity.
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
EXAMPLE
To get the physical quantity “force”, mass has to be raised to the power 1, length to the power 1 and time to the power -2 So, dimensions of force are 1 in mass, 1 in length and -2 in time.
DIMENSIONAL FORMULA
is the dimensional formula of a physical quantity which has dimensions a, b and c in mass, length and time respectively. So, dimensional formula of force is .
Whenever a physical quantity is written in square brackets, it just means that dimensional formula of the physical quantity has to be taken.
DIMENSIONAL EQUATION
Whenever a physical quantity is equated to its dimensional formula, we get a dimensional equation. So, dimensional equation for force is
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
1. The unit of permittivity of free space, ɛ0, is
(a) coulomb/newton-metre
(b) newton-metre2/coulomb2
(c) coulomb2/newton-metre2
(d) coulomb2/(newton-metre)2
Answer: C
2. The main scale of a vernier callipers has n divisions/cm. n divisions of the vernier scale coincide with (n – 1) divisions of main scale. The least count of the vernier callipers is

Answer: C
3. A student measures the distance traversed in free fall of a body, initially at rest, in a given time. He uses this data to estimate g, the acceleration due to gravity. If the maximum percentage errors in measurement of the distance and the time are e1 and e2 respectively, the percentage error in the estimation of g is
(a) e2 – e1 (b) e1 + 2e2
(c) e1 + e2 (d) e1 – 2e2
Answer: B
4. A certain body weighs 22.42 g and has a measured volume of 4.7cc. The possible error in the measurement of mass and volume are 0.01 g and 0.1 cc. Then maximum error in the density will be
(a) 22% (b) 2%
(c) 0.2% (d) 0.02%
Answer: B
5. If the dimensions of a physical quantity are given by MaLbTc, then the physical quantity will be
(a) velocity if a = 1, b = 0, c = – 1
(b) acceleration if a = 1, b = 1, c = – 2
(c) force if a = 0, b = – 1, c = – 2
(d) pressure if a = 1, b = –1, c = –2
Answer: D
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT NEET QUESTIONS
6. Which of the following dimensions will be the same as that of time?
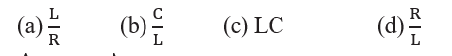
Answer: A
7. According to Newton, the viscous force acting between liquid layers of area A and velocity gradient ∆v/∆z is given by F=A , where ƞ is constant called coefficient of viscosity. The dimensional formula of ƞ is
(a) [ML–2T–2] (b) [M0L0T0]
(c) [ML2T–2] (d) [ML–1T–1]
Answer: D
8. The velocity v of a particle at time t is given by v = at , where a, b and c are constants. The dimensions of a, b and c are
(a) [L], [LT], and [LT-2]
(b) [LT-2], [L], and [T]
(c) [L2], [T], and [LT-2]
(b) [LT-2], [LT], and [L]
Answer: B
9. Turpentine oil is flowing through a tube of length l and radius r. The pressure difference between the two ends of the tube is P. The viscosity of oil is given by ƞ= where v is the velocity of oil at a distance x from the axis of the tube. The dimensions of ƞ are
(a) [M0L0T0] (b) [MLT-1]
(c) [ML2T–2] (d) [ML–1T–1]
Answer: D
10. The frequency of vibration f of a mass m suspended from a spring of spring constant k is given by a relation f = amxky, where a is a dimensionless constant. The values of x and y are

Answer: D
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS NEET QUESTIONS