Table of Contents
WORK AND ENERGY
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY

11.An object of mass, m is moving with a constant velocity, v. How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?
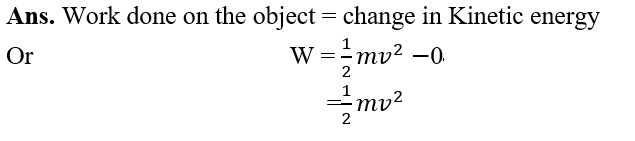
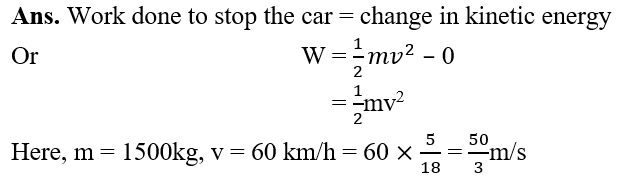
13.When a body falls freely towards the earth, then its total energy:
(A).Increase
(B).Decreases
(C).Remains constant
(D).First increase and then decreases
Ans. C
14.A car is a accelerated on leveled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In the process the potential energy of the car:
(A).Does not change
(B).Becomes twice to that of initial
(C).Becomes 4 times that of initial
(D).Becomes 16 times that of initial
Ans. A
15.In case of negative work the angle between the force and displacement is:
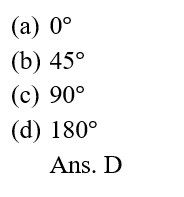
(A). Acceleration
(B). Momenta
(C). Potential energy
(D). Kinetic energy
Ans. A
17.A girl carrying a school bag of 3 kg mass on her back and moves 200 m on a leveled road. The work done against the gravitational force will be (g = 10ms-2)
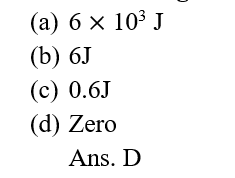
(A). Joule
(B). Newton metre
(C).Kilowatt
(D).Kilowatt hour
Ans. C
19.The work done on an object does not depend upon the:
(A).Displacement
(B).Force applied
(C).Angle between force and displacement
(D). Initial velocity of the object
Ans. D
20.Water stored in a dam possesses:
(A).No energy
(B).Electrical energy
(C).Kinetic energy
(D).Potential energy
Ans. D
DOWNLOAD MOBILE APPLICATION TO LEARN MORE: WORK AND ENERGY
