DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Table of Contents
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Fill in the banks
(i) …….. is the blood plasma from which fibrinogen has been removed.
Ans. Serum
(ii) The red blood corpuscles are ……… and ……… shaped cells without
Ans. biconcave, disc, nucleus
(iii) The iron pigment……… gives red colour to the blood.
Ans. hemoglobin
(iv) Oxygen combines with hemoglobin present in RBC and forms ……..
Ans. oxyhaemoglobin
(v) RBCs are produced in…….
Ans. bone marrow
(vi) ……… and monocytes are phagocytic cells.
Ans. Neutrophils
(vii) Thromboplastin is required for ……. in the body.
Ans. blood clotting
(viii) ……… ions play a significant role in clotting.
Ans. Calcium
(ix) The membranous covering of the heart is ……….
Ans. pericardium
(x) The heart is made up of special muscles, the ……… muscles.
Ans. cardiac
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
(xi) The blood vessel leaving the left ventricle of the mammalian heart is the ……..
Ans. left aorta
(xii) The chamber of heart which pumps blood into aorta is ……….
Ans. left ventricle
(xiii) Ventricles have …….. walls when compared with those of auricles.
Ans. thick muscular
(xiv) Ventricles give rise to two large blood vessels called ……… and ………
Ans. pulmonary artery, aorta
(xv) The pacemaker is present near the opening of the ……… and the atrioventricular node is found near the …… septum near the tricuspid valve.
Ans. superior vena cava, inter-auricular
(xvi) The blood vessel which transports blood from heart to an organ is called ………
Ans. artery
(xvii) Arteries are ……… walled and the veins are …….. walled blood vessels.
Ans. thick, thin
(xviii) …….. are the blood vessels which usually carry oxygenated blood.
Ans. Arteries
(xix) The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is ……….
Ans. portal vein
(xx) The sequence of one systole followed by one diastole is termed as the …………
Ans. cardiac cycle
(xxi) Cells get oxygen and nutrients from …….. fluid.
Ans. tissue
(xxii) The chief function of lymph nodes is to destroy …….. .
Ans. pathogens
Match the Columns
1. Match the following column.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Basophils | 1. Phagocytes |
| B. Neutrophils | 2.Secrete histamine and heparin |
| C. Eosinophils | 3. Allergic reaction |
| D. Lymphocytes | 4. Immunity |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Ans. A – 2, B – 1, C – 3, D – 4
2. Match the following column.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. SA node | 1. 0.8 seconds |
| B. Muscle fibers located in the heart | 2. Pacemaker |
| C. Cardiac cycle | 3. Cardiac muscle |
| D. Heart muscle | 4. Purkinje fibers |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Ans. A – 2, B – 4, C – 1, D – 3
3. Match the following column.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Superior vena cava | 1. Carries oxygenated blood |
| B. Inferior vena cava | 2. Carries deoxygenated blood |
| C. Pulmonary artery | 3.Brings deoxygenated blood from lower part of the body to the right atrium. |
| D. Pulmonary vein | 4. Brings deoxygenated blood from upper part of the body to the right atrium. |
Ans. A – 4, B – 3, C – 1, D – 2
4. Match the following column
| Column I | Column II |
| A. RBC | 1. Aortic value |
| B. Heart | 2. Pacemaker |
| C. An entrance to aorta | 3. Enucleated |
| D. SA node | 4. Myogenic |
Ans. A – 3, B – 2, C – 1, D – 2
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Questions
1. Briefly explain the term ‘diapedesis’.
Ans. Diapedesis is the process by which white blood cells squeeze out through the walls of capillaries to reach at the site of infection.
2. Which blood cells are involved in leukaemia?
Ans. White Blood Corpuscles (WBCs) are involved in leukaemia.
3. People with blood group O are called universal donors. Why?
Ans. People with blood group O are called universal donors because their RBCs do not have A and B antigens, but have respective antibodies.
4. State the consequence of a situation in which blood does not coagulate.
Ans. The absence of blood clotting mechanism results in a disease called haemophilia, characterised by huge blood loss.
5. Sino-atrial node is called the pacemaker of our heart. Why?
Ans. Sino-atrial node of heart is responsible for initiating and maintaining the rhythmic activity, therefore it is known as pacemaker of the heart.
6. Define venule.
Ans. It is a small blood vessel which allows deoxygenated blood to return from capillary to veins.
7. Choose between the two options to answer the question specified in the brackets for the following.
(i) Blood in the renal artery or renal vein (Which one has more urea?)
(ii) Blood in the pulmonary artery or pulmonary vein (Which one contains less oxyhaemoglobin?)
Ans. (i) Renal artery (ii) Pulmonary artery
8. All veins carry deoxygenated blood. Do you agree?
Ans. No, pulmonary vein is an exception because it carries oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium.
9. From where to where do the following blood vessels carry blood?
(i) Hepatic vein
(ii) Hepatic portal vein
Ans. (i) Hepatic vein carries blood from liver to posterior vena cava.
(ii) Hepatic portal vein carries blood from intestine
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
10. Name the following.
(i) The two fluids that circulate in the body.
(ii) The iron containing respiratory pigment in erythrocytes.
(iii) The compound formed when hemoglobin combines with carbon dioxide in blood.
(iv) The mineral element essential for the clotting of blood.
(v) The protective covering of the heart.
(vi) The blood vessel which supplies blood to the liver.
(vii) The phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract.
(viii) The instrument used to measure heartbeat.
Ans. (i) Blood and lymph are the two main body fluids which circulate in human body.
(ii) Haemoglobin is the iron containing respiratory pigment found in erythrocytes.
(iii) Carbaminohaemoglobin
(iv) Calcium is the mineral element essential for the clotting of blood.
(v) Pericardium is the protective covering of heart.
(vi) Hepatic artery is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.
(vii) Auricular systole is the phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract.
(viii) Stethoscope.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
11. Give the biological/technical terms for the following.
(i) Fluid portion of blood.
(ii) WBCs squeeze through the walls of the capillaries into the surrounding tissue.
(iii) Cellular components of blood containing hemoglobin.
(iv) The process by which white blood cells engulf harmful microbes.
(v) The relaxation phase of the heart.
(vi) The vein which drains the blood from the intestine to liver.
(vii) Blood vessels carrying blood to the left atrium.
Ans. (i) Plasma
(ii) Diapedesis
(iii) Erythrocyte
(iv) Phagocytosis is the process by which white blood cells engulf harmful microbes
(v) Diastole
(vii) Vena cava
(vi) Hepatic portal vein
12. Give one reason for the following statements.
(i) Erythrocytes are biconcave discs and lack nucleus.
(ii) A matured mammalian erythrocyte lacks nucleus and mitochondria.
(iii) The wall of the ventricles is thicker than the auricles.
(iv) Blood flows in arteries with spurts and high pressure.
Ans. (i) RBCs/Erythrocytes are biconcave, disc-like structures that lack nucleus to provide large surface area to volume ratio for maximum absorption and transport of oxygen.
(ii) Lack of nucleus and mitochondria helps in providing more surface area for maximum absorption and transport of oxygen.
(iii) Ventricles have thicker walls than auricles because they are meant to pump blood with high pressure so that it reaches to larger distances.
(iv) The blood is pumped from heart with high pressure to the various parts of the body by arteries so, it flows with spurts and high pressure.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
12. Mark the odd one out.
(i) Basophils, Neutrophils, monocytes, Eosinophils.
(ii) Mitral valve, tricuspid valve, semilunar valve, venous valve.
(iii) Mitral valve, sino-atrial node, aorta, pulmonary vein.
(iv) Lumen, muscular tissue, connective tissue, pericardium
Ans.(i) Odd one is monocytes,
Category It is an agranulocyte. The remaining three of the given set are granulocytes.
(ii) Odd one Venous valve.
Category Location of the valves.
Other valves are located inside the heart.
(iii) Odd one is Sino-Atrial (SA) node.
Category It is the structure present in the right side of the heart and the remaining three are found in the left side of the heart.
(iv) Odd one Pericardium
Category Components of blood vessels
14. State the main function of following.
(i) Lymphocytes of blood.
(ii) Thrombocytes.
(iii) Coronary artery.
Ans. (i) Lymphocytes keep away infection by producing antibodies against foreign particles.
(ii) Thrombocytes help in blood clotting.
(iii) Coronary artery supplies oxygenated blood to the walls of heart.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
15. Write down the difference between the following pairs with reference to what is given within the brackets.
(i) Plasma and serum (on the basis of composition).
(ii) Erythrocytes and leucocytes (function).
(iii) Lubb and Dupp (name of the valves whose closure produces the sound).
(iv) Bicuspid valve and tricuspid valve (function).
(v) Beginning of the ventricular systole and the end of ventricular diastole (type of heart sound). Ans. (i) Plasma contains fibrinogen, which is lacking in serum.
(ii) Difference between erythrocytes and leucocytes is as follows
| Erythrocytes | Leucocytes |
| Transport respiratory gases. | Produce antibodies and protect the body from disease causing germs. |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
(iii) Lubb Mitral and tricuspid valve.
Dupp Aortic and pulmonary semilunar valve.
(iv) The difference between bicuspid valve and tricuspid valve is given below
| Bicuspid Valve | Tricuspid Valve |
| It guards the opening when blood rushes from left auricle into left ventricle. | It guards the opening when blood rushes from right atrium to right ventricle. |
(v) Heart sound produced at the beginning of the venticular sytole is called Lubb and at the other end of ventricular systole is called Dupp.
16. Blood vessels are the branched tube which extends from heart to all parts of the body. Answer the following questions
(i) Which blood vessel carry blood away from heart and towards any other organ?
(ii) In which blood vessel semilunar valves are found?
(iii) State the function of capillary.
(iv) In which blood vessel blood flows under high pressure?
(v) Which vein carry oxygenated blood?
Ans. (i) Artery
(ii) Veins
(iii) Capillaries have the ability of contracting and dilating with the decrease and increase in the blood supply to various body parts.
(iv) Artery
(v) All veins in human body carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein which carry oxygenated blood.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
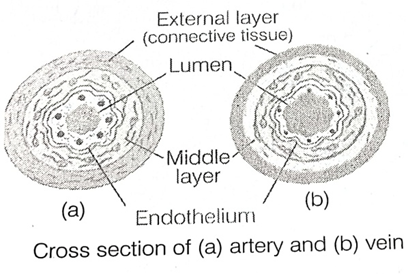
17. The given diagram represents a section of the human heart. Answer the question that follows.

(i) Which parts of heart are in the diastolic phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
(ii) Label the parts numbered ‘1’ and ‘2’ in the diagram. What type of blood flows through them?
(iii) What causes the heart sounds ‘lubb’ and ‘dupp”?
(iv) Name the blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscles.
(v) Draw neat labelled diagrams of a cross section of an artery and a vein.
Ans. (i) In the given figure, ventricles are in diastolic phase. The tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open. It occurs only when pressure in the ventricles falls. As a result blood flows from the atria into the ventricles.
(ii) 1-Pulmonary artery It carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs for purification.
2-Pulmonary veins They bring oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
(iii) Lubb’ sound is produced when tricuspid and mitral valves get closed, while ‘dupp’ sound is produced when pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves get closed.
(iv) Blood vessel that supplies blood to the walls of the heart is ‘coronary artery’
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
(V)
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
ALSO VISIT:
10th ICSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
