DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
POINTS TO REMEMBER
•In 1808, John Dalton suggested that atom is the smallest indivisible particle of matter.
•Sir J.J. Thomson proved that atom is not the smallest particle but is made up of still smaller particles called sub-atomic particles i.e. , electrons, protons and neutrons.
•J.J. Thomson in 1897 found that cathode rays are emitted from the cathode and negative charge. The constituent particles of the cathode rays are electrons.
•Charge on the electron = -1.6 * 10-19 C also called one unit negative charge
Mass of electron = 9.11*10-31 kg which is nearly (1/1840)th
•An electron is the sub-atomic or fundamental particle which carries one unit negative charge and has mass nearly (1/1837)th of that of hydrogen atom.
•Goldstein in 1886 discovered another set of rays having positively charged particles and the rays were named as anode rays or canal rays or positive rays.
•Proton is a sub-atomic or fundamental particle which carries one unit positive charge and has mass nearly equal to that of hydrogen atom.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
•In 1904, J.J. Thomson proposed the Plum-Pudding model according to which an atom is a positively charged sphere in which electrons are embedded which neutralize the positive charge, so that atom as a whole is electrically neutral.
•In 1911, Rutherford performed an experiment on scattering of alpha particles.
•Based on the scattering experiments, Rutherford put forward atomic model of atom, according to this model, an atom consists of a small heavy positively charged nucleus in the centre and electrons revolve around it in circular orbits as the planets revolve around the sun. Therefore, these electrons are also referred to as planetary electrons.
•The drawback of Rutherford’s model, the revolving electron will lose energy continuously. Its orbit will become smaller and smaller and ultimately, the electron should fall into the nucleus i.e. , atom will not be stable.
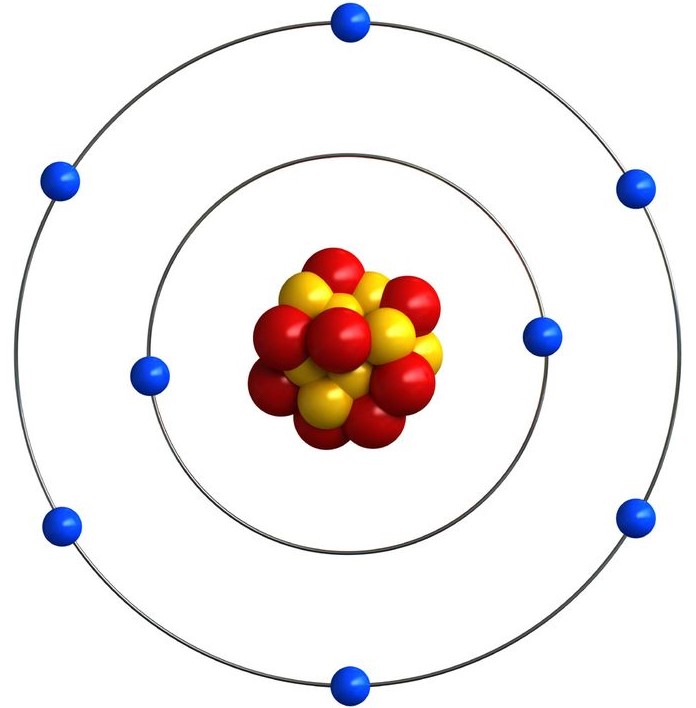
•In 1913, Neils Bohr put forward his theory regarding the structure of an atom. He proposed that an atom consists of a heavy positively charge body called the nucleus in the centre and the electrons revolve in certain discrete orbits having fixed energies called stationary. These orbits are also called energy levels.
•In 1932, James Chadwick discovered the neutron.
• A neutron is a sub-atomic or fundamental particle which is neutral but has mass nearly equal to that of proton.
•Nucleus contains the protons and neutrons (collectively called the nucleons) and the electrons are present in the extranuclear region.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
•No. of protons = No. of electrons, in atom, therefore, an atom is electrically neutral.
•Atomic number (Z) is equal to the number of protons present in the nucleus. For a neutral atom, it is also equal to the number of electrons present in the extranuclear part.
Atomic no. (Z) = No. of protons = No of electrons
•Mass number (A) is equal to the sum of protons and neutrons
Mass no. (A) = No of protons + No. of neutrons
•No. of neutrons = Mass no. (A) – Atomic No. (Z)
•Distribution of electrons (Electronic configuration) – Bohr – Bury scheme:
(i) Maximum no. of electrons in nth shell = 2n2.
(ii) Outermost shell cannot have more than 8 electrons even if the first rule is violated.
(iii) The penultimate shell cannot have more than 18 electrons. Infact, when 3rd shell (M-shell) has got 8 electrons, filling of 4th shell (N-shell) starts. When the 4th shell (N-shell) has got 2 electrons, filling again starts in the 3rd shell (M-shell) till it has got 18electrons.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
•Valence electrons and valence shell: The electrons present in the outermost shell of the atom of an element are called valence electrons. The outermost shell is called the valence shell.
•Valency: The number of electrons lost, gained or shared by an atom of an element so as to complete its octet is called its valency. It is equal to the number of valence electrons or 8 – No. of valence electrons.
•Formation of ions: Ions are formed from an atom by loss or gain of electrons so as to complete their octet. Cations (or positive ions) are formed by the loss of electrons while anions (or negative ions) are formed by gain of electrons.
•Protons and electrons are equal only in a neutral atom. In cation (positively charged), electrons are less than the protons while in anion (negatively charged), these are more than the protons.
•Isotopes are the atoms of the same element with same atomic number but different mass numbers. They contain the same number of protons and the same number of electrons but have different number neutrons.
•Isobars are atoms of different elements having different atomic number but same mass number. They contain different number of protons, electrons and neutrons.
•Fractional atomic masses: atomic masses of most of the elements are fractional because they are the average values of the atomic masses of different isotopes.
•Radio-isotopes are isotopes having unstable nuclei and hence, alpha beta and gamma-rays.
•Application of radio-isotopes:
(i) As nuclear fuel e.g. , U-235
(ii) In medical field e.g. , Co-60 for the treatment of cancer, P-32 for leukaemia, I-131 for thyroid diseases, etc.
(iii) In carbon dating, C-14 is used to find the age of fossils.
(iv) In uranium dating, the age of rock on the earth is found.
(v) In industry e.g. , in detecting the leakage in the underground oil pipes, gas pipes, etc.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
Table of Contents
STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
1.If Z = 3, what would be the valency of the element?
a)1
b)2
c)3
d)4
Ans.1
2.J.J Thomson proposed that the nucleus of an atom contain only nucleons.
a)True
b)False
c)Partial true
d)Partial false
Ans. False
3.A neutron is formed by an electron and a proton combining together. Therefore, it is neutral.
a)False
b)True
c)Partial false
d)Partial true
Ans. False
4.The mass of an electron is about 1 / 2000 times that of proton
a)False
b)True
c)Partial true
d)Partial false
Ans. True
5.Isotope of iodine is used for making tincture iodine, which is used as a medicine.
a)False
b)True
c)Partial true
d)Partial false
Ans. False
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
6.How will find the valency of chlorine?
a)1
b)3
c)4
d)6
Ans.1
7.How will find the valency of sulphur?
a)2
b)4
c)3
d)8
Ans. 2
8.How will fund the valency of magnesium?
a)4
b)2
c)3
d)1
Ans.2
9.Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment was responsible for the discovery of:
a)Atomic nucleus
b)Electron
c)Proton
d)Neutron
Ans. Atomic nucleus
10.Isotopes of an element have:
a)The same physical properties
b)Different chemical properties
c)Different number of neutrons
d)Different atomic numbers
Ans.Different number of neutrons
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
11.Number of valence electrons in Cl- ion are:
a)16
b)8
c)17
d)18
Ans. 8
12.Which one of the following is a correct electronic configuration of sodium?
a)2, 8
b)8, 2, 1
c)2, 1, 8
d)2, 8, 1
Ans. 2, 8, 1
13.Which of the following correctly represents the electronic distribution in the Mg atom?
a)3, 8, 1
b)2, 8, 2
c)1, 8, 3
d)8, 2, 2
Ans. 2, 8, 2
14.Rutherford’s alpha particles scattering experiment resulted into discovery of:
a)Electron
b)Proton
c)Nucleus in the atom
d)Atomic mass
Ans.Nucleus in the atom
15.Dalton’s atomic theory successfully explained:
Law of conservation of mass
Law of constant composition
Law of radioactivity
Law of multiple proportions
a)(i), (ii), and (iii)
b)(i), (iii) and (iv)
c)(ii), (iii) and ( iv)
d)(i), (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (i), (ii) and (iv)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
16.Which of the following statement/s about Rutherford’s model of atom are correct?
Considered the nucleus as positively charged
Established that the alpha particles are four times as heavy as a hydrogen atom.
Can be compared to solar system
Was in agreement with Thomson’s model.
a.(i) and (iii)
b.(ii) and (iii)
c.(i) and (iv)
d.Only (i)
Ans. (i) and (iii)
17.Which of the following are true for an element?
Atomic number = number of protons + number of electrons
Mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons
Atomic mass = number of protons = number of neutrons
Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons
a)(i)and (ii)
b)(ii)and (iii)
c)(ii)and (iii)
d)(ii) and (iv)
Ans.(ii) and (iv)
18.Rutherford’s alpha particle scattering experiment showed that:
Electrons have negative charge.
The mass and positive charge of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Neutron exists in the nucleus.
Most of the space in atom is empty
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)(i) and (iii)
b)(ii) and (iii)
c)(iii) and (iv)
d)(ii) and (iv)
Ans. (ii) and (iii)
19.The ion of an element has 3 positive charges, mass number of atom is 27 and the number of neutrons is 14. What is the number of electron in the ion?
a)13
b)10
c)14
d)16
Ans. 10
20.In a sample of ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H5), the two oxygen atoms have the same number of electrons but different number of neutrons. Which of the following is the correct reason for it?
a)One of the oxygen atoms has gained electrons.
b)One of the oxygen atoms has gained two neutrons.
c)The two oxygen atoms are isotopes.
d)The two oxygen atoms are isobars.
Ans.The two oxygen atoms are isobars
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: STRUCTURE OF ATOM CLASS 9 MCQ
