DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
KEY POINTS TO REMEMBER
Three Different Methods of Measuring National Income
(i) Product Method (or Value Added Method)
(ii) Income Method,
(iii) Expenditure Method Product Method (or Value Added Method) is that method which measures the gross value added (or gross domestic product) at market price as the sum total of value added by all the producing units within the domestic territory of the country, during the period of an accounting year It is adjusted to find national income

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Precaution: Add only the market value of final goods and services, do not include market value of intermediate goods and services.
Or
Avoid double counting.
Double Counting and Avoiding it: Double counting occurs if output of all the producers is added up without considering the fact that output of one producer may have been used as an input by the other. It can be best avoided by adding up value added, rather than output of different firms.
Value Added = Value of output-Intermediate consumption (referring to expenditure on intermediate goods and services) Income Method is that method which measures domestic income as the sum total of factor incomes (rent + interest+ profit+ wages) generated within the domestic territory of a country during the period of an accounting year. Net factor income from abroad is added to domestic income to find national income
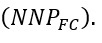
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Precaution: Add only the market value of final goods and services, do not include market value of intermediate goods and services.
Or
Avoid double counting.
Double Counting and Avoiding it: Double counting occurs if output of all the producers is added up without considering the fact that output of one producer may have been used as an input by the other. It can be best avoided by adding up value added, rather than output of different firms.
Value Added = Value of output-Intermediate consumption (referring to expenditure on intermediate goods and services) Income Method is that method which measures domestic income as the sum total of factor incomes (rent + interest + profit+ wages) generated within the domestic territory of a country during the period of an accounting year. Net factor income from abroad is added to domestic income to find national income
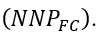
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Precaution: Add only factor incomes, do not include transfer payments Also, do not include income generated through illegal activities (like, gambling). Expenditure Method is that method which measures the gross domestic product at market price as the sum total of the expenditure (consumption expenditure and investment expenditure) on the purchase of final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of the economy during the period of an accounting year it is adjusted to find national income

Precaution: Consider only the expenditure on final goods that causes: (i) final consumption, or (ii) capital formation (also called investment); do not include expenditure on intermediate goods and services. Also, do not consider expenditure on second-hand goods or on shares and bonds.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Table of Contents
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Choose the correct option:
1. Household inventory is
(a) not included in national income
(b) a stock concept
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
2. Remittances from a relative working abroad are
(a) included in national income
(b) not included in national income
(c) transfer payments
(d) both (b) and (c)
3. Own account production of goods is included in national income because:
(a) goods are tangible
(b) their valuation is possible
(c) goods are more productive than services
(d) none of these
4. Value added refers to:
(a) production of durable goods
(b) output-intermediate consumption
(c) production of non-durable goods
(d) expenditure on intermediate goods
5. Gross domestic capital formation is the sum total of
(a) expenditure on fixed assets
(b) gross domestic fixed capital formation and change in stock
(c) net domestic fixed capital formation+ inventory investment + depreciation
(d) both (b) and (c)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
6. Value added method measures the contribution of which of the following within the domestic territory of a country?
(a) Household consumers
(b) The producing enterprises owned by residents of the country
(c) The producing enterprises owned by the non-residents of the country
(d) Both (b) and (c)
7. Which of the following items is not included while estimating national income by income method?
(a) Rent
(b) Mixed income
(c) Foxed investment
(d) Undistributed profits
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
8. Which of the following is not an element of final consumption expenditure?
(a) Household expenditure on food
(b) Government final consumption expenditure
(c) Household expenditure on education
(d) Expenditure on raw material
9. As a result of double counting, national income is:
(a) over-estimated
(b) underestimated
(c) correctly estimated
(d) not estimated for the entire year of accounting
10. Which of the following is not included in national income?
(a) Receipt of a gift cheque sent by your parents settled abroad.
(b) Repatriation of wages earned by the NRls to their parents in India
(c) Excise duty on domestic production
(d) All of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
11. Which of the following is not a transfer payment?
(a) interest on national debt
(b) Retirement pensions
(c) Old age pensions
(d) Donations
12. Which of the following items is not included while estimating GNP of a country at market price?
(a) Sales of the enterprises
(b) indirect taxes
(c) Remittances by R
(d) Subsidy
13. Own account production of services is not included in national income because
(a) services are different from goods
(b) services are not productive
(c) it is difficult to measure market value of such services
(d) none of these
14. Difference between closing stock and opening stock during an accounting year is known as
(a) increase in stock
(b) change in stock
(c) it decrease in stock
(d) none of these
15. Compensation of employees includes:
(a) wages and salaries in cash
(b) wages and salaries in kind
(c) pension on retirement
(d) all of these
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
16. Operating surplus =
(a) Rent+ Profit interest
(b) Rent + interest Compensation of employees
(c)
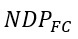
– Compensation of employees – Mixed income of self-employed
(d) both (a) and (c)
17. Which of the following is not included in inventory investment?
(a) Change in stock of finished goods
(b) Change in stock of semi-finished goods
(c) Change in stock of raw material
(d) Change in sales during the year
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
18. Which of the following is not a part of final expenditure?
(a) Consumer goods purchased by the government
(b) Consumer goods exported to rest of the world
(c) Seeds purchased by the farmers
(d) Government fixed investment expenditure
19. Problem of double counting can be avoided by using
(a) final output method
(b) value added method
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) neither (a) nor (b)
20. Which of the following is irrelevant in the estimation of companion of employees ?
(a) Free accommodation provided to the school principals
(b) Free education of the students whose parents are working in schools
(c) Wages and salaries in cash
(d) Old age pensions
Answers
| 1. (c) | 11. (b) |
| 2. (d) | 12. (c) |
| 3. (b) | 13. (c) |
| 4. (b) | 14. (b) |
| 5. (d) | 15. (d) |
| 6. (d) | 16. (d) |
| 7. (c) | 17. (d) |
| 8. (d) | 18. (c) |
| 9. (a) | 19. (c) |
| 10. (d) | 20. (d) |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
D. Matching the Correct Statements
I. From the set of statements given in Column I and Column Ii, choose the correct pair of statements:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Imputed rent of owner occupied houses | (i) Included in the estimation of national income |
| (b) Net exports | (ii) Difference between imports and exports during an accounting year |
| (c) Pension on retirement | (iii) Old age pension |
| (d) Expenditure on second-hand goods | (iv) Included in the estimation of national income |
| (e) Gifts from abroad | (v) Factor payments |
Answer :-
| (a) Imputed rent of owner occupied houses | (i) Included in the estimation of national income |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
II. Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with respective items in Column I:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Old age pensions | (i) A component of corporate profit |
| (b) Value of non factor inputs | (ii) Closing Stock-Opening Stock |
| (c) Corporate tax | (iii) Factor Payment Method |
| (d) Change in stock | (iv) Unilateral Payments |
| (e) Income method | (v) Intermediate consumption |
Answer :- (a) – (iv)
(b) – (v)
(c) – (i)
(d) – (ii)
(e) – (iii)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
E. Very Short Answer Objective Type Questions
1. Name the methods for measuring national income
Ans. (i) Product method or value added method, (ii) Income method, and (iii) Expenditure method.
2. What is meant by value added method?
Ans. Value added method is that method which measures GDP as the sum total of value addition by all producing units within the domestic territory of a country.
3. What do you mean by the error of double counting?
Ans. Error of double counting occurs when the value of some goods produced in the economy is counted more than once in the estimation of national income. Example: Entire value of wheat sold by the farmers is considered along with the value of wheat purchased by the miller who uses wheat as an input for producing wheat flour.
4. What is meant by income method?
Ans. Income method is that method which measures national income as the sum total of factor incomes (compensation of employees, rent, interest and profit) earned by normal residents of a country during an accounting year.
5. What is meant by expenditure method?
Ans. Expenditure method is that method which measures national income in terms of the expenditure (consumption expenditure investment expenditure) on the purchase of final goods and services produced in the economy during the period of an accounting year.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
6. How is expenditure on final goods and services produced within the domestic territory identical with
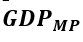
?
Ans. Expenditure on final goods and services produced within the domestic territory is identical with

because goods and services are purchased at the market price, and

refers to the market price of goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
7. Why should the producers maintain inventory stocks?
Ans. Inventory stocks of finished goods are maintained to cope with demand for these goods in the near future Inventory stocks of raw material are maintained to avoid all time dependence on the market which is full of uncertainties.
8. Why are exports included in the estimation of domestic income?
Ans. Exports are included in the estimation of domestic income because exports are a part of domestically, produced goods and services, or because exports are a part of goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country.
9. Why are imports considered as a negative item in the estimation of domestic income?
Ans. Imports are considered as a negative item in the estimation of domestic income because imports are not an expenditure on the domestically produced goods and services in an accounting year. It is an expenditure on the goods produced abroad.
10. How is net export different from net factor income from abroad?
Ans. Net export refers to the difference between exports and imports during an accounting year.
Net Exports = Exports – imports
Net factor income from abroad refers to :
Factor income earned by our residents from rest of the world
-Factor income earned by non-residents from the domestic territory of our country.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
2. Reason-based Questions (Comprehension of the Subject-matter)
Read the following statements carefully. Write True or False with a reason.
1. Value addition occurs even when goods do not undergo any material transformation
Ans. True Value addition occurs even when goods are purchased for resale, without any material transformation.
2. Export of goods is not a part of expenditure on the domestic production.
Ans. False Export of goods is a part of the expenditure on the domestic production because it is the foreign demand for domestic product
3. Change in stock’ is not a stock variable.
Ans. True. Change in stock is measured per unit of time period. Accordingly, it is a flow variable
4. Change in stock is not a component of aggregate expenditure in the economy.
Ans. False Change in stock as a part of investment expenditure is a component of aggregate expenditure in the economy.
5. Money spent by the NRIs settled abroad on the on-line purchase of domestic products is a transfer
Ans. False Any on-line purchase of domestic products by the people settled abroad is to be treated as exports.
6. Undistributed profits are not a part of domestic factor income.
Ans. False Undistributed profits are retained earnings of the firms. These are a part of domestic factor income.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
7. GDP is estimated only in the context of a closed economy
Ans. False GDP is estimated in the context of an open economy as well Exports-Imports are a part of GDP, and are related to an open economy.
8. Remittances by the NRIs are a part of our national income.
Ans. False Remittances by the NRIs are transfer payments.
9. Mixed income of self-employed includes transfer payments.
Ans. False Mixed income of the self-employed includes only factor incomes payment.
10. Compensation of employees includes compensation received after retirement.
Ans. True. Compensation of employees = Wages and salaries in cash+ Payment in kind + Employer’s contribution to social security schemes + Pension on retirement.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
11. Capital formation includes capital goods only.
Ans. False. Change in the inventory stock is an important component of capital stock. And inventory stock includes both capital goods as well as consumer goods.
12. Purchase of machinery from abroad is never considered as intermediate consumption.
Ans. False. Purchase of machinery from abroad is considered as intermediate consumption when it is purchased for purpose of resale.
13. Purchase of machinery from abroad is a part of domestic capital formation.
Ans. True. Purchase of machinery from abroad is a part of domestic capital formation. Because, it adds to the existing stock of capital in the domestic economy.
14. Salaries to Indian employees working in Indian embassies abroad are a part of net factor income from abroad.
Ans. False. Indian embassies abroad are a part of domestic territory of India. Therefore, salaries to Indian employees working in Indian embassies abroad are a part of domestic factor income.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
15. Profits earned by non-resident companies in India are not a part of our domestic income.
Ans. False. It is a part of domestic factor income of India because non-resident companies are within the domestic territory of India.
16. The market value of both final and intermediate goods is included in the estimation of national income.
Ans. False. Only the value of final goods is included in the estimation of national income Reason: The value of intermediate goods is reflected in the value of final goods.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
17. Expenditure on the purchase of second-hand plant and machinery from rest of the world is a part of domestic capital formation.
Ans. True. Expenditure on the purchase of second-hand plant and machinery from rest of the world is a part of domestic capital formation. Because, it adds to the stock of capital in the domestic economy.
18. Expenditure by the households on the construction of residential buildings should not be treated as investment expenditure.
Ans. False. Expenditure on the construction of residential buildings by the households is a part of investment expenditure. Because, residential buildings are income generating fixed assets.
19. Imputed rent on owner occupied houses does not involve any payment to othe₹ Accordingly, it should not be included in the estimation of national income.
Ans. False. Imputed rent is included in the estimation of national income as a component of rent. Houses are income generating assets, no matter who occupies them.
20. Goods produced but retained for self-use (and not sold in the market) are not included in the estimation of national income.
Ans. False. Goods produced and retained for self-use are included in the estimation of national income. Because these goods involve value-addition.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
21. Free dress provided to nurses by the hospital is included in the estimation of national income.
Ans. False. Free dress provided to nurses by the hospital is not included in the estimation of national income if the dresses a uniform provident by the hospital at the time of work. It is to be treated as an intermediate consumption.
22. Investment on the purchase of shares is a part of net capital formation.
Ans. False, Net capital formation wants to increase in the stock of capital whereas shares only lead to the transfer of ownership.
23. In the estimation of GDP (using expenditure method), we focus only an expenditure by the residents of a country.
Ans. False, In the estimation of GDP, we include all expenditure on the domestically produced goods both by the residents as well as non-residents of a country
24. Income from exports is a part of net factor income from abroad.
Ans. False, income from exports is a part of it exports and therefore a component of gross domestic product.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Q. How do you distinguish between old-age pensions and retirement pensions in the context of estimation of national income?
Ans. Old-age pensions are unilateral payments or transfer payments. These are not included in the estimation of national income. On the other hand, retirement pensions are like a deferred wage. These are related to factor services rendered by the recipients prior to their retirement. Accordingly, these are included in the estimation of national income.
Q. Operating surplus does not arise in (i) subsistence sector, and (ii) general government sector of the economy. Why?
Ans. Operating surplus does not arise in the subsistence sector and in the general government sector because of the following reasons:
(i) in the subsistence sector, production is meant only for subsistence of the producing families. Production is not meant for sale in the market. There is no marketable surplus. Accordingly, there is no operating surplus.
(ii) In the general government sector production is meant only for collective consumption (or consumption by the general public). Goods and services are produced not for sale in the market, but for general welfare of the people. Example: Services of law & order and defence are available to the people free of charge. Accordingly, there is no operating surplus in the general government’ sector.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Q. What causes increase in inventory stock?
Ans. Increase in inventory stock is caused by two factors:
(i) Unexpected Fall in Demand in the Current Year: Example: Producers may have expected demand to the tune of 50, 000 umbrellas but, owing to the failure of monsoon, only 10, 000 umbrellas are sold during an year. Accordingly, 40,000 umbrellas are added to the existing stock.
(ii) Expected Rise in Demand in the Near Future: Producers may expect a spurt (rise) in demand (and therefore, increase in price) in the near future. Accordingly, they pile up stocks during the current year.
Q. Export receipts are not a part of net factor income from abroad. Why?
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Ans. This is because of two reasons
(i) Exports refer to the purchase of domestically produced goods by the rest of the world. Goods produced within the domestic territory of a country are to be treated as a part of GDP.
(ii) Export receipts refer to revenue of the firms from the sale of its output. These are not the receipts of factor incomes from abroad which are available in the form of rent, interest, profit and wages
2. Exports are just sales yielding revenue, not income. Comment.
Ans. It is true that exports are just sales and yield revenue, not income. Exports are just sales because these are purchases of rest of the world from the domestic economy. Accordingly, exports yield revenue (receipts from sales). These do not yield income. Because, income is in the form of rent, these are purchases of rest of the world from the domestic economy. Accordingly, exports yield (Note: It is out of revenue that a firm distributes incomes to the owners of factors of production. interest, profit or wages Exports do not yield any of these directly
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
3. HOTS & Applications
1. Is net factor income from abroad zero in case exports imports?
Ans. No. Net factor income from abroad is the difference between the factor income earned by normal residents of a country from abroad and the factor income earned by non-residents in our country it has nothing to do with exports and imports.
2. Is brokerage paid to Real Estate Agents on the sale and purchase of only new (and not the old) houses included in the estimation of national income?
Ans. No Brokerage aid to Real Estate Agents in the sale and purchase of new as well as old houses is included in the estimation of national income. Reason Brokerage relates to payment for services, no matter on now or old houses.
3. Show how the sum of value added is equal to sum of factor incomes.
Ans. All value added is distributed as factor incomes. Therefore, sum total of value added is bound to be equal to sum total of factor incomes.
4. Do you think income in the form of capital gains is a part of capital formation?
Ans. come in the form of capital gains means income accruing to the individuals on account of increase as prices of land, shares, bonds etc. They do not add to the stock of physical capital Hence, taking income in the form of capital gains as capital formation is wrong.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
5. National income exceeds domestic income only when exports are greater than imports. Comment.
Ans. The given statement is incorrect. When factor income from abroad is greater than factor income to abroad national income exceeds domes income Exports/ports have nothing to do with net factor income from abroad.
6. Only those goods are included in the estimation of domestic product which are sold or purchased in domestic market of a country Defend or refute.
Ans. The above statement is incorrect Exports are also a part of domestic product. Exports include goods produced in the domestic economy and sold in rest of the world.
7. How are dividends, corporate taxes and undistributed profits treated in national income?
Ans. (i) Dividends: These are included in the estimation of national income as these are a part of factor payments.
(ii) Corporate Taxes: These are not included, as all taxes are transfer payments.
(iii) Undistributed Profits: These are retained earnings of the firms and are a part of factor payments. Therefore, these are included in the estimation of national income.
8. Giving reason, explain the treatment assigned to the following while estimating national income :
(i) Expenditure on maintenance of an office building.
(ii) Expenditure on adding a floor to the office building.
Ans. (i) Expenditure on maintenance of an office building is not included in national income, as it is a part of intermediate consumption.
(ii) Expenditure on adding a floor to the office building is included in national income because it is a part of investment expenditure or capital formation.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
9. Calculate Operating Surplus from the following data:
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Compensation of employees | 300 | |
| (ii) Indirect taxes | 200 | |
| (iii) Consumption of fixed capital | 100 | |
| (iv) Subsidies | 50 | |
| (v) Gross domestic product at market price | 600 |
Ans. Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost
= Gross domestic product at market price – Consumption of the capital – indirect taxes + Subsidies
= ₹ 600 crore – ₹ 100 crore – ₹ 200 crore + ₹ 50 crore
= ₹ 350 crore
Operating Surplus
= Net domestic product at factor cost – Compensation of employees
= ₹ 350 crore – ₹ 300 crore
= ₹ 50 crore
Operating Surplus = ₹ 50 crore
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
10. From the following data relating to a firm, calculate its Net Value Added at Factor Cost :
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Subsidy | 40 | |
| (ii) Sales | 800 | |
| (iii) Depreciation | 30 | |
| (iv) Exports | 100 | |
| (v) Closing stock | 20 | |
| (vi) Opening stock | 50 | |
| (vii) Intermediate purchases | 500 | |
| (viii) Purchase of machinery for own use | 200 | |
| (ix) Import of raw material | 60 |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Ans. Gross Value Added at Market Price
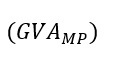
= Sales + Change in stock (Closing stock – Opening stock) – Intermediate consumption
= ₹ 800 lakh – (₹ 20 lakh – ₹ 50 lakh – ₹ 500 lakh
= ₹ 800 lakh – ₹ 30 lakh – ₹ 500 lakh
= ₹ 270 lakh
Net Value Added at Factor Cost
=

– Depreciation + Subsidy
= ₹ 270 lakh – ₹ 30 lakh + ₹ 40 lakh
= ₹ 280 lakh
Net value added at factor cost = ₹ 280 lakh.
(Note: Exports are treated as part of total sales.]
11. Calculate Gross Fixed Capital Formation from the following data
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Private final consumption expenditure | 1000 | |
| (ii) Government final consumption expenditure | 500 | |
| (iii) Net exports | (-)50 | |
| (v) Net factor income from abroad | 20 | |
| (v) Gross domestic product at market price | 2,500 | |
| (vi) Opening stock | 300 | |
| (vii) Closing stock | 200 |
Ans. Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Gross domestic product at market price – Private final consumption expenditure – Government final consumption expenditure – Net exports – Change in stock (Closing stock – Opening stock)
= ₹2,500 crore – ₹ 1,000 crore – ₹500 crore – (-)₹ 50 crore – (₹ 200 crore – ₹ 300 crore)
= ₹2,500 crore – ₹ 1,000 crore – ₹500 crore + ₹ 50 crore + 100 crore
= ₹ 1,150 crore
Gross fixed capital formation – ₹ 1,150 crore
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
12. Calculate Net Value Added at Factor Cost from the following data
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Purchase of machinery to be used in the production unit | 100 | |
| (ii) Sales | 200 | |
| (iii) Intermediate costs | 90 | |
| (iv) Indirect taxes | 12 | |
| (v) Change in stock | 10 | |
| (vi) Excise duty | 6 | |
| (vii) Stuck of raw material | 5 |
Ans. Gross Value Added at Market Price
= Sales + Change in stock – Intermediate costs
= ₹ 200 crore + ₹ 10 crore – ₹90 crore
= ₹120 crore
Net Value Added at Factor Cost
= Gross value added at market price – Indirect tax
= ₹120 crore – ₹12 crore
= ₹108 crore
Net value added at factor cost = ₹108 crore
[Note: Indirect taxes include excise duty].
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
13. From the following data calculate Gross National Product at Factor Cost by (a) Income Method, and (b) expenditure method:
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Net domestic capital formation | 500 | |
| (ii) Compensation of employees | 1.850 | |
| (iii) Consumption of fixed capital | 100 | |
| (iv) Government final consumption expenditure | 1,100 | |
| (v) Private final consumption expenditure | 2,600 | |
| (vi) Rent | 400 | |
| (vii) Dividend | 200 | |
| (viii) Interest | 500 | |
| (ix) Net exports | (-) 100 | |
| (x) Profit | 1,100 | |
| (xi) Net factor income from abroad | (-) 50 | |
| (xii) Net indirect taxes | 250 |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
Ans. (a) Income Method
Gross National Product at Factor Cost
Compensation of employees + Operating surplus (Rent + Interest + Profit) Consumption of fixed capital + Net factor come from abroad
= ₹ 1,850 crore + (₹400 crore + ₹ 500 crore + ₹ 1,100 crore) + ₹100 crore + (-)₹ 50 crore
= ₹1,850 crore + ₹ 2, 000 crore + ₹ 100 crore – ₹ 50 crore
= ₹ 3, 900 crore
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
(b) Expenditure Method
= Private final consumption expenditure Government final consumption expenditure + Gross domestic capital formation + Net exports – Net indirect taxes + Net factor income from
abroad
= ₹2,600 crore + ₹ 1,100 crore + (₹ 500 crore + ₹ 100 crore) + (-)₹ 100 – ₹ 250 crore + (-)₹ 50 crore
+1-17 50 core
= ₹2,600 crore + ₹1,100 crore + ₹600 crore – ₹100 crore – ₹ 250 crore – ₹ 50 crore
= ₹ 3,900 crore
(a) Gross national product at factor cost (by income method) = ₹ 3,900 crore.
(b) Gross national product at factor cost (by expenditure method) = ₹ 3,900 crore.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
14. The government exports goods worth ₹ 60,000 and imports goods worth ₹ 65, 000 . Domestic find consumption expenditure = ₹ 5, 0000 and there is no change in the stock of national capital. Replacement investment = ₹ 10,000. There are no subsidies, rather the producers are to pay excise duty of ₹ 5,000 to the government. Find factor income generated within the domestic economy.
Ans. Factor Income
Exports – imports + Domestic final consumption expenditure – Excise duty
= ₹ 60,000 – ₹ 66.000 + ₹ 5,00,000 – ₹ 5,000
= ₹ 4,90,000
Factor income = ₹ 4,90,000
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
15. Given the following data, find Net Value Added at factor Cost by a farmer producing wheat :
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Sale of wheat by the farmer in the local market | 6,80,000 | |
| (ii) Purchase of a tractor | 5,00,000 | |
| (iii) Procurement of wheat by the government from the farmer | 20,000 | |
| (iv) Consumption of wheat by the farming family during the year | 5,000 | |
| (v) Subsidy | 2,000 | |
| (vi) Expenditure on the maintenance of existing capital stock | 10,000 |
Ans. Net Value Added at Factor Cost
= Sale of wheat by the farmer in the local market + Procurement of wheat by the government from the farmer + Consumption of wheat by the farming family during the year + Subsidy – Expenditure on the maintenance of existing capital stock
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
= ₹ 6,80,000 crore + ₹ 20.000 crore + ₹ 5,000 crore + ₹ 2,000 crore – ₹ 10,000 crore
Net value added at factor cost = ₹ 6,97,000 crore.
16. From the following data, calculate National income :
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Profit | 1,500 | |
| (ii) Rent | 1,300 | |
| (iii) Net indirect taxes | 350 | |
| (iv) Mixed income of self-employed | 600 | |
| (v) Compensation of employees | 3,000 | |
| (vi) Reimbursement to the employees for medical expenses | 300 | |
| (vii) Depreciation | 200 | |
| (viii) Excess of factor income to rest of the world over factor income from rest of the world | 50 | |
| (ix) Excess of imports over exports | 40 | |
| (x) Interest | 1,100 |
Ans. National Income
= Compensation of employees Profit + Rent + interest + Mixed income of self – employed – Excess of factor income to rest of the world over factor income from rest of the world
= ₹ 3,000 crore + ₹ 1,500 crore + ₹1,300 crore + ₹ 1,100 crore + ₹ 600 crore – ₹ 50 crore
= ₹7,450 crore
National income – ₹7,450 crore.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
17. From the following data estimate: (a) Net indirect Taxes, and (b) Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost.
| Items | (₹ In crore) | |
| (i) Net national product at market price | 1,400 | |
| (ii) Net factor income from abroad | (-) 20 | |
| (iii) Gross national product at factor cost | 1,300 | |
| (iv) Consumption of fixed capital | 100 | |
| (v) National debt interest | 18 |
Ans. (a) Net Indirect Taxes
= Net national product at market price – Net national product at factor cost (Gross national product at factor cost – Consumption of fixed capital)
= ₹1, 400 crore – (₹ 1, 300 crore – ₹100 crore)
= ₹1,400 crore – ₹ 1,200 crore
= ₹ 200 crore
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
(b) Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost
= Gross national product at factor cost – Consumption of fixed capital – Net factor income from abroad
= ₹1,300 crore – ₹100 crore – (-)₹ 20 crore
= ₹1,300 crore – ₹100crore + ₹ 20core
= ₹1,220 crore
(a) Net indirect taxes = ₹ 200 crore
(b) Net domestic product at factor cost = ₹ 1,220 crore.
18. State whether the following statements are true or false. Give reasons for your answer.
(i) Nominal GDP can never be less than Real GDP.
(ii) Gross domestic capital formation is always greater than gross fixed capital formation.
Ans. (i) The statement is false. Nominal GDP can be less than real GDP when price of goods and services prevailing during the base year is greater than the price of goods and services prevailing dung the current year.
(ii) The statement is false. We know that,
Gross Domestic Capital Formation = Gross fixed capital formation + Change in stock.
Accordingly, gross domestic capital formation can be less than gross fived capital formation when change in stock (closing stock-opening stock is negative.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
19. Giving reason, explain the treatment assigned to the following while estimating national income:
(i) Subsidy on the wheat produced
(ii) Contribution to provident fund by the employees.
(iii) Contribution to provident fund by the employe₹
Ans. (i) Subsidy on the wheat produced is not included while estimating national income. It simply lowers the market value of the final goods and services to given to the producers as a transfer payment.
(ii) Contribution to provident fund by the employees is not separately included in the estimation of national income as it is paid out of their income.
(iii) Contribution to provident fund by the employers & included in national income because it is paid by the employers on behalf of the employees. It is included in national income as a part of the compensation of employees.
20. Ceasefire violations by Pakistan have led to the death of many Indian soldiers in Jammu and Kashmir. Will the payment of family pension to the families of the soldiers be included in the estimation of national income?
Ans. Yes. Because payment of family pension payment of the retirement pension. It is related to the employment contract signed by the government with the soldie₹
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
21. Mona purchased a car worth ₹ 5, 50, 000 to commute between her home and the office. Would you treat it as an intermediate consumption and therefore not included in t estimation of national income? Justify your answer.
Ans. Car purchased try Mone will not be treated as intermediate good. Because, Mona is not using her car for purpose of value adding through intermediate consumption. Mona’s car would be treated as a final good, being finally used by her as a consumer durable. Mona’s expenditure on car would be treated as private final consumption expenditure.
22. In what sense can defense and security services provided by the government be treated as intermediate services?
Ans. Defense and security services provided by the government can be treated as intermediate services in the sense that these services offer a peaceful environment to the producers for the production of goods and services
23. Cash transfer of subsidy on LPG raises annual income of the households.
Does it mean a rise in domestic income? Justify your answer.
Ans. No. Cash transfer of subsidy is to be treated as transfer payment Of course, it increases annual income of the households. But this increase is not related to factor services rendered by the households. Accordingly, transfer of cash subsidy does not lead to any rise in domestic income.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
4. Analysis & Evaluation
1. How can estimates of GDP using income method and expenditure method be identical when households do not spend their entire income on the purchase of goods and services, and a part of them remain unsold during an accounting year?
Ans. Goods which remain unsold during the year are treated as a part of change in stock during the year. These goods become a part of inventory investment of the produce₹ Accordingly, income method and expenditure method must yield identical estimates of GDP.
2. Explain the economic value of using net output method for the estimation of GDP.
Ans. Net output method refers to value added method of estimating national income. Because:
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
output – Intermediate consumption = Net output = Value added:
When we estimate value added by each producing unit in the country, we make an assessment of the level of production activity in the economy. Low value added in the economy (compared to other economies of the world) implies low level of output, and therefore, low level of income and employment. It points to low quality of life of the people.
Since value added is estimated across different sectors of the economy (primary, secondary and tertiary sectors), we are also able to assess the relative contribution of these sectors in GDP. This helps the government to formulate sector wise policies of growth and development. GST is based on the use of value added method. It is a single tax replacing all indirect taxes in the economy.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
ALSO VISIT : BASIC CONCEPTS OF ECONOMICS
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME CLASS 12
