DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE

DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Table of Contents
EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Fill in the Blanks
(i) The process of removal of waste products formed by metabolic activities is called…….
Ans. excretion
(ii) The renal artery carries blood which supplies high concentration of……. and …… for tissue respiration in the kidney cells.
Ans. oxygen, nutrients
(iii) Urochrome helps in breakdown of……..in liver.
Ans. haemoglobin
(iv) ……..and ………are reabsorbed by passive transport.
Ans. Water, urea
(v) The colour and pH of urine may vary with ………of the person.
Ans. diet
(vi) …….of excess amino acids in liver produces urea which is excreted by the……..
Ans. Deamination, kidney
(vii) The outer part of a kidney is………. and the inner part is………
Ans. cortex, medulla
(viii) Water along with other useful substances like salts, amino acids, glucose, etc., are reabsorbed in…….
Ans. renal tubule
(ix) The process of uropoiesis that helps in maintenance of ionic and acid-base balance is……
Ans. tubular secretion
(x) The process of release of urine is……
Ans. micturition
Match the Columns
1. Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Liver | 1. Blood supply to glomerulus |
| B. Skin | 2. Knot-like tuft of blood capillaries in Bowman’s capsule |
| C. Kidney | 3. Breakdown of proteins |
| D. Glomerulus | 4. Sweat glands |
| E. Henle’s loop | 5. Bean-shaped excretory organ |
| 6. Hairpin-shaped |
Ans. A – 3, B – 4 , C – 5, D – 2, E – 6
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
2. Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Proximal convoluted tubule | 1. Formation of concentrated urine |
| B. Distal convoluted tubule | 2. Filtration of blood |
| C. Henle’s loop | 3. Reabsorption of 70-80% of electrolytes |
| D Micturition | 4. Ionic balance |
| E Renal corpuscle | 5. Process of release of urine from the body |
| 6. Deamination |
Ans. A-3, B-4, C-1, D-5, E-2
3. Match the following columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Maximum Reabsorption of water | 1. Yellow pigment in urine |
| B. Temporary storage of urine | 2. Proximal convoluted tubule urine |
| C. Water-salt regulation | 3. Removal of urea |
| D. Skin | 4. Below the diaphragm |
| E Urochrome | 5. Osmoregulation |
| 6. Maintenance of body temperature | |
| 7. Urinary bladder |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Ans. A-2, B-7, C-5, D-6, E-1
Questions/Answer
1. The renal cortex has a dotted appearance, why?
Ans. Renal cortex is dark in colour and presence of numerous nephrons in a highly coiled manner gives this region a dotted
2. Write special functional activity of the ureter.
Ans. Ureter carries urine from kidney to the urinary bladder.
3. How does CNS receive the signals when there is an urge to pass urine?
Ans. Stretch receptors present in the walls of urinary bladder send signal to CNS by setting up reflexes.
4. Define Micturition.
Ans. The process of expelling out of the urine is known as Micturition.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
5. Name the following.
(i) An organic waste produced in man.
(ii) The structure formed by Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus together.
(iii) The branch of renal artery entering the Bowman’s capsule.
(iv) The pH of the normal urine.
(v) The organisms excreting urea as their excretory product.
(vi) The functional units of kidney.
(vii) The organic constituents of normal urine.
(viii) The organ which produces urea.
(ix) Knot-like mass of blood capillaries inside the Bowman’s capsule.
(x) The branch of renal vein leaving the Bowman’s capsule.
(xi) The process by which kidneys regulate the water content of the body.
(xii) The two main stages of urine formation.
(xiii) The organ in humans concerned with maintenance of water balance in body.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Ans. (i) Carbon dioxide is an organic waste produced in man.
(ii) The structure formed by Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus together is Malpighian body.
(iii) Branch of renal artery entering the Bowman’s capsule is afferent arteriole.
(iv) pH of normal urine is 6
(v) Ureotelic organisms excrete urea as their excretory product.
(vi) Nephron is functional unit of kidney.
(vii) Organic constituents of urine include urea, uric acid and creatinine.
(viii) Liver is the organ that produces urea.
(ix) Glomerulus is the knot-like mass of blood capillaries found inside the Bowman’s capsule.
(x) Efferent arteriole
(xi) Kidneys regulate the water content of the body via Osmoregulation.
(xii) The two main stages of urine formation are
(a) Ultrafiltration
(b) Selective Reabsorption
(xiii) Kidney is the organ in humans which concerned with maintenance of water balance in body.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
7. Given below is the set of five terms. In this case arrange and rewrite the set, so as to be in a logical sequence.
Renal vein, renal artery, afferent arteriole, efferent arteriole, glomerulus (Pathway of blood through glomerulus).
Ans. Logical sequence for pathway of blood through glomerulus is as follows renal artery, afferent arteriole, glomerulus, efferent arteriole, renal vein.
8. Correct and rewrite the following statements by changing the biological term that is underlined word for each statement.
(i) Normal pale yellow colour of the urine is due to the presence of the pigment melanin.
(ii) The kidney is composed of neurons.
Ans. (i) Normal pale yellow colour of the urine is due to the presence of the pigment Urochrome.
(ii) The kidney is composed of number of nephrons.
9. State the exact location of the following.
(i) Proximal convoluted tubule
(ii) Selective Reabsorption of glomerulus filtrate takes place
(iii) ‘Loop of Henle’.
(iv) The process of secretion occurring in Nephron.
Ans. (i) Cortex region of kidney.
(ii) The selective Reabsorption of glomerulus filtrate takes (PCT) and place in Proximal Convoluted Tubule Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT).
(iii) Henle’s loop is a U-shaped or hairpin-shaped region of renal tubule that runs in the medulla region of kidney. It has a descending limb that ends into the medulla and an ascending limb that extends back from medulla into the cortex.
(iv) Secretion occurs in Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT), Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) and loop of Henle
10. Give the biological/technical terms for the following.
(i) Pigment providing colour to urine
(ii) The removal of nitrogenous wastes from the body
(iii) Osmoregulation
(iv) Homeostasis
(v) Ureotelism
(vi) The hormone increasing Reabsorption of water by kidney tubules.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Ans. (i) Urochrome provides colour to urine.
(ii) Excretion is process of removal of nitrogenous waste from the body.
(iii) Osmoregulation is the process by which an organism regulates the water and salt (electrolyte) balance in the body, in order to maintain homeostasis.
(iv) Homeostasis is defined as the ability of an organism to maintain a constant internal environment with respect to changes occurring in outside environment.
(v) The process by which organisms excrete out urea as a waste product is called Ureotelism. e.g. mammals are Ureotelic.
(vi) Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) increase Reabsorption of water by kidney tubules.
10. Give biological reason for the following.
(i) Certain useful products like glucose, salt, etc., are filtered but not excreted by Ultrafiltration.
(ii) Reabsorption is called as selective Reabsorption.
(iii) It is necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration of the blood.
(iv) Dialysis is done in certain patient.
(v) Urine is slightly thicker in summer than in winter.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
Ans. (i) Glucose, salt, etc., get reabsorbed in the proximal part of renal tubules, hence are not filtered.
(ii) Only certain selected materials such as glucose, some salts, etc., are reabsorbed in the renal tubule. Thus, it is called selective Reabsorption.
(iii) To keep the body cells in a steady state, it is essential to maintain the osmotic concentration of blood.
(iv) Dialysis is done when both kidneys of a patient are impaired to carry out their normal functions.
(v) In summer, considerable part of water is lost due to perspiration. So, more water is reabsorbed in the kidney. Thus, making the urine thicker in summer than in winter.
11. Choose the odd one out of the following terms given and name the category to which the other belong.
(i) Bile, urea, uric acid, ammonia
(ii) Urethra, uterus, urinary bladder, ureter. Bile
Ans. (i) Odd one Bile
Category It helps in the digestion of lipid in small intestine. Rest three are the type of excretory material in different organisms.
(ii) Odd one Uterus
Category It is the part of reproductive system. Other three are the part of excretory system.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
12. Write down the difference between the following pairs with reference to what is given within the brackets.
(i) Bowman’s capsule and Malpighian capsule (parts included).
(ii) Renal cortex and renal medulla (parts of the nephrons present).
(iii) Afferent arteriole and efferent arteriole (function).
Ans. (i) Difference between Bowman’s capsule and Malpighian capsule is as follows
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
| Bowman’s Capsule | Bowman’s Capsule |
| It is a cup-shaped structure that indicates the beginning of Nephron. It is made up of two layers inner visceral and outer parietal. | It is comprised of glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. |
(ii) Difference between renal cortex and renal medulla is as follows
| Renal Cortex | Renal Medulla |
| Malpighian body, Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) and Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) are found in renal cortex. | Henle’s loop is found in renal medulla. |
(iii) Difference between afferent arteriole and efferent arteriole is as follows
| Afferent Arteriole | Efferent Arteriole |
| Carries blood containing more amounts of waste materials. | Carries blood containing lesser amount of waste materials. |
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
13. The diagram given below represents a Nephron and its blood supply. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
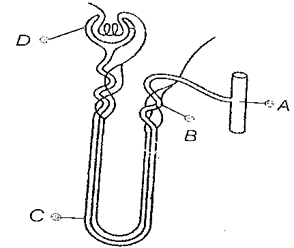
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
(i) Label parts A, B, C and D.
(ii) State the reason for the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
(iii) Name the blood vessel which contains the least amount of urea in this diagram.
(iv) Name the part of the Nephron which lies in the renal medulla.
Ans. (i) Different parts in the diagram are labelled as A – Collecting duct, B-Distal convoluted tubule, C-Loop of Henle, D-Bowman’s capsule.
(ii) The high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus is because of reduced diameter of capillaries of afferent man arterioles.
(iii) Blood vessel that contains the least amount of urea in this diagram is efferent arteriole that connects to renal vein.
(iv) Loop of Henle is the part of renal tubule that lies in medulla region of kidney.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
ALSO VISIT :
10th ICSE
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: EXCRETORY SYSTEM 10 ICSE
