1.
The tops of two poles of height 20 m and 14 m are connected by a wire. If the wire makes an angle of 30° with horizontal, the length of the wire is
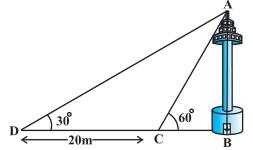
2.
In given figure, the value of angle ACB is
3.
A ladder 15 m long just reaches the top of a vertical wall. If the ladder makes an angle of 60° with the wall, then the height of the wall is
4.
The angle of depression of a car, standing on the ground, from the top of a 75 m high tower, is 30°. The distance of the car from the base of the tower (in m) is:
5.
In given figure, the value of AE is
6.
Two poles are 25 m and 15 m high and the line joining their tops makes an angle of 45° with the horizontal. The distance between these poles is
7.
The shadow of a tower is equal to its height at 10:45 a.m. The sun’s altitude is
8.
In given figure, the length of AP is
9.
A plane is observed to be approaching the airport. It is at a distance of 12 km from the point of observation and makes an angle of elevation of 60°. The height above the ground of the plane is
10.
The angle of elevation of top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the foot of the tower is 30°. The length of the tower is
11.
If two towers of heights h1 and h2 subtend angles of 60° and 30° respectively at the mid-point of the line joining their feet, then h1 : h2 =
13.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point 20 metres away from its base is 45°. The height of the tower is
14.
The angles of elevation of the top of a rock from the top and foot of 100 m high tower are respectively 30° and 45°. The height of the rock is
15.
In figure given ABCD is a rectangle, the value of CE is
16.
In given Fig., the angle of depression from the observing position D and E of the object at A are
17.
In given figure, the value of CE is
18.
The upper part of a tree is broken by the wind and makes an angle of 30° with the ground. The distance from the foot of the tree to the point where the top touches the ground is 5 m. The height of the tree is
19.
The line drawn from the eye of an observer to the point in the object viewed by the observer is known as