Table of Contents
Archimedes Principle Class 9
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE CLASS 9
This topic covers the objective type questions for Archimedes principle.
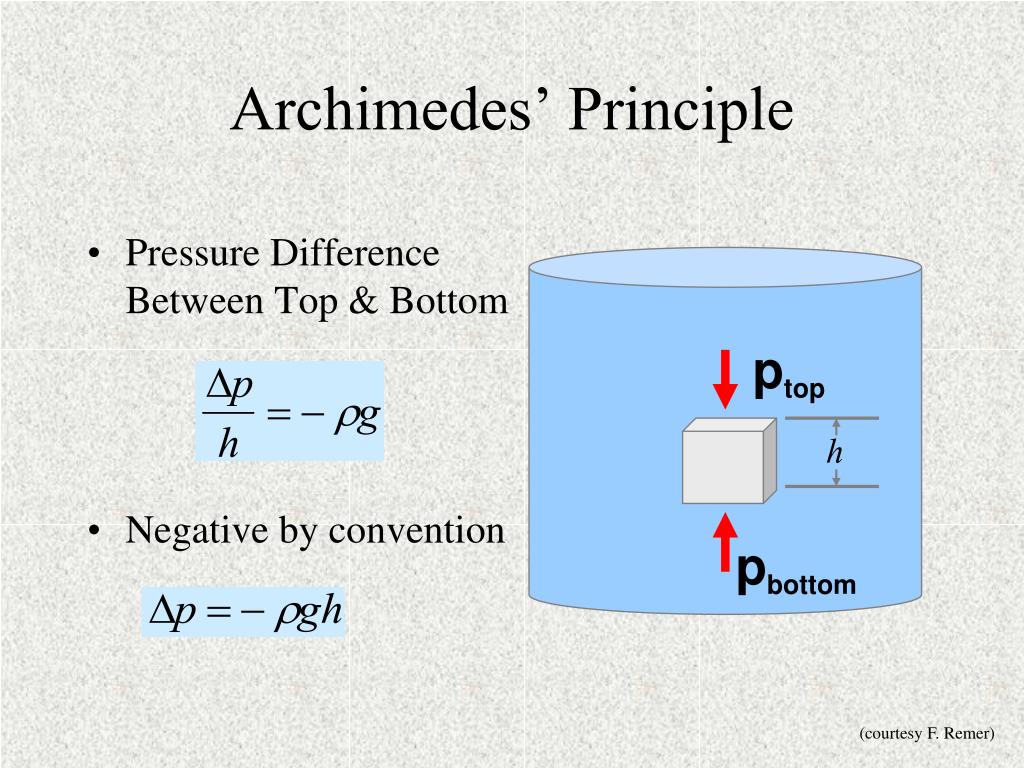
A body at rest in a fluid is acted upon by a force pushing upward called the buoyant force, which is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. If the body is completely submerged, the volume of fluid displaced is equal to the volume of the body. If the body is only partially submerged, the volume of the fluid displaced is equal to the volume of the part of the body that is submerged.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE CLASS 9
Archimedes Principle Class 9
1. Impulse is
(a) a scalar quantity
(b) a vector quantity
(c) neither a scalar nor a vector
(d) sometimes a scalar and sometimes a vector
2. Choose the wrong statement.
(a) 1 kg wt = 9.8 N
(b) Momentum is a vector quantity
(c) Force is always conserved
(d) Momentum is conserved in the absence of an external force
3. A long-jumper runs before jumping because
(a) he covers a greater distance
(b) he maintains momentum conservation
(c) he gains energy by running
(d) he gains momentum
4. If a rock is brought from the surface of the moon
(a) its mass will change
(b) its weight will change, but not mass
(c) both mass and weight will change
(d) its mass and weight will remain the same
5. The force acting on a mass of 1 g due to the gravitational pull on the earth is called 1 gwt. One gwt equals
(a) 1N
(b) 9.8 N
(c) 980 dyne
(d) none of these
6. The weight of a body would not be zero
(a) at the centre of the earth
(b) during a free fall
(c) in interplanetary space
(d) on a frictionless surface
7. An iron ball and a wooden ball of the same radius are released from a height H in vacuum. The times taken by both of them to reach the ground are
(a) roughly equal
(b) unequal
(c) exactly equal
(d) in the inverse ratio of their diameters
8. A man is standing on a boat in still water. If he walks towards the shore the boat will
(a) move away from the shore
(b) remain stationary
(c) move towards the shore
(d) sink
9. A driver accelerates his car first at the rate of 1.8 m/s2 and then at the rate of 1.2 m/s2 ratio of the forces exerted by the engines will The be respectively equal to
(a) 2 : 3 (b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 1 (d) 3 : 2
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE CLASS 9
10. A body of mass 5 kg undergoes a change in speed from 30 to 40 m/s. Its momentum would change in increase by
(a) 50 kg m/s (b) 75 kg m/s
(c) 150 kg m/s (d) 350 kg m/s
11. The force needed to produce an a acceleration of 6 m/s2 in a ball of mass 4 kg will be
(a) 24 N (b) 30 N
(c) 32 N (d) 36 N
12. A body of mass 5 kg undergoes a change in speed from 20 to 0.20 m/s. The momentum of the body would
(a) increase by 99 kg m/s (b) decrease by 99 kg m/s
(c) increase by 101 kg m/s (d) decrease by 101 kg m/s
13. A bullet of mass 0.01 kg is fired from a gun weighing 5.0 kg. If the initial speed of the bullet is 250 m/s, calculate the speed with which the gun recoils.
(a) – 0.50 m/s (b) – 0.25 m/s
(c) + 0.05 m/s (d) + 0.25 m/s
14. A body of mass 100 g is moving with a velocity of 15 m/s. The momentum associated with the ball will be
(a) 0.5 kg m/s (b) 1.5 kg m/s
(c) 2.5 kg m/s (d) 3.2 N s
15. In the above problem, if we increase the pull at P gradually, the string will break
(a) below the stone (b) at the point P itself
(c) above the stone (d) nothing can be decided
16. The above problem can be explained on the basis of the property of
(a) inertia (b) force
(c) momentum (d) torque
17. The combined effect of mass and velocity is taken into account by a physical quantity called
(a) torque (b) moment of force
(c) momentum (d) moment of momentum
18. Momentum is a measure of
(a) weight (b) mass
(c) quantity of motion (d) velocity
19. Momentum has the same units as that of
(a) impulse (b) torque
(c) moment of momentum (d) couple
Answer key: Archimedes Principle Class 9
1. (b) 2. (c) 3. (d) 4. (b) 5. (a)
6. (c) 7. (a) 8. (c) 9. (a) 10. (d)
11. (a) 12. (a) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (b)
16. (c) 17. (a) 18. (c) 19. (c)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE CLASS 9
Also Visit: Electrical Charges
