DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF

POINTS TO REMEMBER
- Work done on an object is defined as the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance moved by the object in the direction of the applied force. The unit of work is joul :
1 joule = 1 newton x 1 metre.
- Work done on an object by a force would be zero if the displacement of the object is zero. •
- An object having capability to do work is said to possess energy. Energy has the same unit as that of work.
- An object in motion possesses what is known as the kinetic energy of the object. An object of mass m moving with velocity v has a kinetic energy K = 1/ 2 mv2
- The energy possessed by a body due to its change in position or shape is called the potential energy. The gravitational potential energy of an object of mass m, raised through a height, h from the earth’s surface is given by U = mgh.
- If a force changes the velocity of the body from u to v then total work done is:
W = 1/2mv2 – 1/2mu2
- According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can only be transformed from one form to another, it can neither be created nor destroyed. The total energy before and after the transformation always remains constant.
- Energy exists in nature in several forms such as kinetic energy, potential energy, heat energy, chemical energy etc. The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of an object is called its mechanical energy.
- Power is defined as the rate of doing work power P= W/T. The S.I. unit of power is watt. IW=1J/s.
- The energy used in one hour at the rate of 1 kW is called 1 kWh or 1 unit.
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
Table of Contents
WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
- A porter lifts a luggage of 15kg from the ground and puts it on his head 1.5 m above the ground. Calculate the work done by him on the luggage.
Solution: Mass of luggage, m = 5kg and displacement, s = 1.5 m
Work done, W = F
= 225 kg ms-2 = 225 Nm = 225 J
Work done is 225 J
2. An object of mass 15 kg is moving with a uniform velocity of 4 m s-1. What is the Kinetic energy possessed by the object?
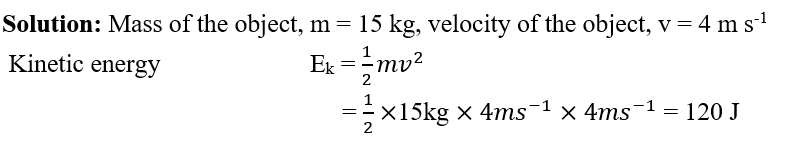
- 3. Find the energy possessed by an object of mass 10kg when it is at a height of 6 m above the ground. Given, g = 9.8 ms-2
Solution: Mass of the object, m = 10kg, displacement (height), h = 6m and acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 ms-2
Potential energy = mgh
= 10 kg
= 588 J
4. An object of mass 12 kg is at a certain height above the ground. If the potential energy of the object is 480J, find the height at which the object is with respect to the ground. Given, g = 10 ms-2.

- 5. A boy of mass 50kg runs up a stair case of 45 step sin 9 s. If the height of each step is 15cm, find his power. Take g = 10 ms-2
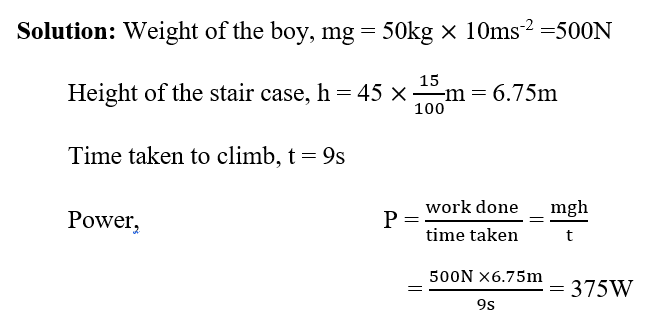
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
- 6. An electric bulb of 60 W is used for 6 h per day. Calculate the ‘units’ of energy consumed in one day by the bulb.
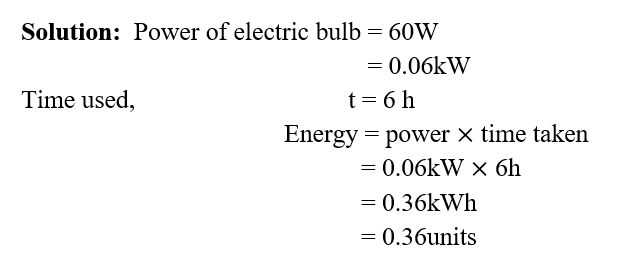

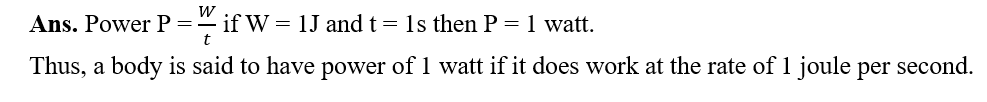
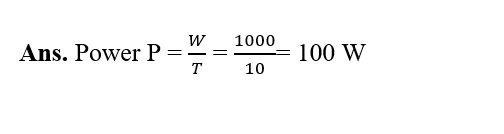
10.An electric heater is rated 1500W. how much energy does it use in 10 hours?
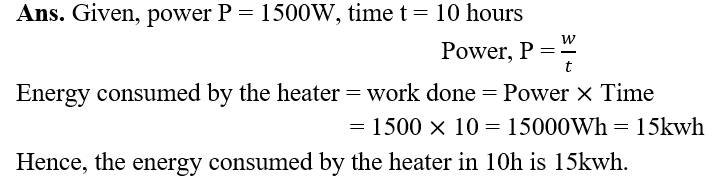
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
11.An object of mass, m is moving with a constant velocity, v. How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?
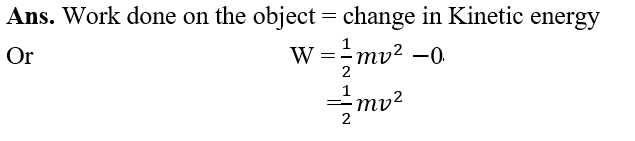
12.Calculate the work required to be done to stop a car of 1500kg moving at a velocity of 60km/h?
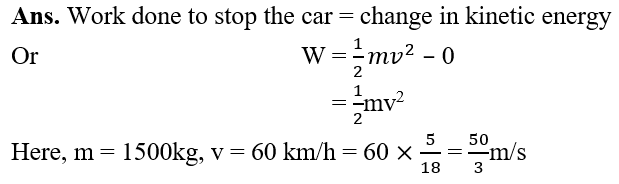
(a) Increase
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains constant
(d) First increase and then decreases
Ans. C
14.A car is a accelerated on leveled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In the process the potential energy of the car:
(a) Does not change
(b) Becomes twice to that of initial
(c) Becomes 4 times that of initial
(d) Becomes 16 times that of initial
Ans. A
15.In case of negative work the angle between the force and displacement is:
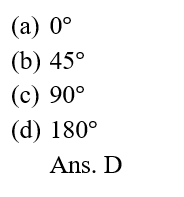
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
16.An iron sphere of mass 10kg has the same diameter as an aluminium sphere of mass is 3.5kg. Both spheres are dropped simultaneously from a tower. When they are 10m above the ground, they have the same:
(a)Acceleration
(b)Momenta
(c)Potential energy
(d)Kinetic energy
Ans. A
17.A girl carrying a school bag of 3 kg mass on her back and moves 200 m on a leveled road. The work done against the gravitational force will be (g = 10ms-2)
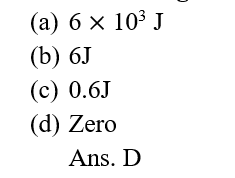
(a) Joule
(b) Newton metre
(c) Kilowatt
(d) Kilowatt hour
Ans. C
Ans. D
19.The work done on an object does not depend upon the:
(a) Displacement
(b) Force applied
(c) Angle between force and displacement
(d) Initial velocity of the object
Ans. D
20.Water stored in a dam possesses:
(a) No energy
(b)Electrical energy
(c)Kinetic energy
(d)Potential energy
Ans. D
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
21.A body is falling from a height h. After it has fallen a height h/2, it will possess:
(a)Only potential energy
(b)Only kinetic energy
(c)Half potential and half kinetic energy
(d)More kinetic and less potential energy
Ans. C
22.Can any object have mechanical energy even if its momentum is zero? Explain.
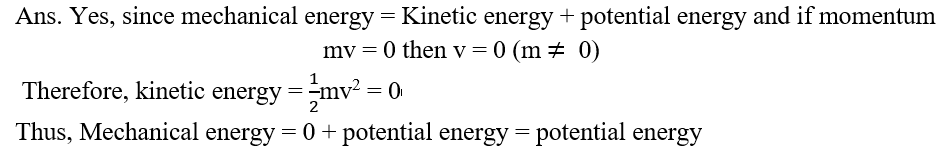
23.Can any object have momentum even if its mechanical energy is zero? Explain.
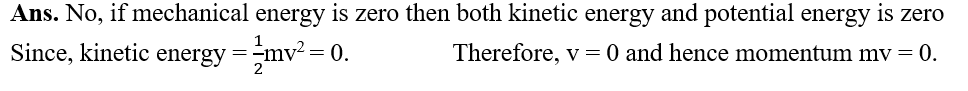
24.The power of a motor pump is 2kW. How much water per minute the pump can raise to a height of 10m? (Given g = 10ms-2)
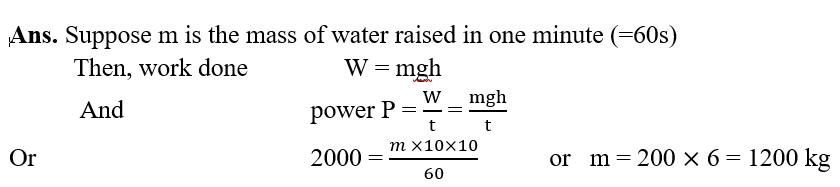
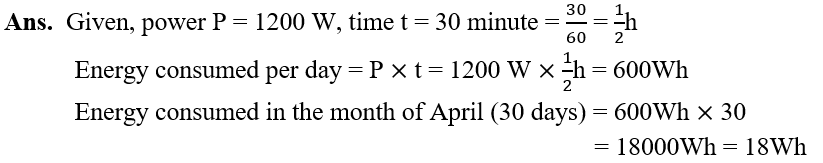
(a) How much work is done on the trolley?
(b) How much work is done by the girl?
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF

(a) How much work is done by the men in lifting the box?
(b) How much work do they do in just holding it?
(c) Why do they get tired while holding it? (g = 10ms-2)
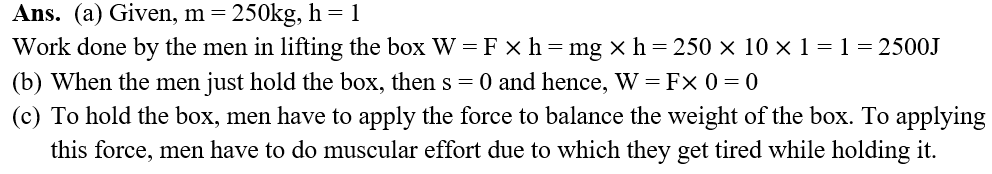
28. Avinash can run with a speed of 8 ms-1 against the frictional force of 10N and Kapil can move with a speed of 3ms-1 against the frictional force of 25N. Who is more powerful and why?
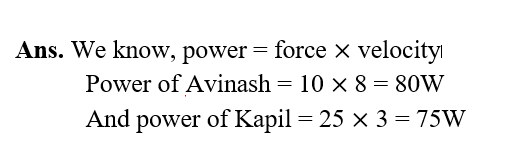

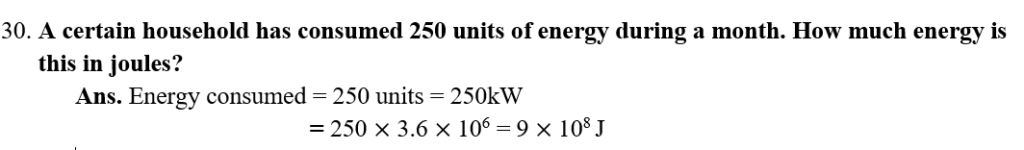
ALSO VISIT : GRAVITATION CLASS 9
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY CLASS 9 PDF
